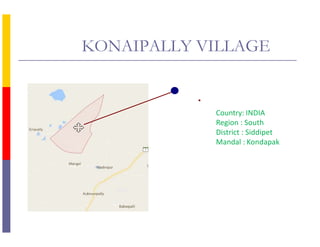
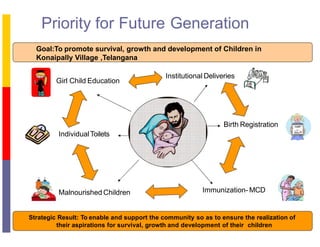
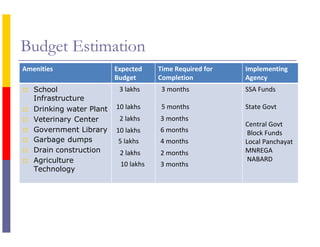
The document outlines an integrated village development plan for Konaipally Village in India. The plan aims to promote survival, growth, and development of children in the village. It includes 11 points for the development of children, such as birth registration, immunization, nutrition, education, and child marriage prevention. It also details plans for personal development, human development, agriculture development, soil health cards, and involvement of children, women, and youth in development activities. The document identifies issues at the community, government, and constraints levels and proposes budgets, timelines, and implementing agencies for infrastructure projects to address gaps.