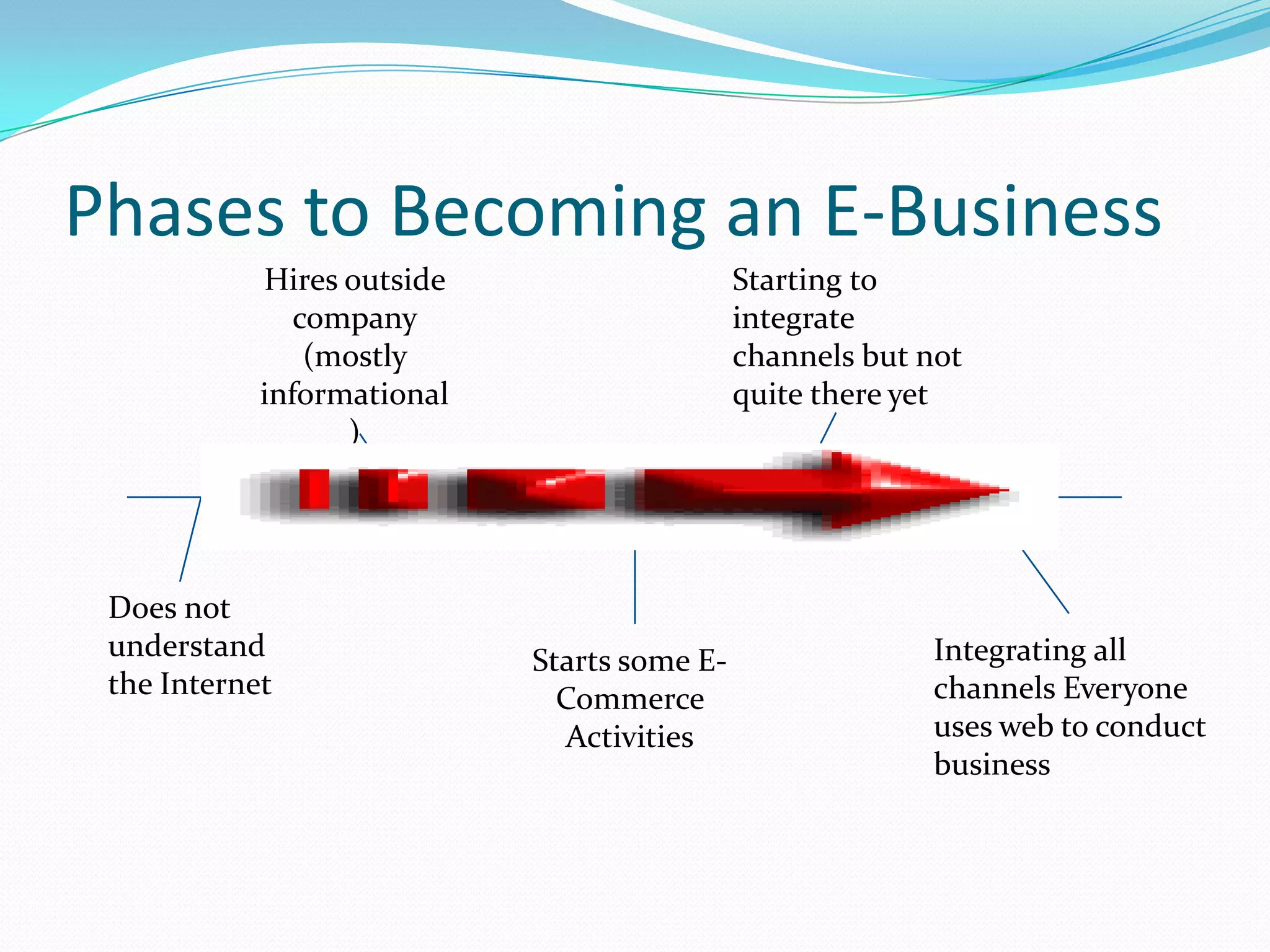
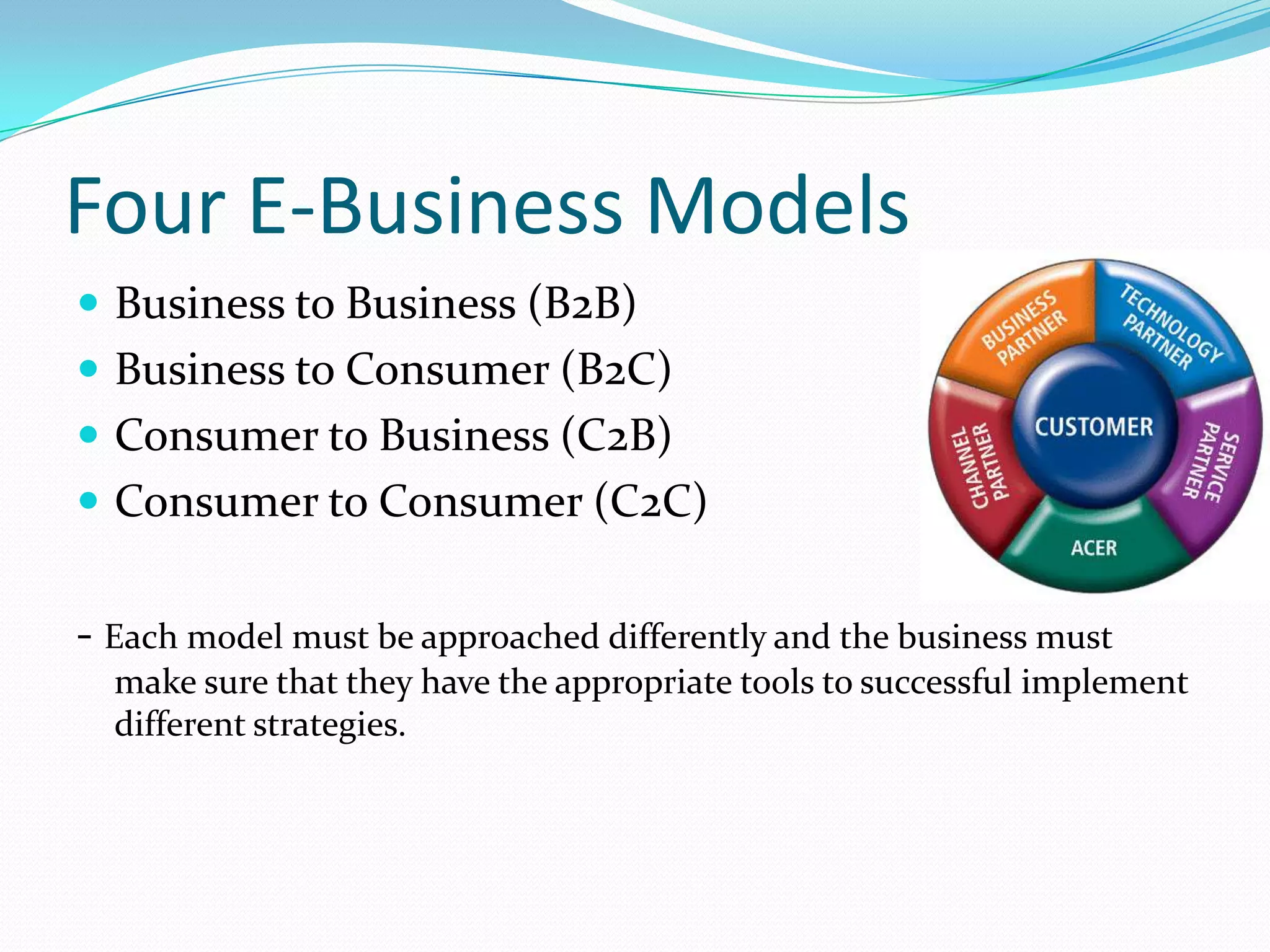
E-commerce involves online transactions, while e-business is broader and incorporates more business processes and information exchange. There are four main e-business models: business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-business, and consumer-to-consumer. E-business impacts marketing by allowing consumers to research and shop anytime from anywhere, and allows for more personalized advertising. It also benefits supply chain management by moving from mass production to demand-driven and shortening supply chains. While e-business provides advantages like reduced costs, it also faces challenges like security and start-up expenses.