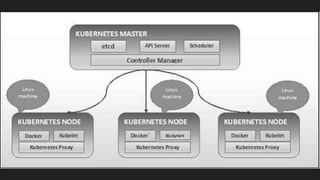
The document provides an overview of Kubernetes architecture, detailing key components like etcd, API server, controller manager, scheduler, Docker containers, kubelet, and proxy. It explains the functions of each component, including how they interact within the cluster to manage workloads and configuration. Additionally, it offers a hands-on approach to deploying a single-node Kubernetes cluster using Minikube, emphasizing operational commands with kubectl.