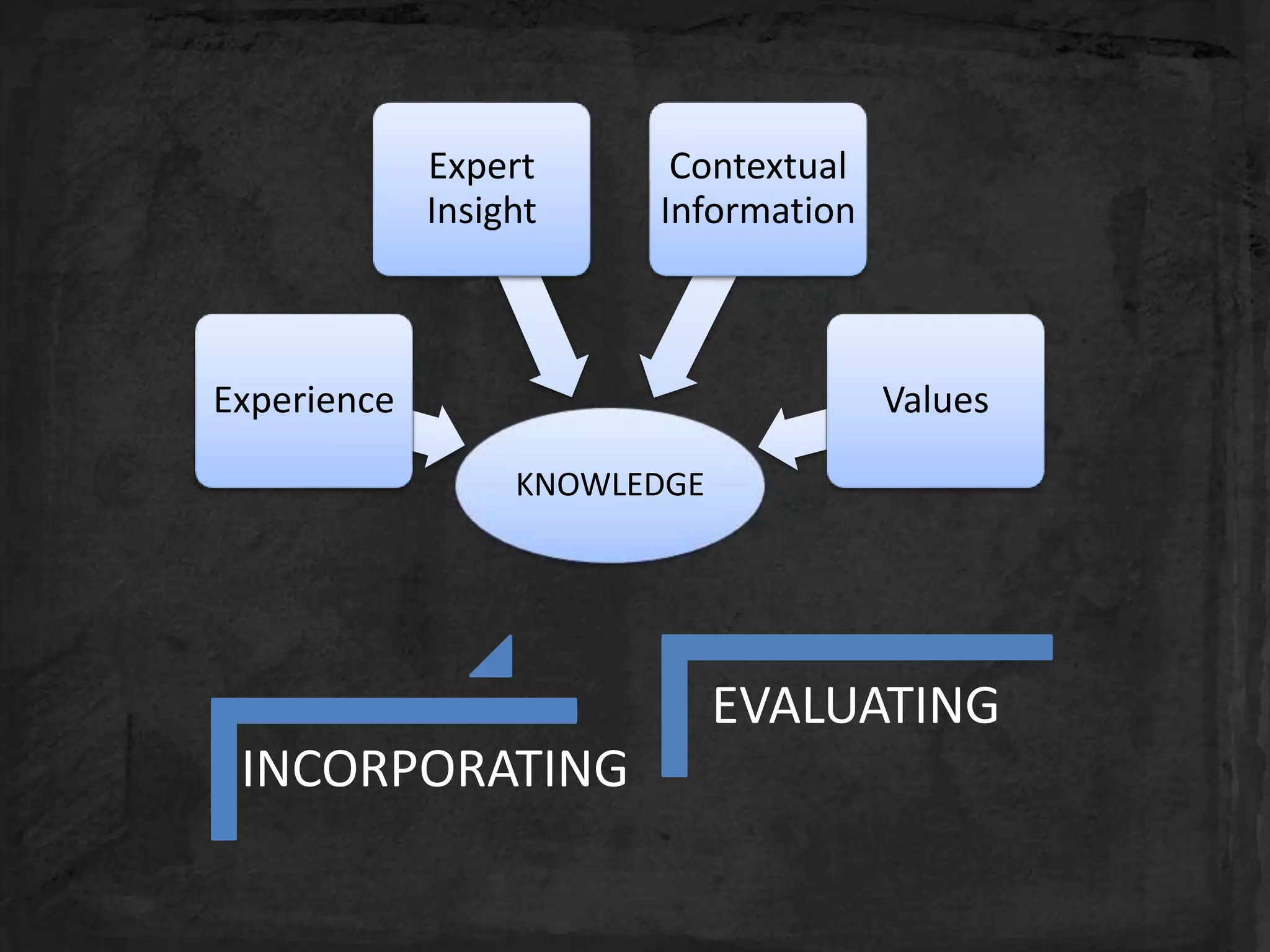
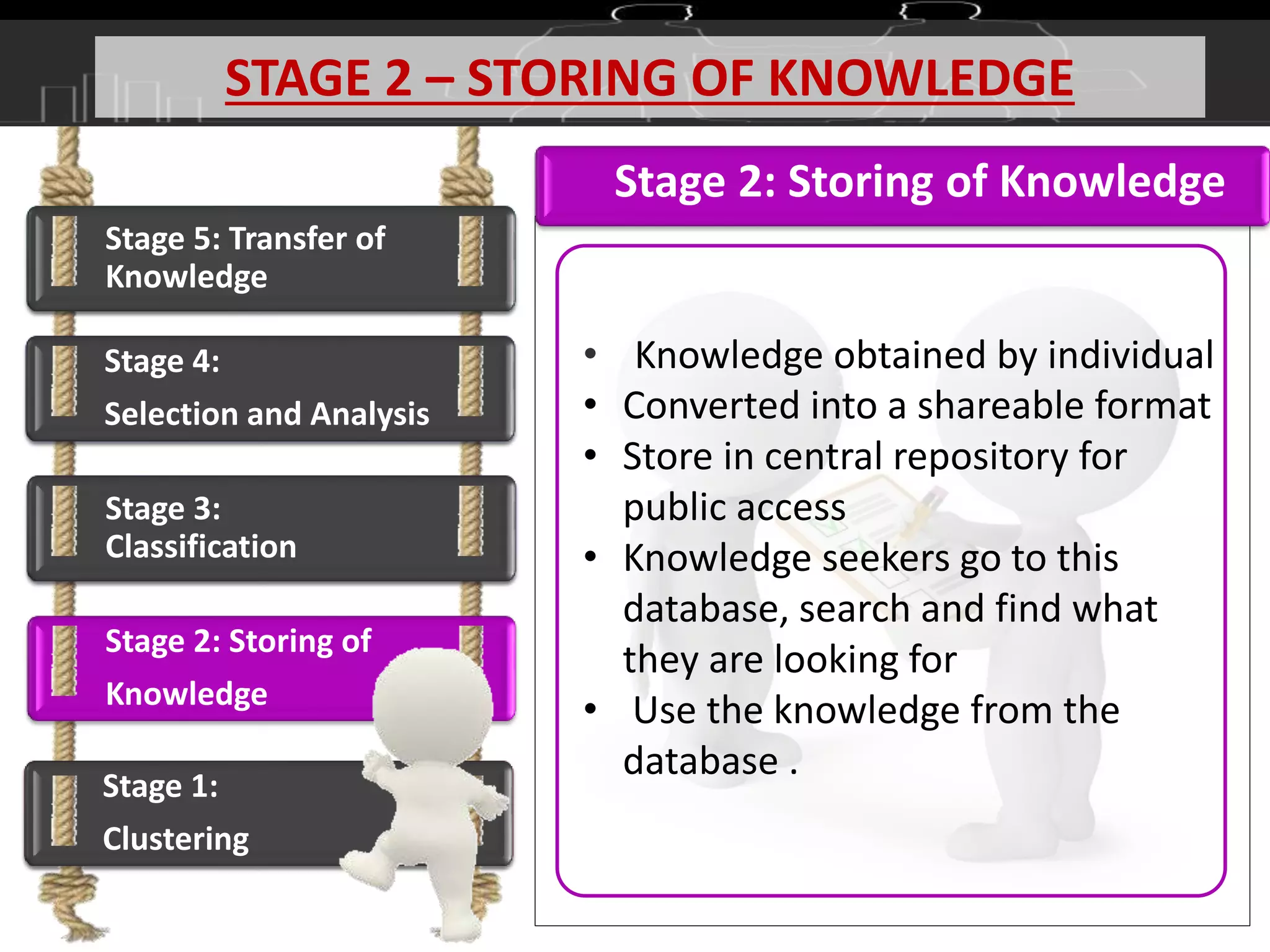
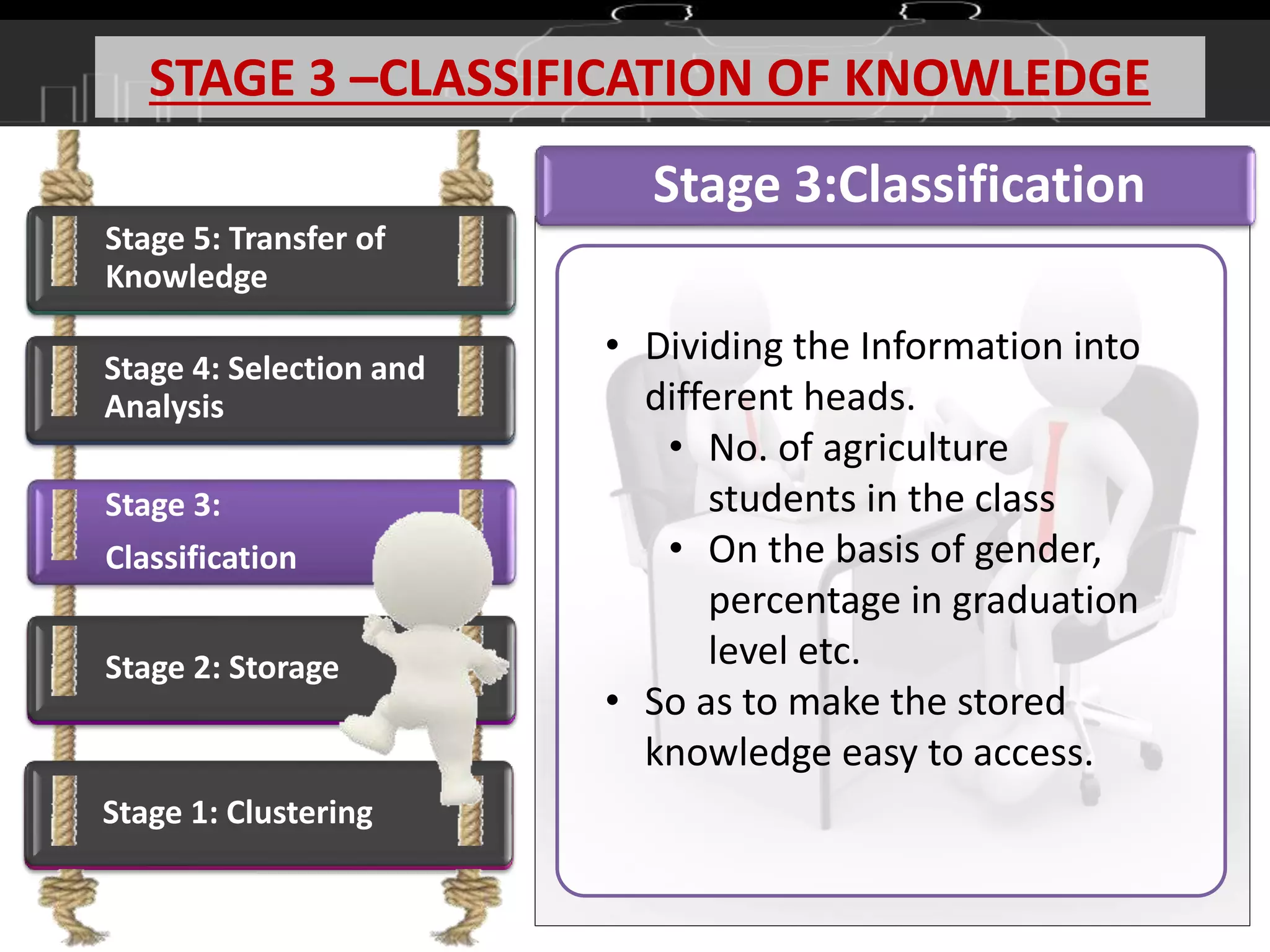
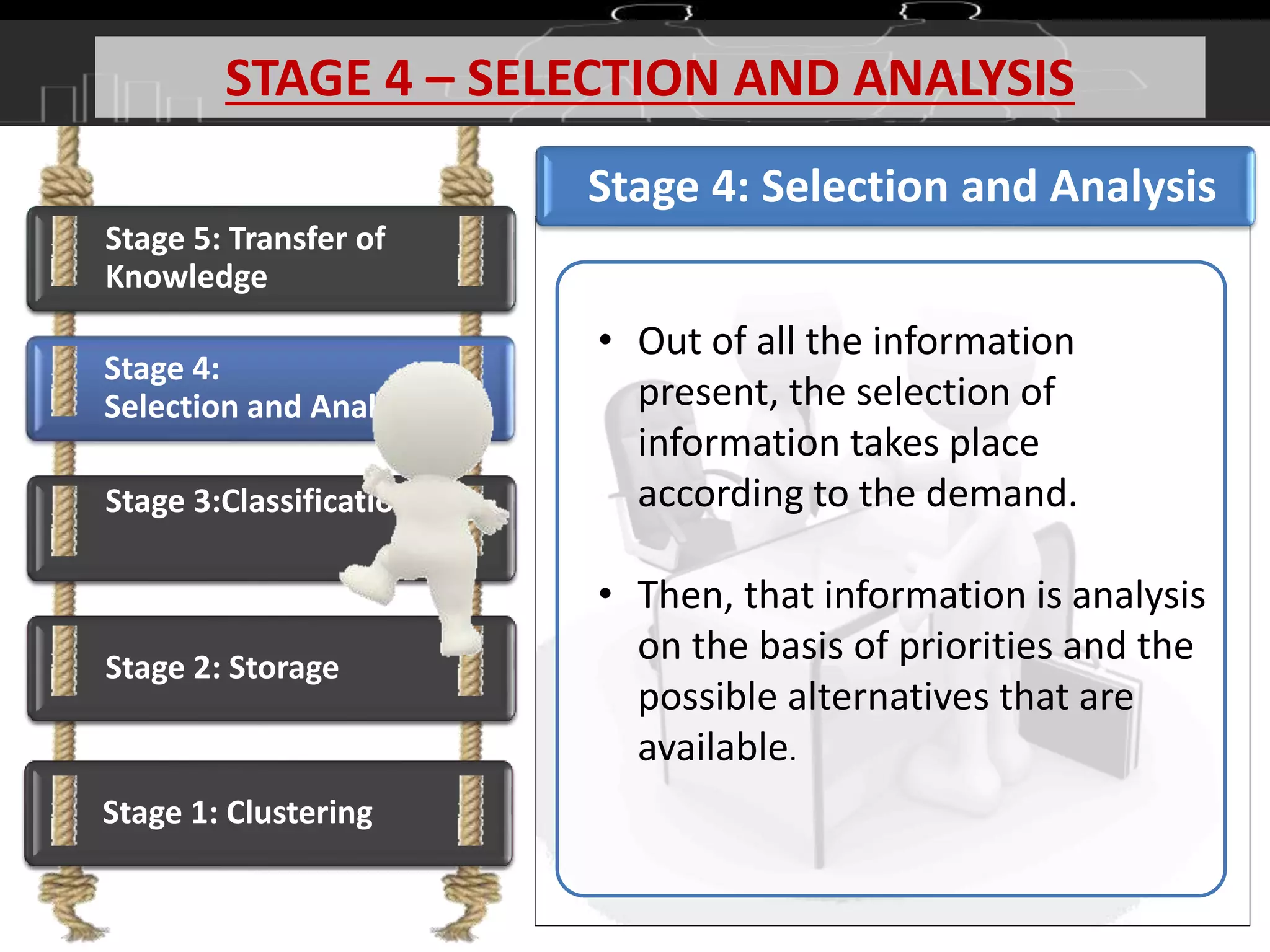
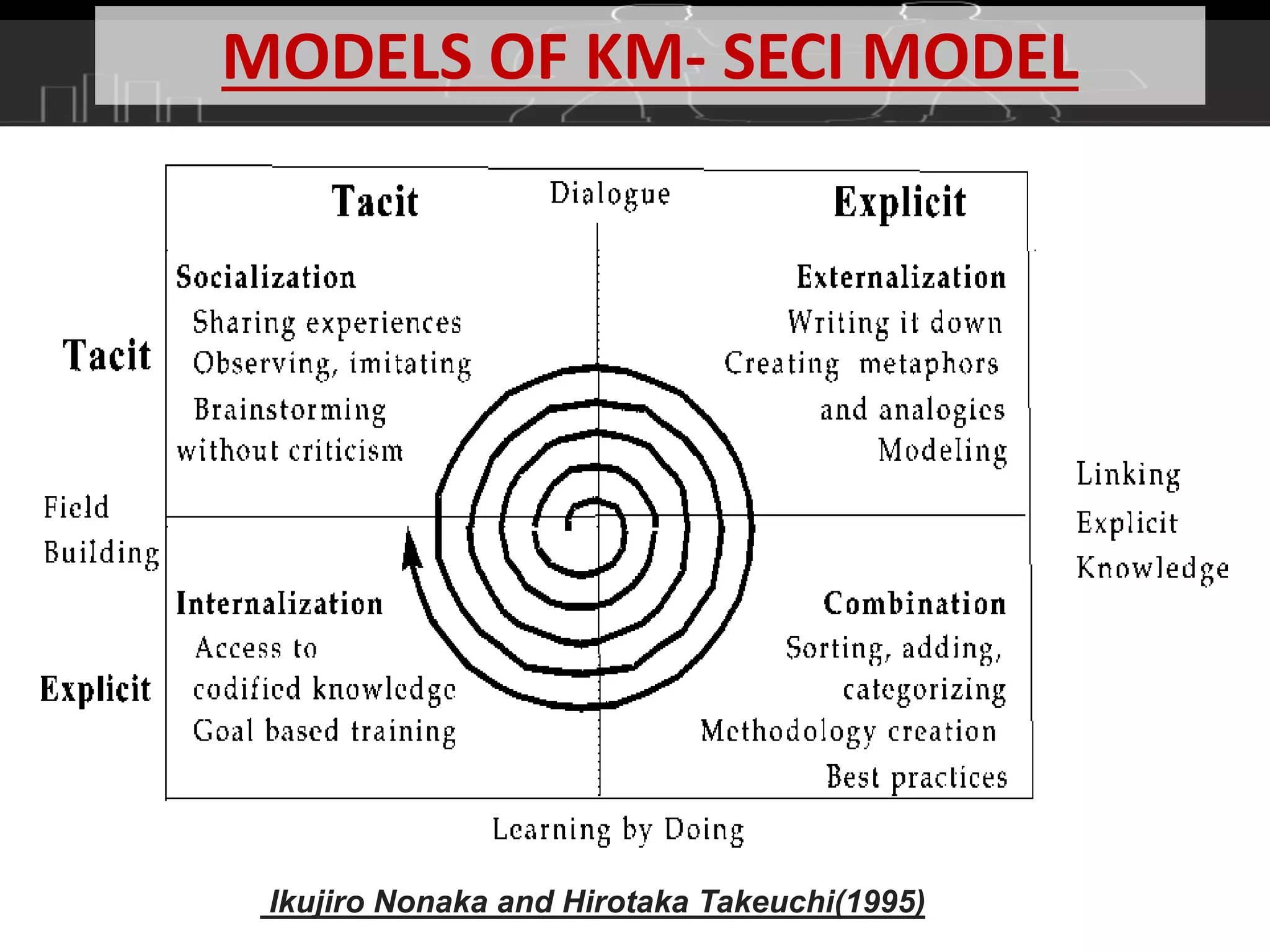
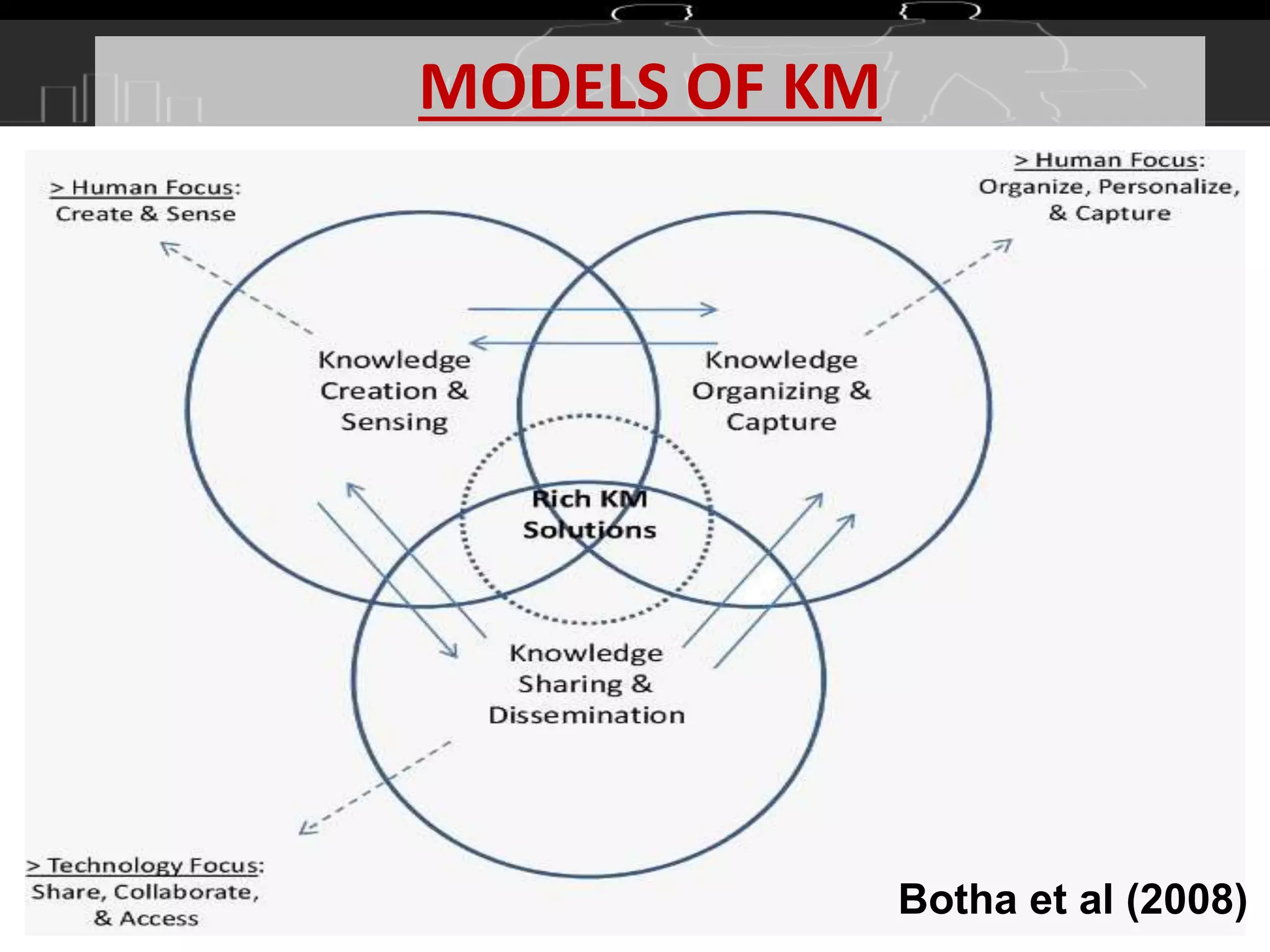
This document discusses knowledge management (KM) as a systematic process for acquiring, organizing, and sharing knowledge to enhance organizational performance. It outlines the definitions and components of KM, emphasizes the importance of both tacit and explicit knowledge, and details the stages of knowledge management processes including clustering, storage, classification, selection and analysis, and transfer of knowledge. Various models of KM, such as the SECI model, are also referenced to illustrate the frameworks for knowledge management.