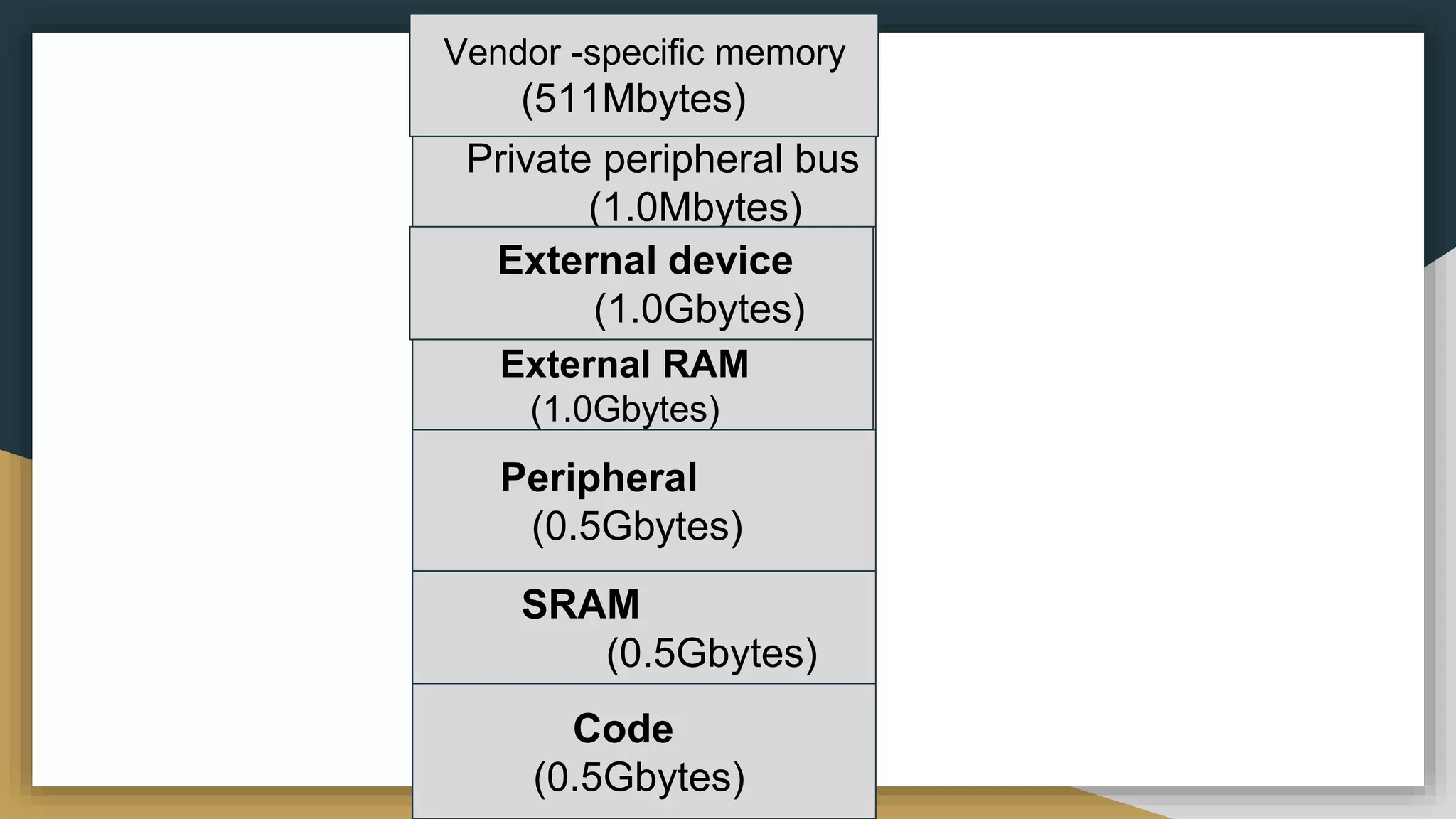
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) allows privileged software to define memory access permissions for up to 16 memory regions. It monitors memory transactions and can trigger exceptions when access violations occur. The MPU supports programming region sizes, access permissions, memory types and other attributes for memory protection and management. Key registers like MPU_RBAR and MPU_RLAR are used to define region bases, limits, and attributes.









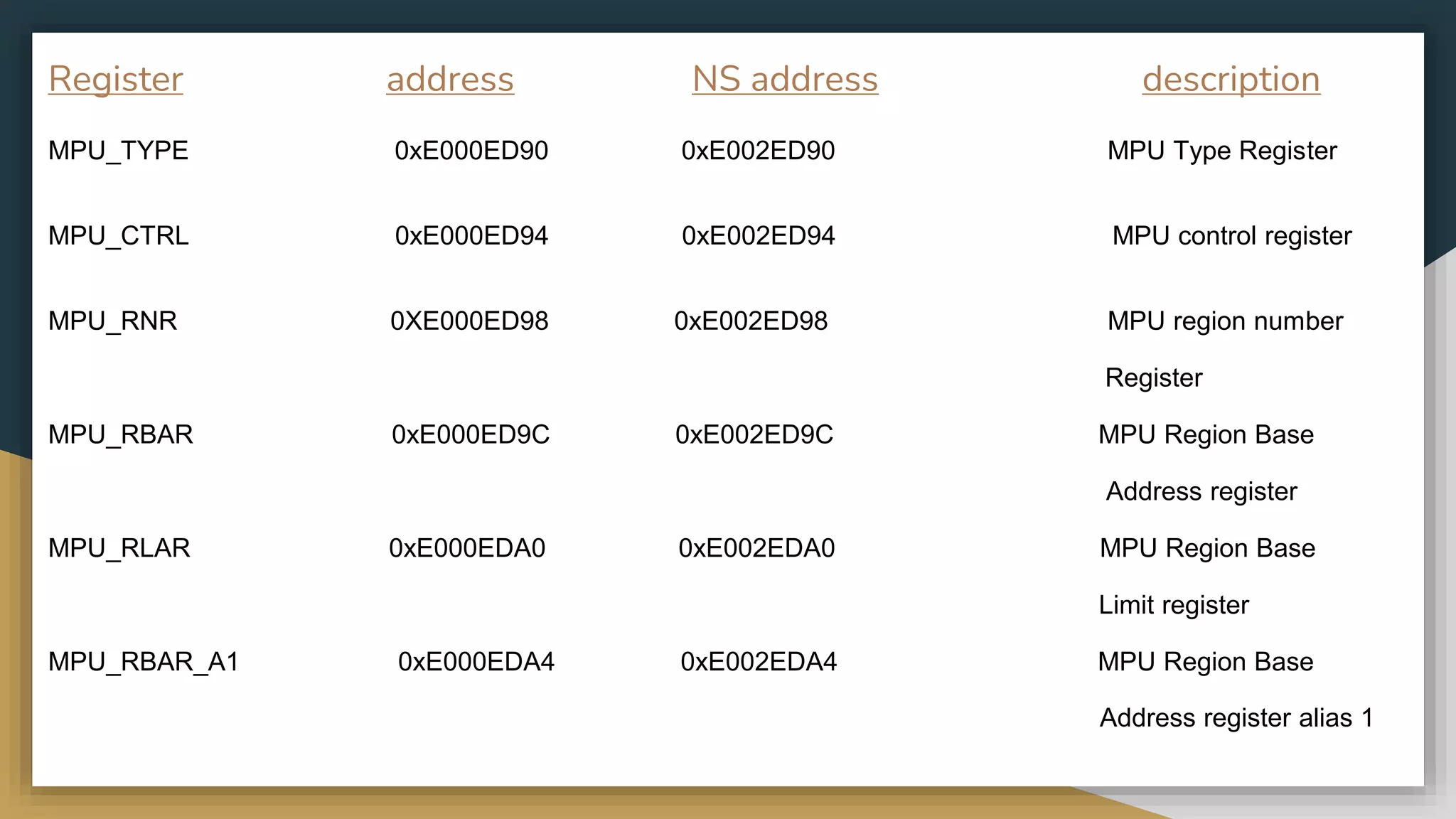
![MPU_TYPE:-
The MPU Type register indicates how many regions the MPU supports for the
selected security state. This register is read only.
[31:16]-> reserved
[15:8] -> region
[7:1] ->reserved
[0] -> separate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memoryprotectionunitmpu1-230411101711-42a85918/75/Memory-Protection-Unit-MPU-1-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![MPU_CTRL:-
The MPU Control register provides various programmable bit fields for MPU enable and features.
[31:3] -> reserved
[2] ->Privileged background region enable
[1] ->MPU Enable for HardFault and NMI(non-maskable)
[0] ->MPU enable/disable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memoryprotectionunitmpu1-230411101711-42a85918/75/Memory-Protection-Unit-MPU-1-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
![MPU_RNR:
The MPU Region Number Register selects the region that is accessed by the
MPU_RBAR and MPU_RLAR
[31:8] -> reserved
[7:0] -> Region number. Selects and indicates the region that is accessed by
the
MPU_RBAR and MPU_RLAR.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memoryprotectionunitmpu1-230411101711-42a85918/75/Memory-Protection-Unit-MPU-1-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
![MPU_RBAR:
The MPU Region Base Address Register defines the starting address of an MPU
region and access permission
[31:5] ->Starting address of MPU region address
[4:3] ->Shareability for Normal memory
[2:1] ->Access permissions
[0] ->eXecute never attribute](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memoryprotectionunitmpu1-230411101711-42a85918/75/Memory-Protection-Unit-MPU-1-pptx-18-2048.jpg)
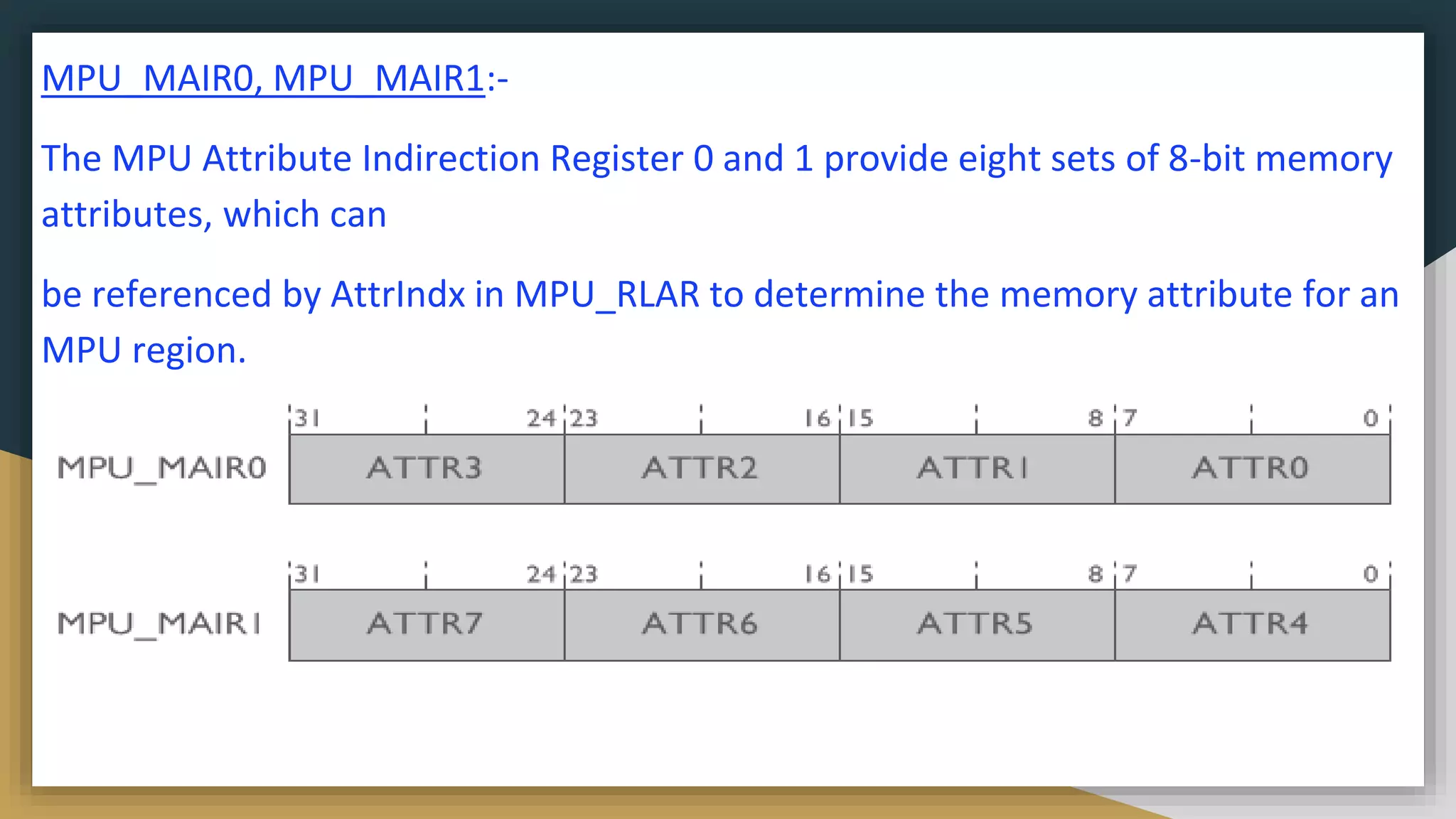
![MPU_RLAR:
The MPU Region Limit Address Register defines the ending address of an MPU region, region
enable, and an indirection index to memory attribute array
[31:5] -> ending address of MPU region address.
[4] -> reserved
[3:1] ->Attribute Index. Select memory attributes from attribute sets
in
MPU_MAIR0 and MPU_MAIR
[0] -> enable /disable the region](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memoryprotectionunitmpu1-230411101711-42a85918/75/Memory-Protection-Unit-MPU-1-pptx-19-2048.jpg)
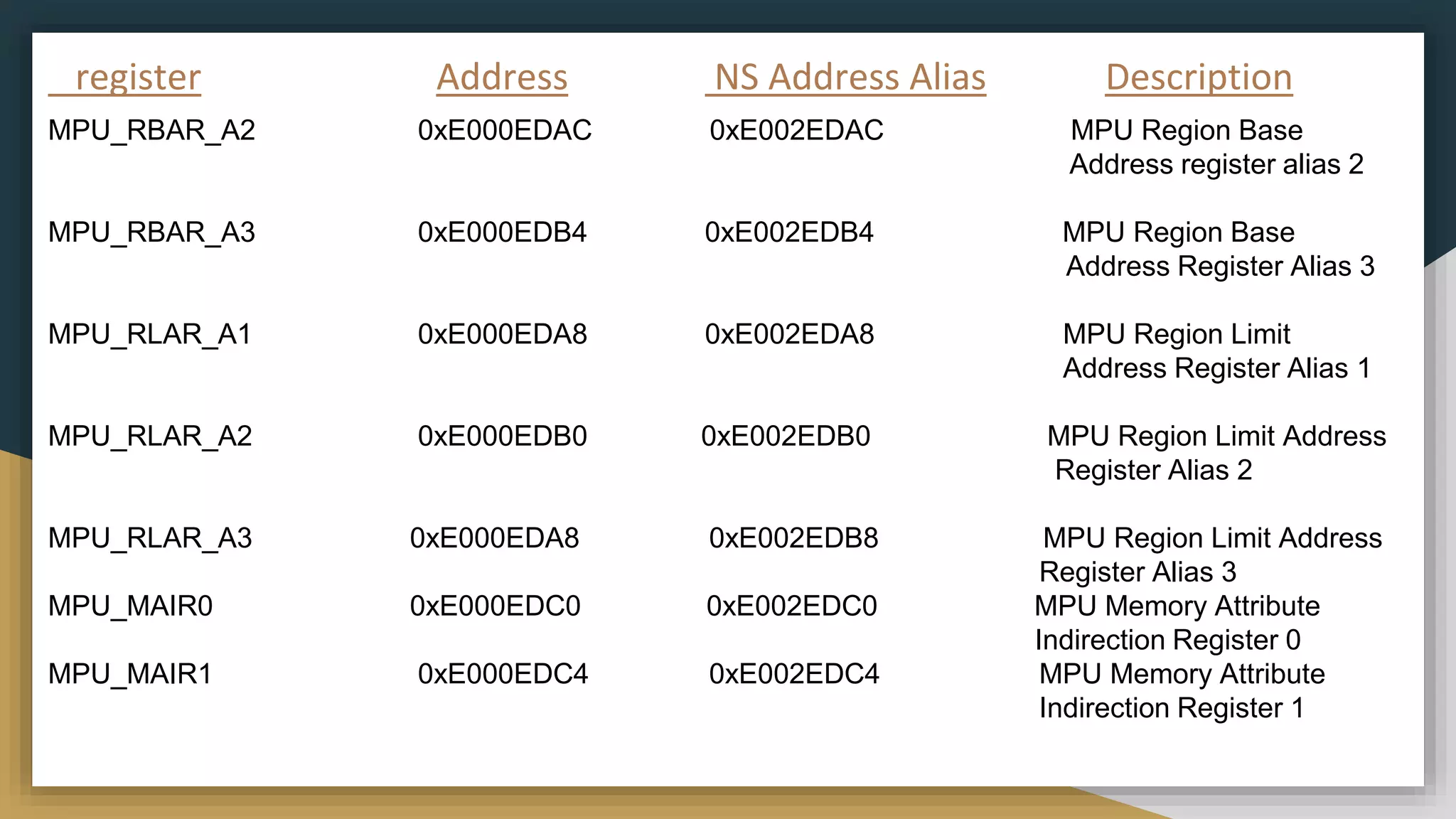
![MPU_RBAR_A1/2/3 and MPU_RLAR_A1/2/3:-
An alias of MPU_RBAR register to allow faster programming of different MPU regions. The region
number that is selected when using MPU_RBARn and MPU_RLARn is equal to (MPU_RNR[7:2]<<2)
Condition When Accessing MPU Region accessed
MPU_RNR=0 MPU_RBAR / MPU_RLAR 0
MPU_PNR=1 MPU_RBAR_A1 / MPU_RLAR_A1 1
MPU_PNR=4 MPU_RBAR / MPU_RLAR 4
MPU_PNR=5 MPU_RBAR_A1 / MPU_RLAR_A1 5
MPU_PNR=6 MPU_RBAR_A2 / MPU_RLAR_A2 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memoryprotectionunitmpu1-230411101711-42a85918/75/Memory-Protection-Unit-MPU-1-pptx-20-2048.jpg)