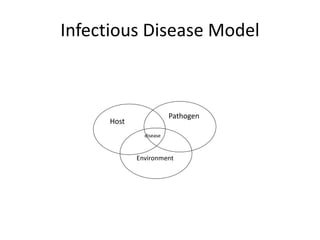
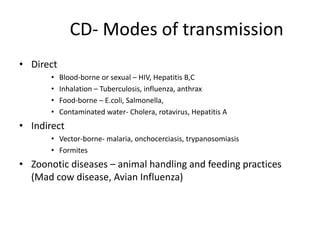
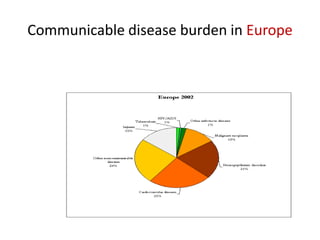
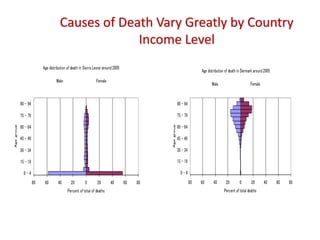
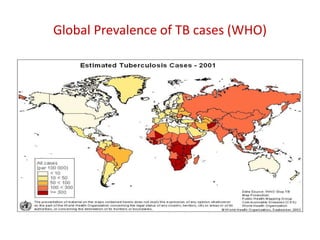
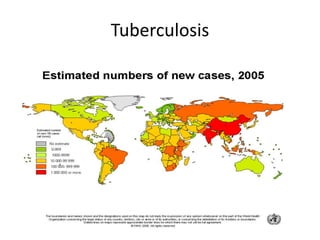
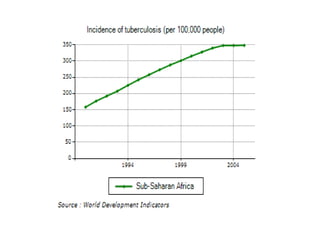
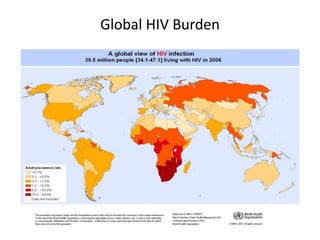
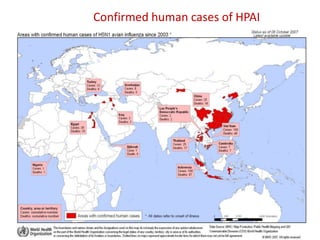
This document provides definitions and discusses key concepts regarding communicable disease epidemiology. It defines epidemiology as the study of health-related states and events in populations. Communicable diseases are illnesses transmitted directly or indirectly between humans, animals, or from the environment. Studying communicable disease epidemiology is important due to changes in disease patterns, discovering new infections, and potential infectious origins of chronic diseases. Terminology discussed includes modes of transmission, hosts, vectors, reservoirs, incidence, prevalence, epidemics, pandemics, and eradication. Tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS, and avian influenza are then summarized as examples of significant communicable diseases.