The document discusses several methods for controlling particulate contaminants, including their working principles:
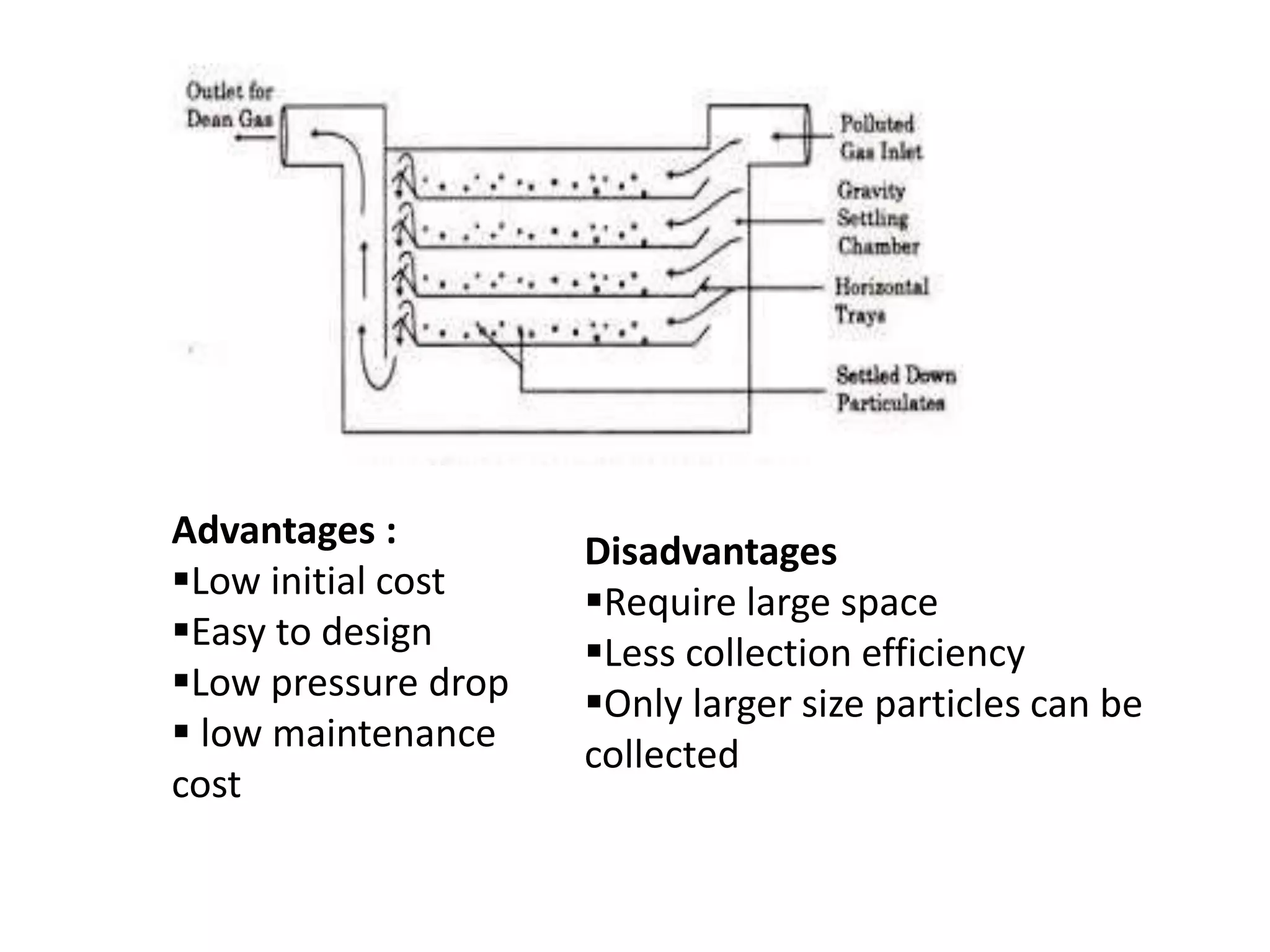
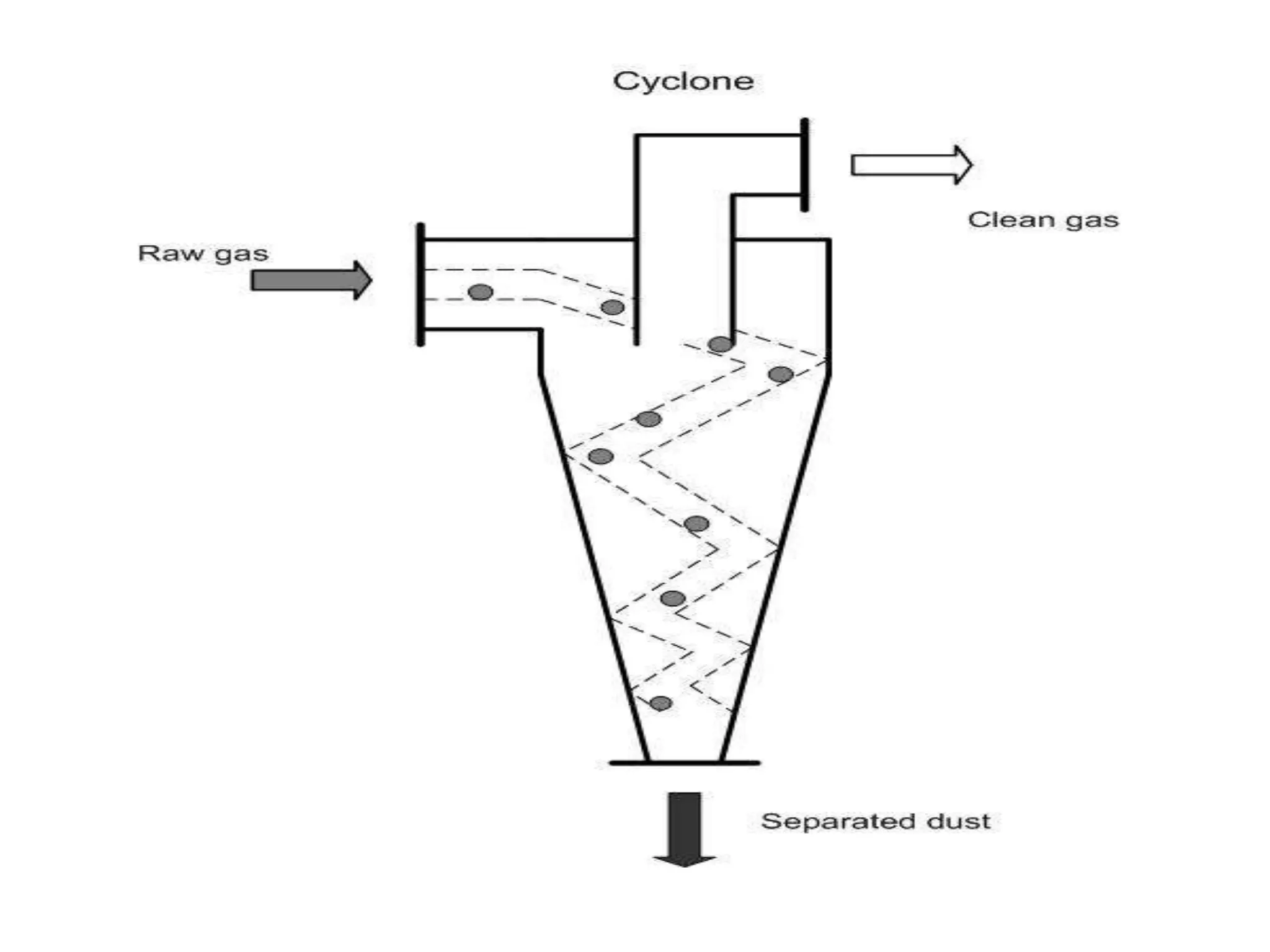
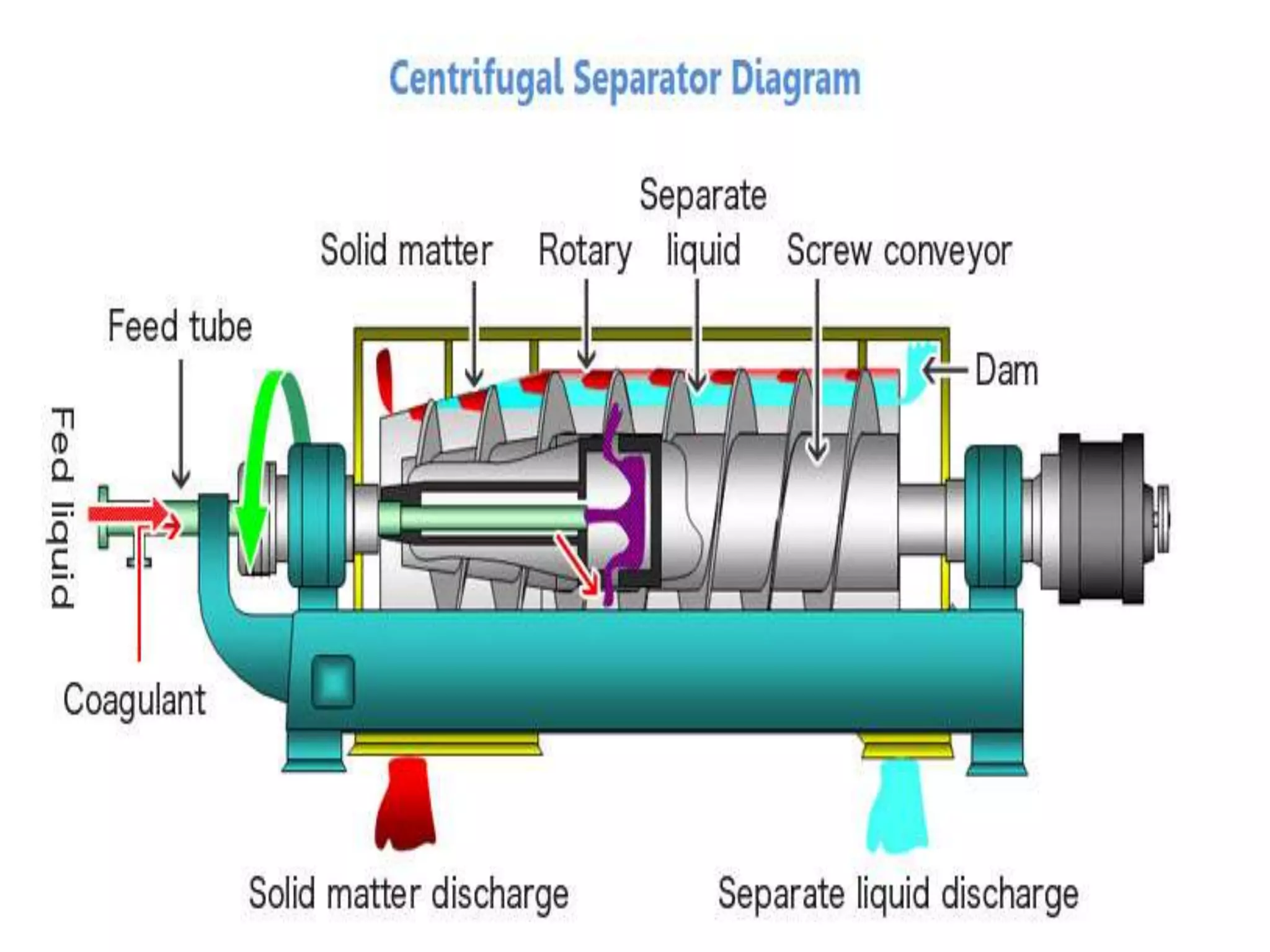
1) Gravity separators and centrifugal separators remove larger particles (>50 μm) from gas streams using gravitational settling or centrifugal forces.
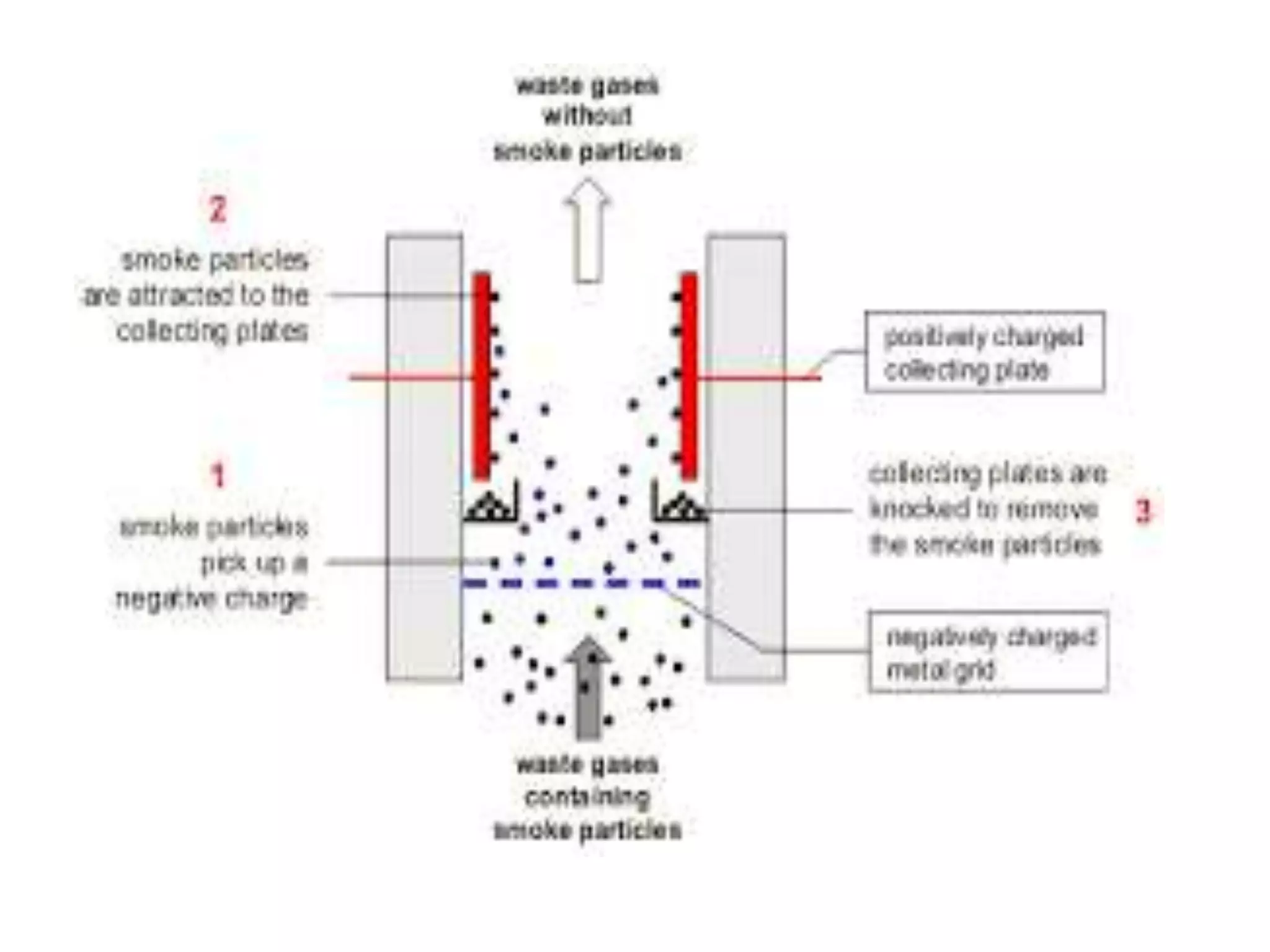
2) Electrostatic precipitators ionize particles and collect them on oppositely charged plates, achieving high removal efficiencies of over 90% for particles over 1 μm.
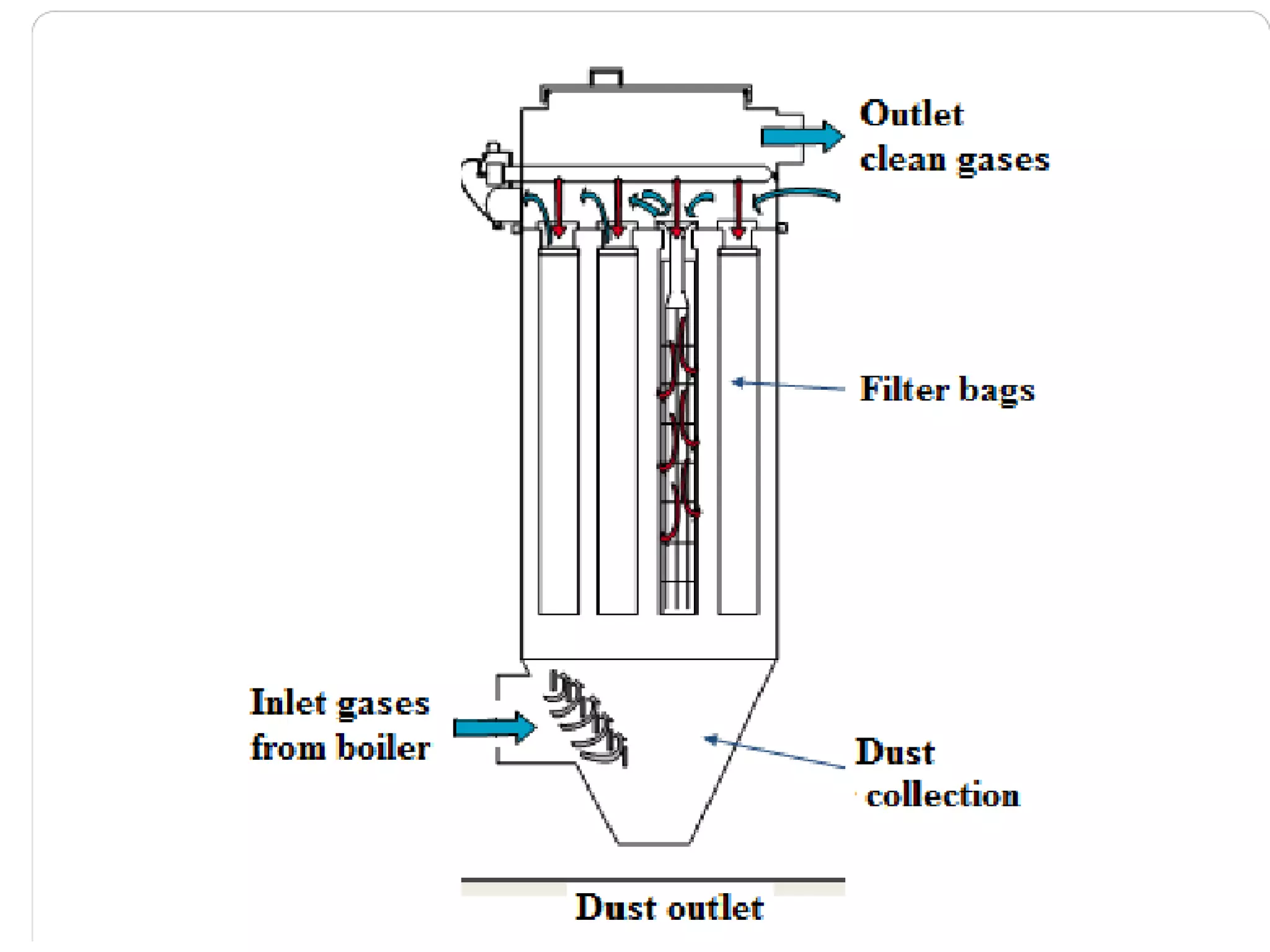
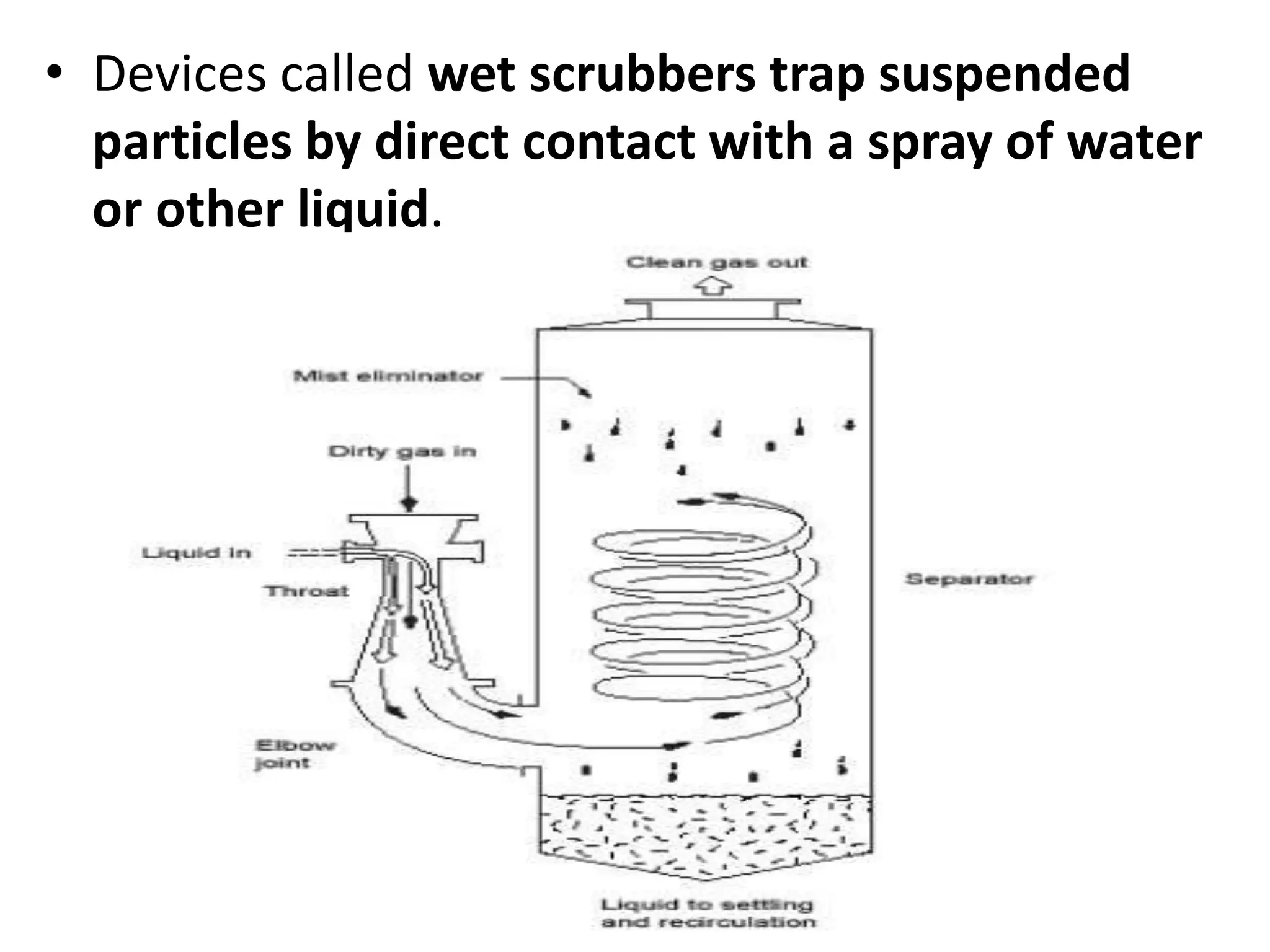
3) Fabric filters and wet scrubbers like particulate scrubbers can remove over 90% of particles less than 10 μm using filtration through fabric or liquid contact. Selection depends on factors like contaminant properties, space, and costs.