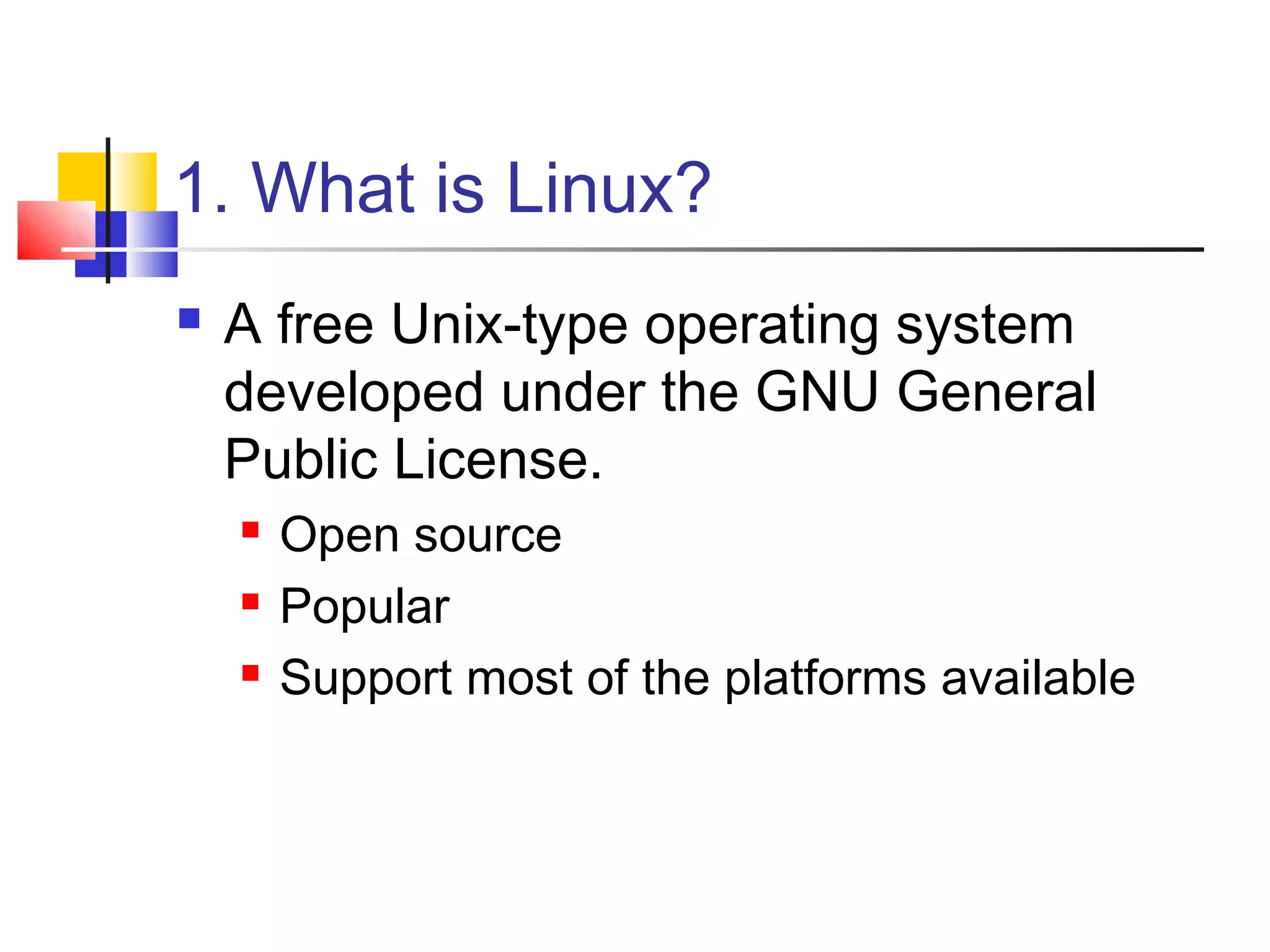
This document provides an overview of Linux basics including:
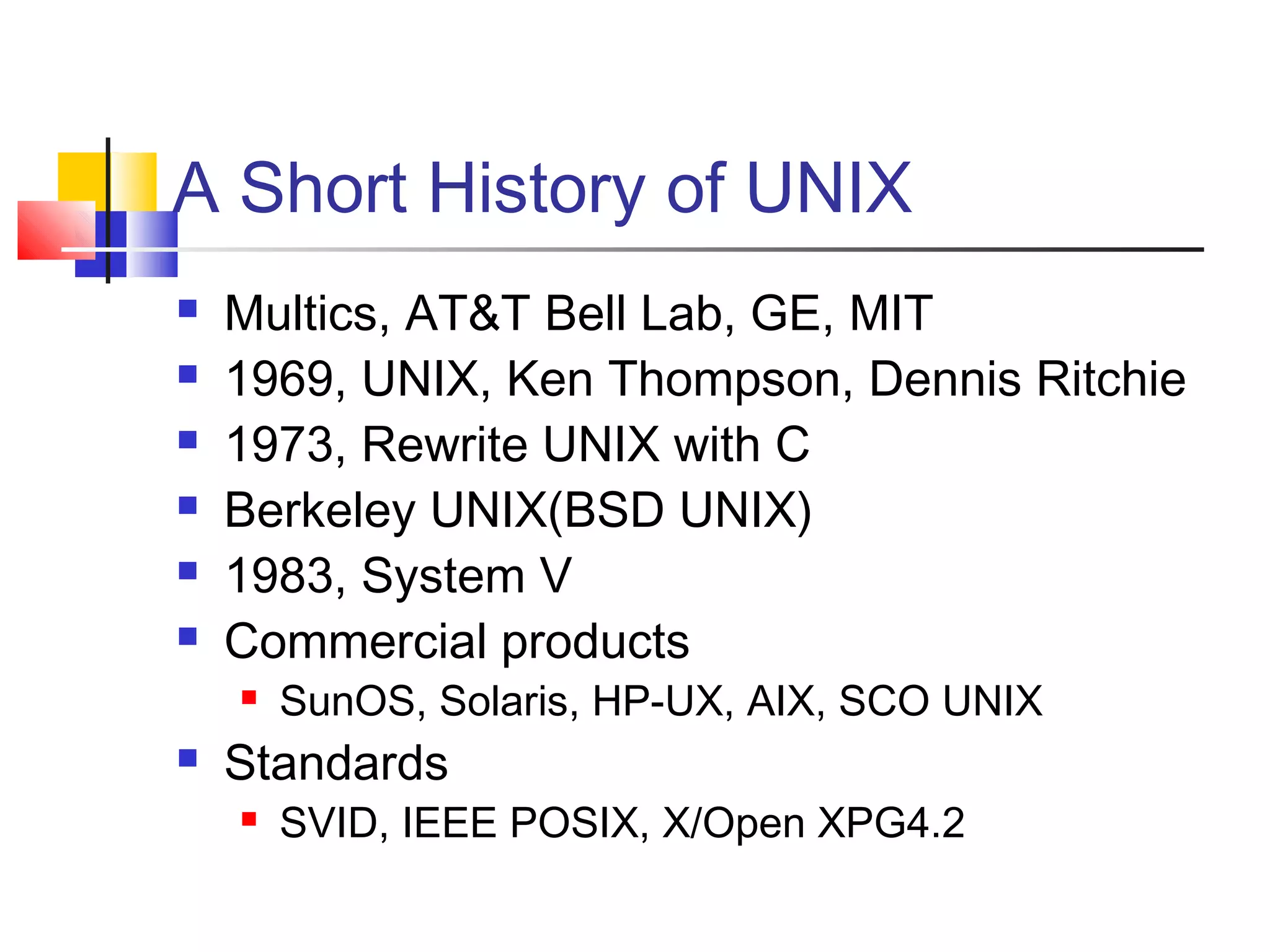
- A brief history of Linux and how it originated from UNIX.
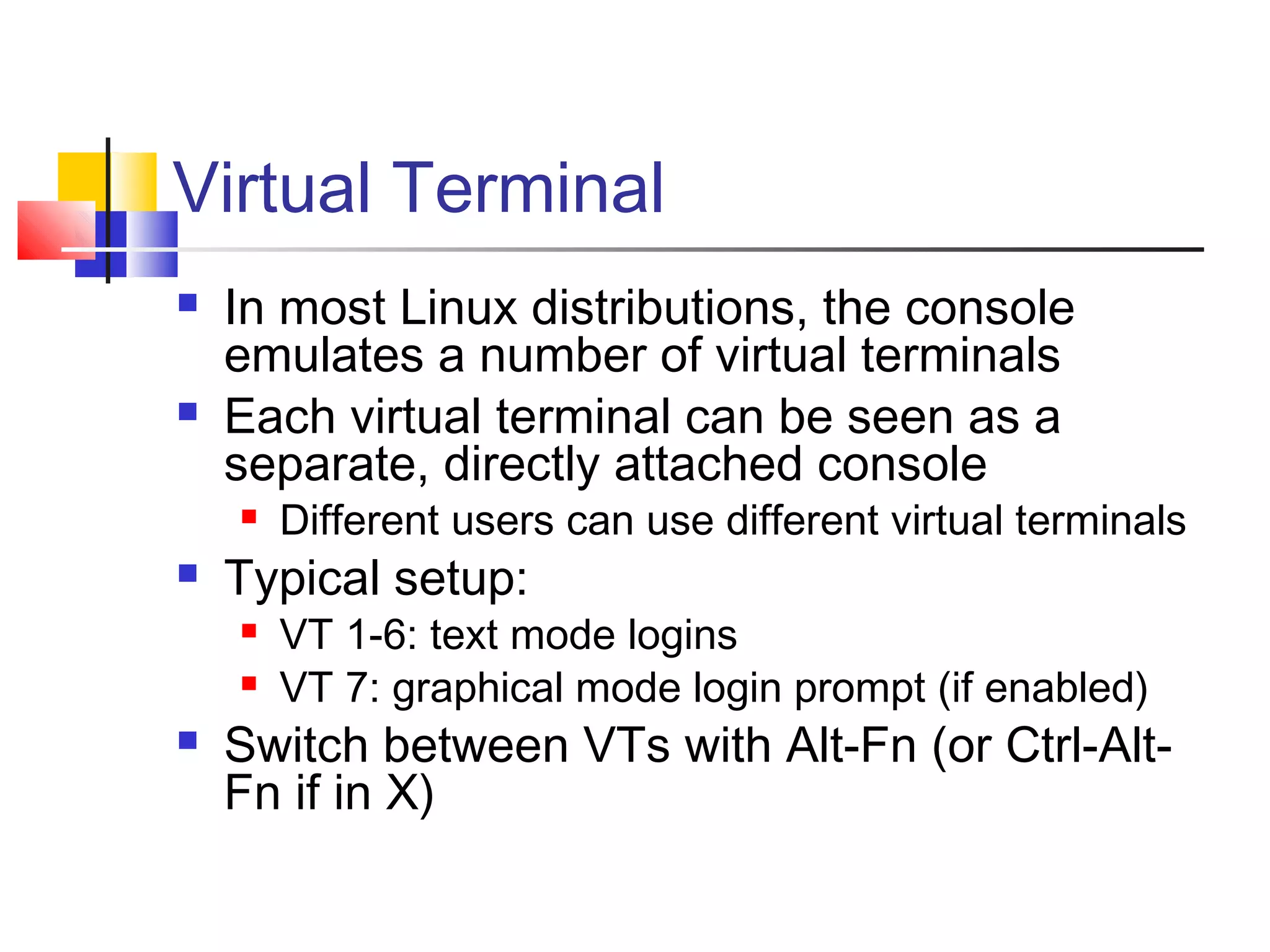
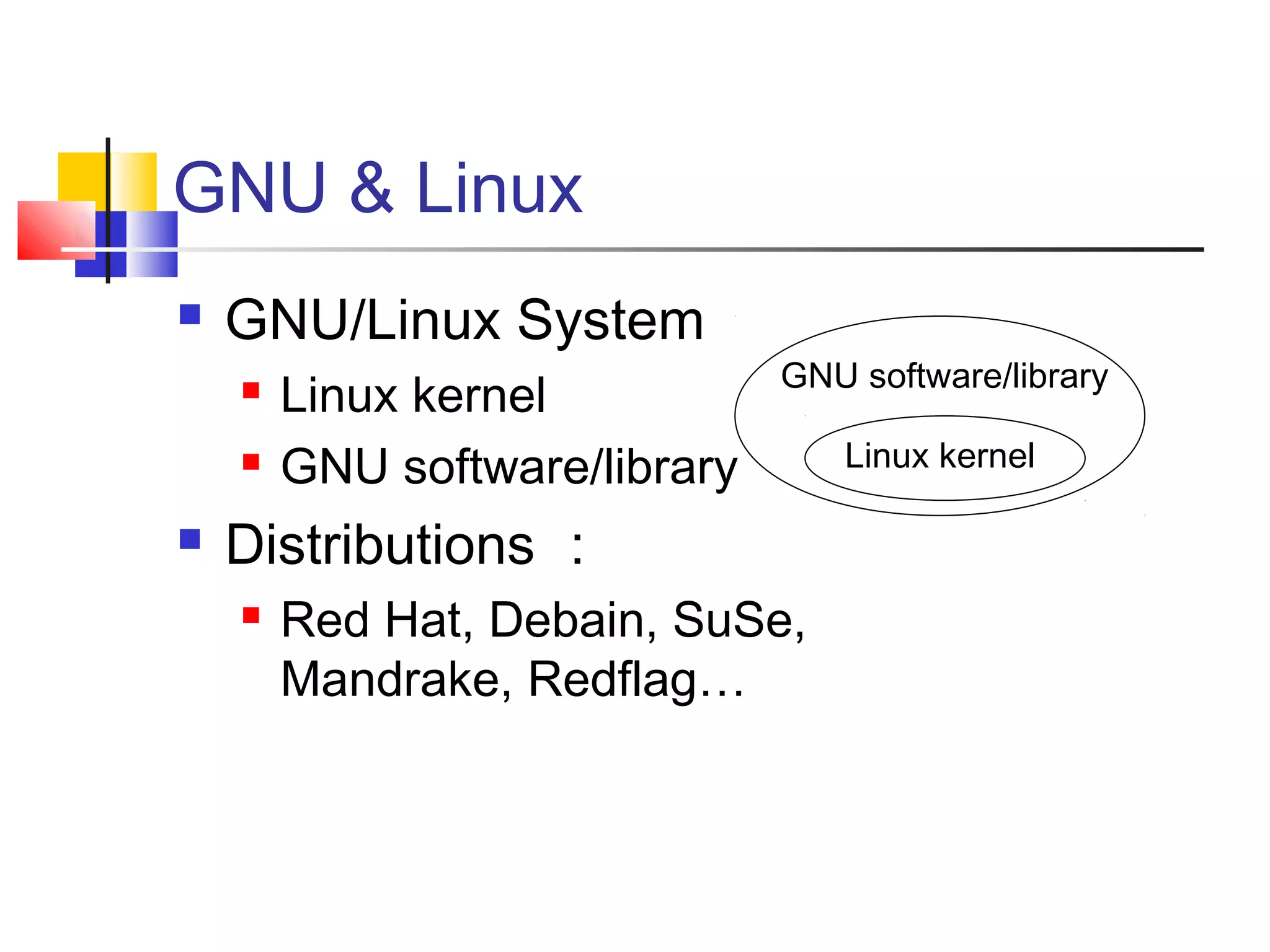
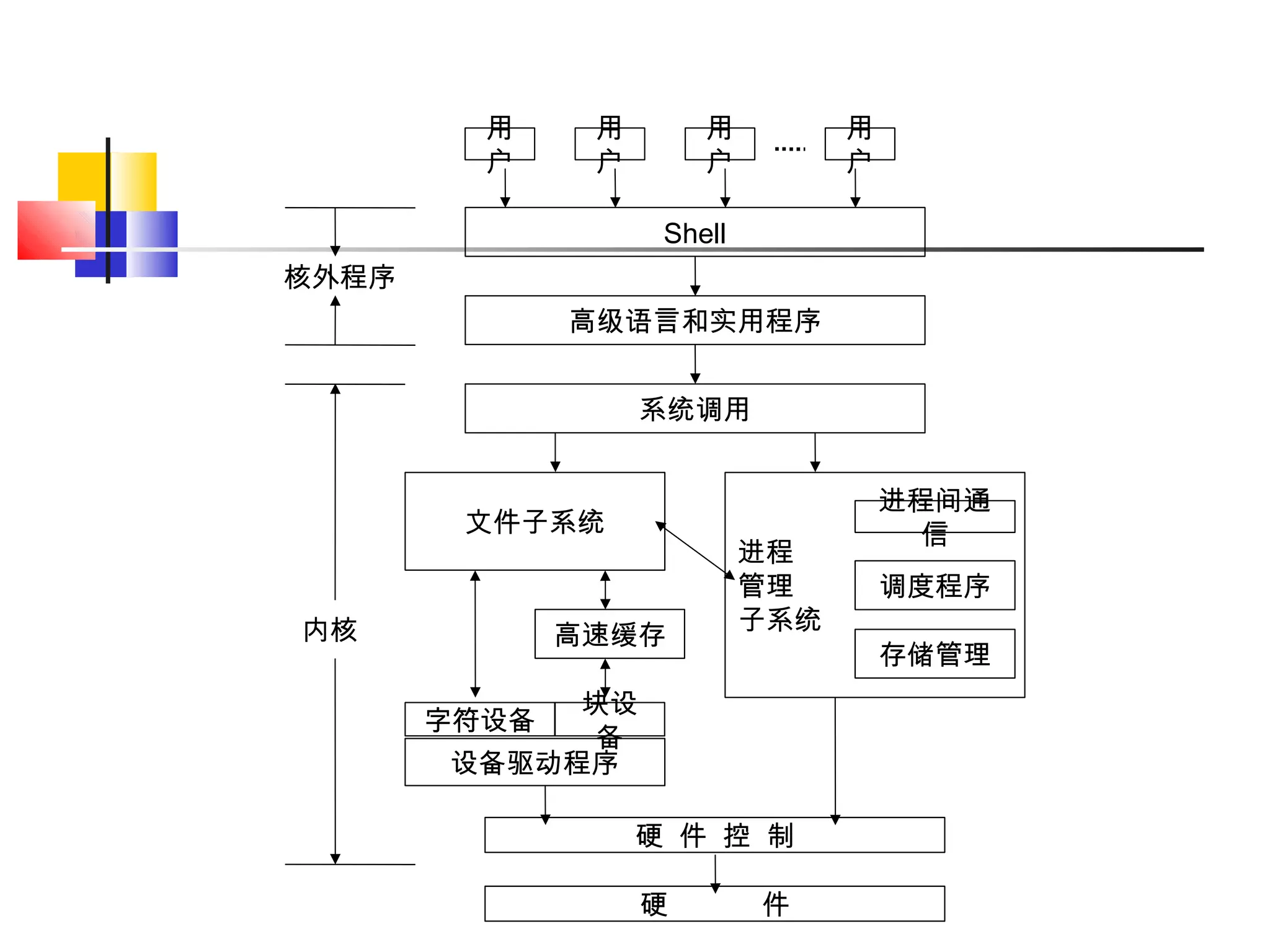
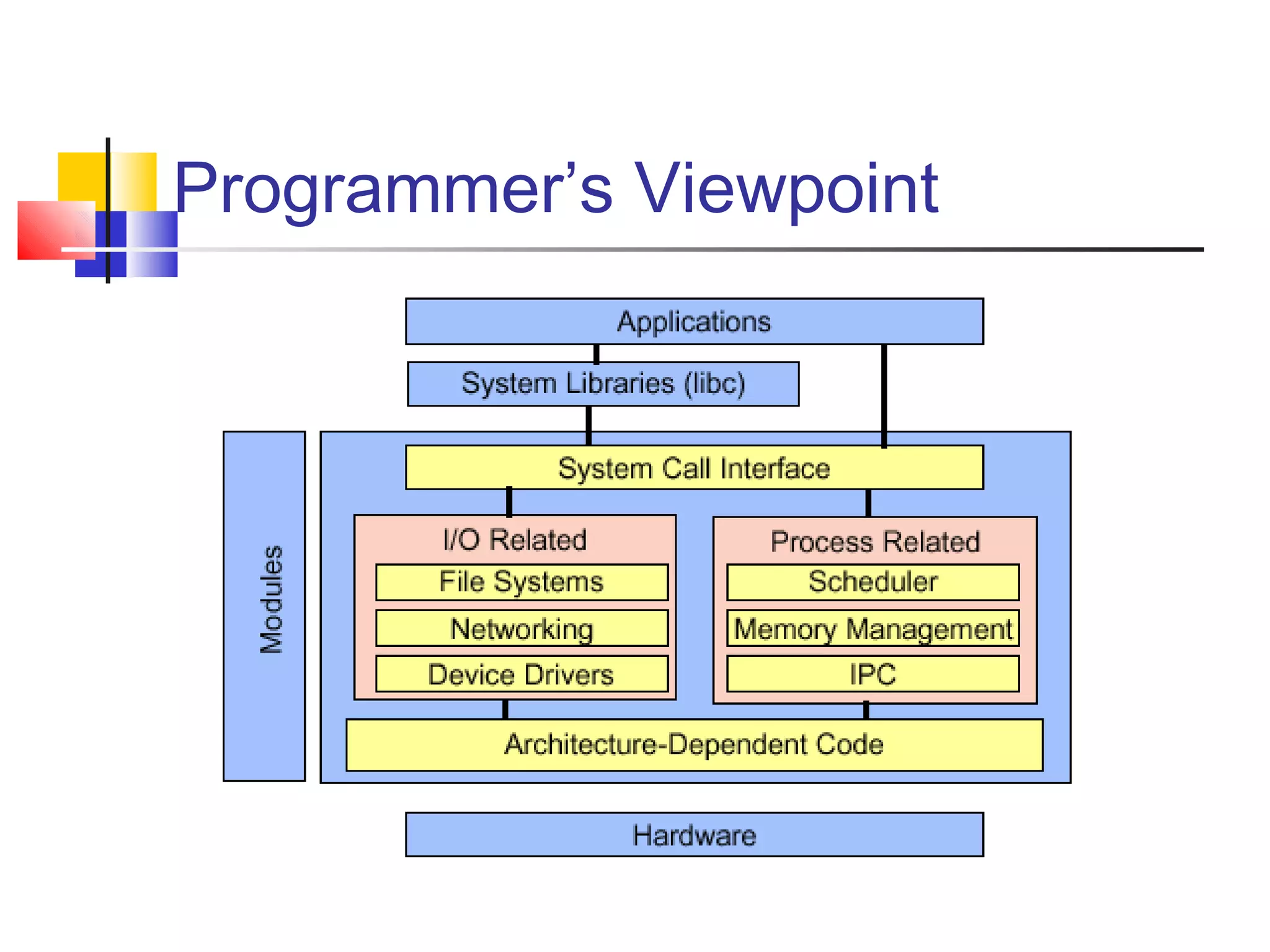
- An overview of Linux components including the kernel, userspace programs, shells, and how they interact.
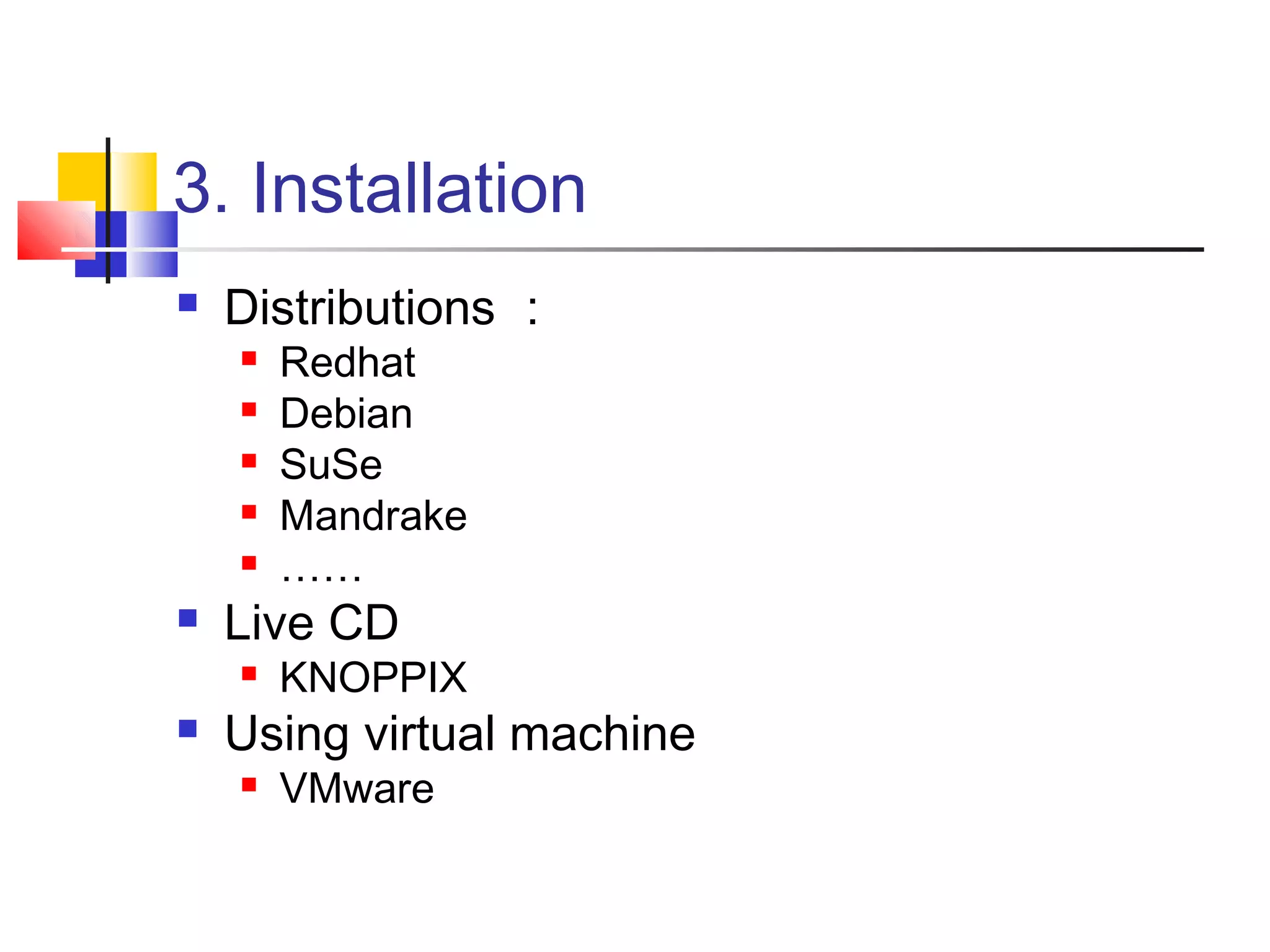
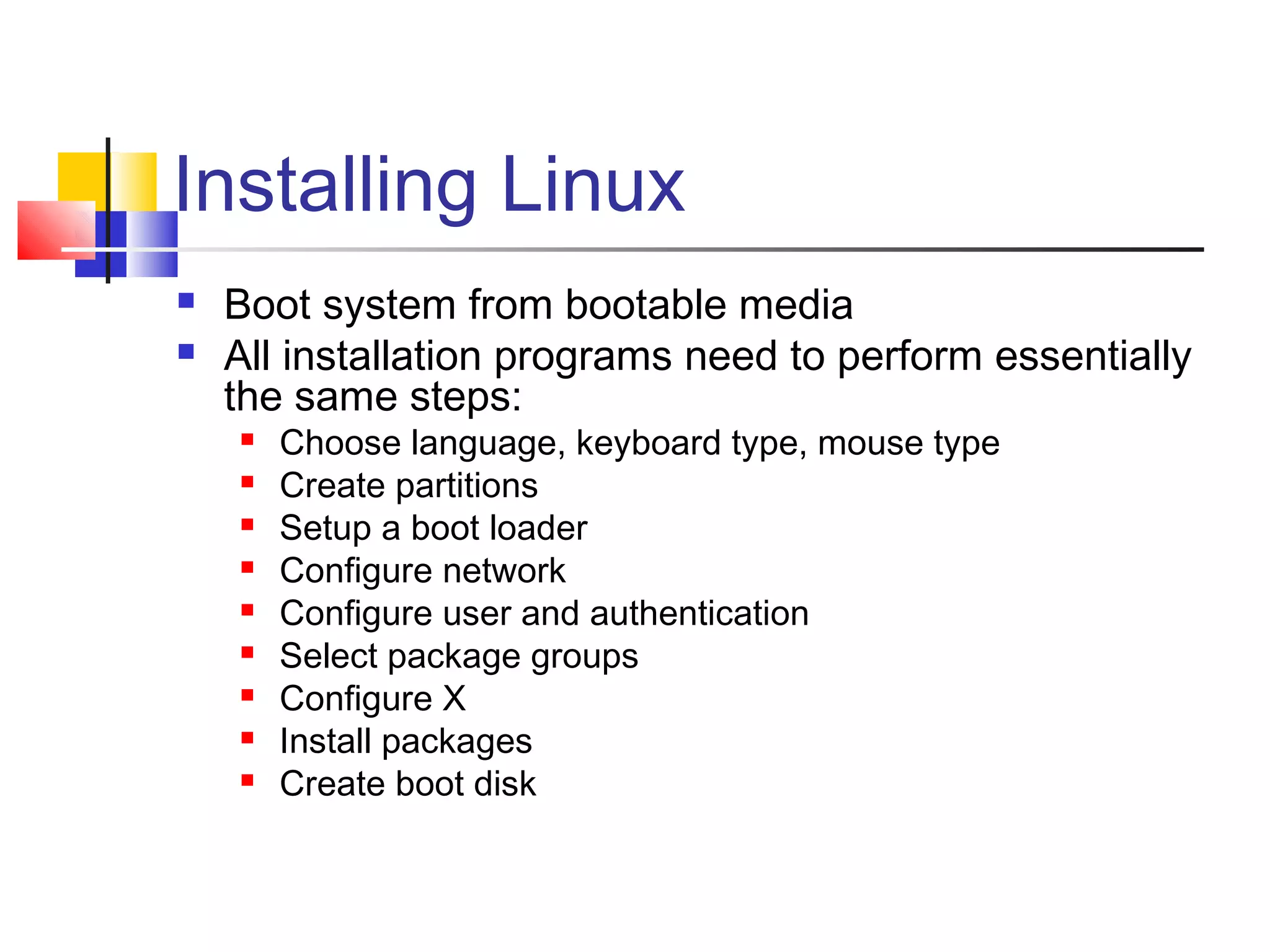
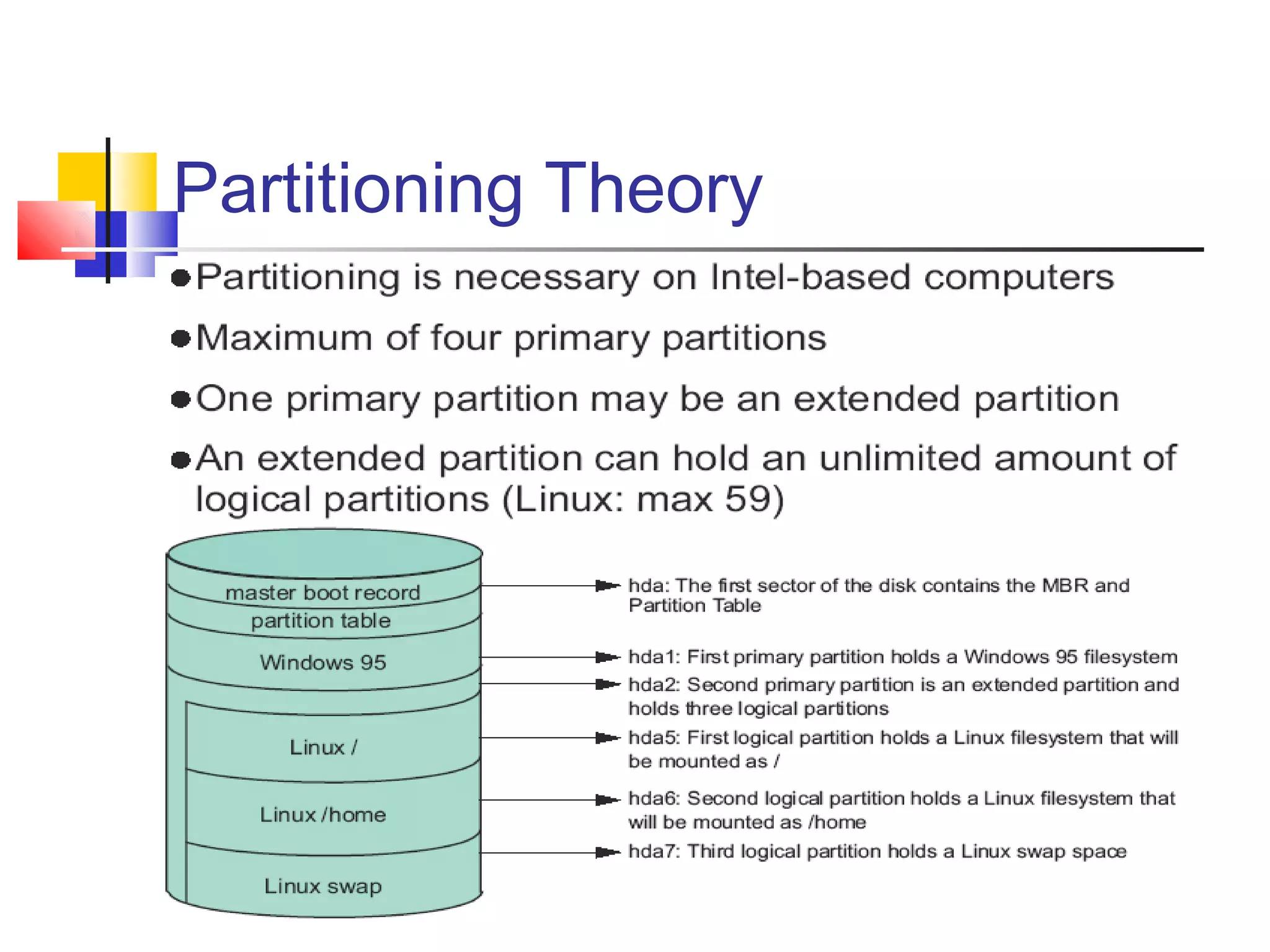
- Instructions for installing Linux distributions like Red Hat, Debian, and SuSE.
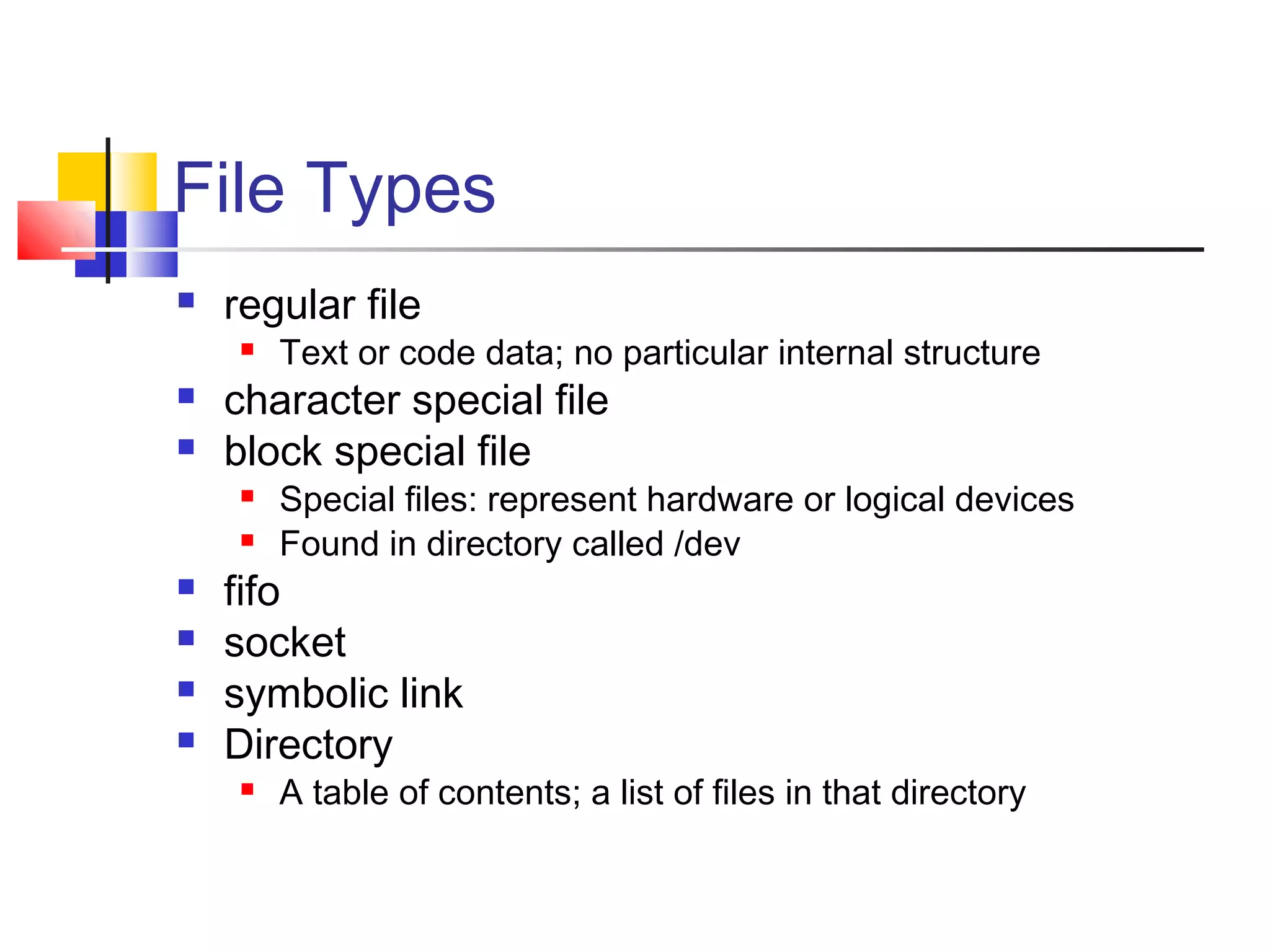
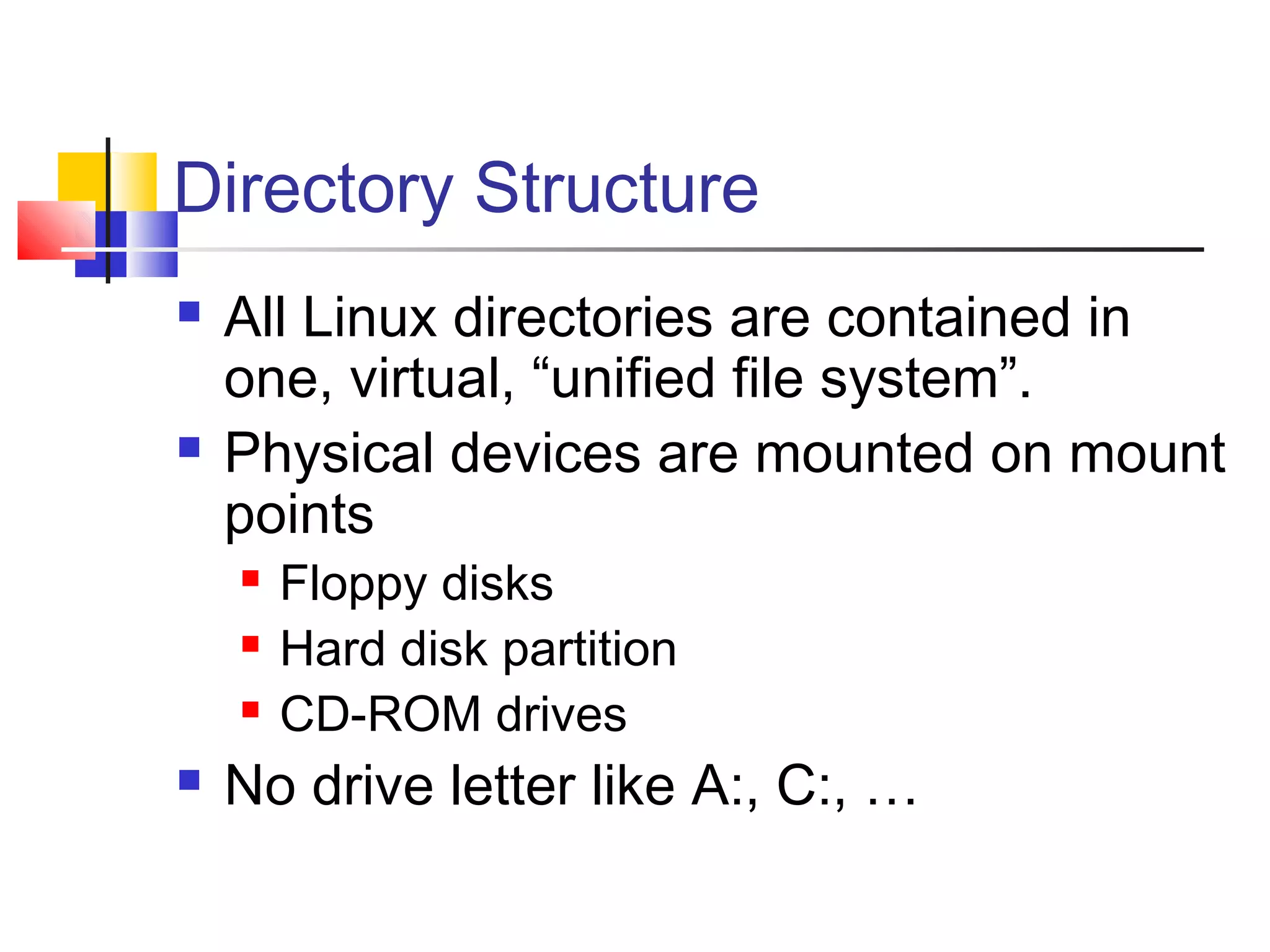
- How to use basic Linux commands and work with files, directories, and processes.
- Where to find Linux documentation using commands like man and info.
It serves as an introductory guide to getting started with the Linux operating system.





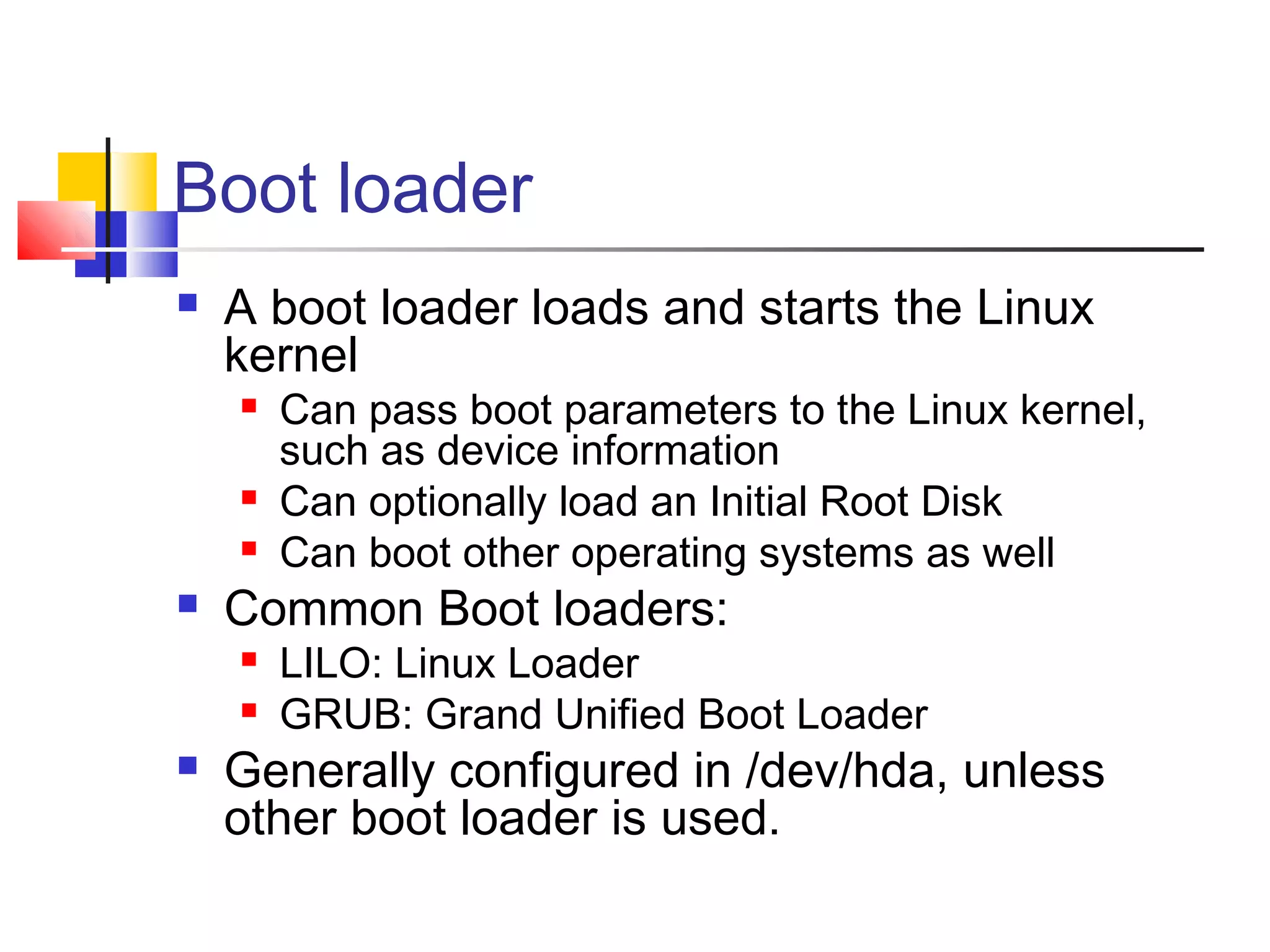
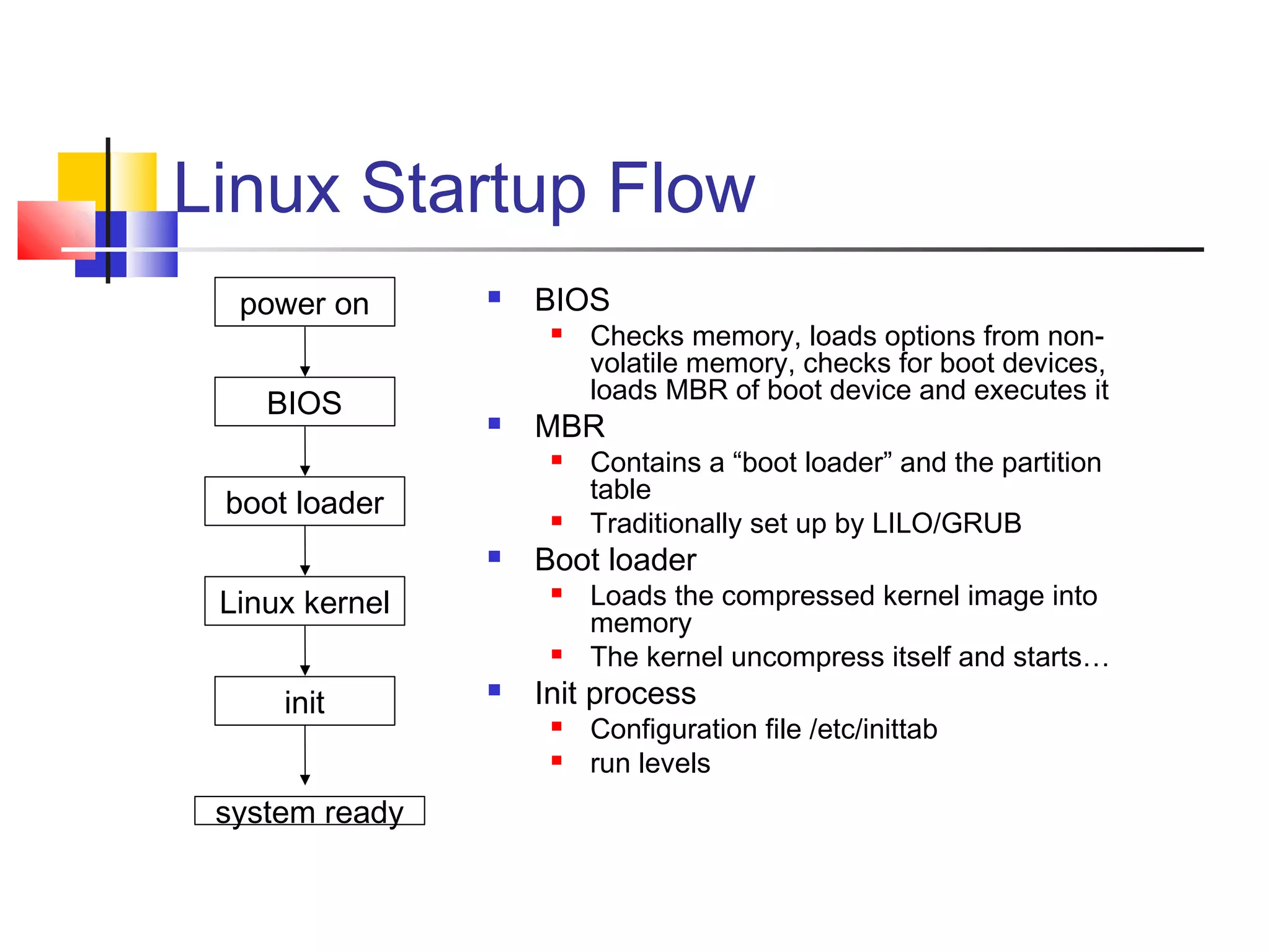
![Boot loader (cont’d)
LILO
Program to set up the MBR
Syntax: lilo [-v] [-v] [-C config-file] [-t]
Configuration file /etc/lilo.conf
Configures MBR according to configuration file
GRUB
Program stored in MBR (first stage) and in /boot/grub (1.5th
and second stage)
Understand file system structure; no need to activate a
configuration as with LILO
Configuration file /boot/grub/grub.conf
Installed in MBR with grub-install](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch1linuxbasics-130114002355-phpapp01/75/Ch1-linux-basics-16-2048.jpg)