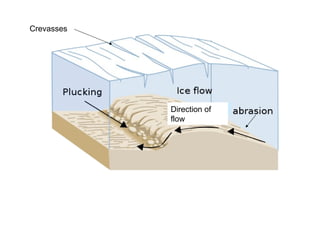
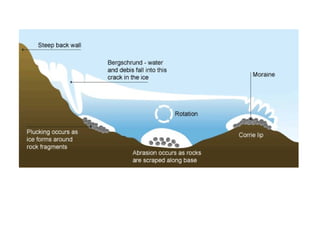
The document discusses key glacial processes including freeze-thaw weathering, erosion through plucking and abrasion, and movement and deposition of material. Freeze-thaw weathering occurs as water enters cracks in bedrock and expands during freezing. Erosion removes rock through plucking, where blocks of rock are torn away, and abrasion, where rock fragments scrape bedrock. Glaciers transport material and eventually deposit moraines when melting reduces their ability to carry material further.