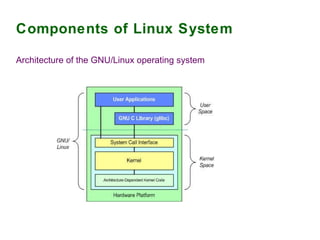
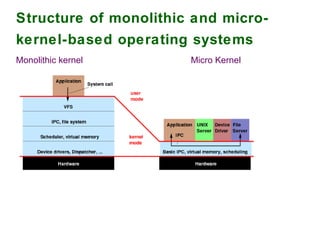
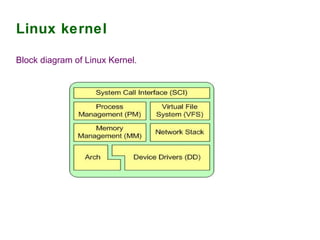
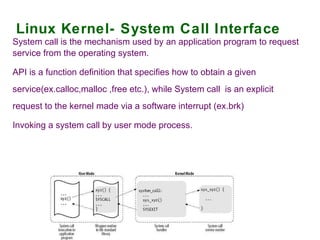
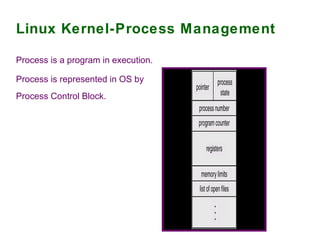
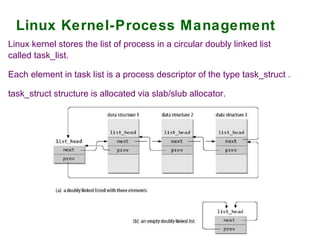
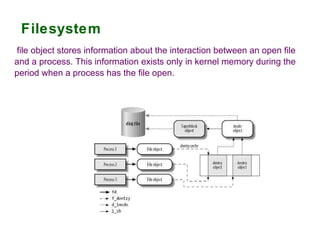
The document provides an overview of the key components of the Linux operating system, including:
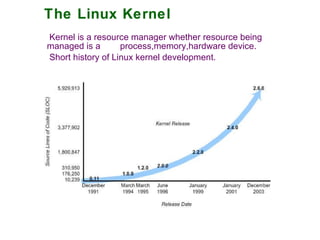
1) The Linux kernel, which acts as a resource manager for processes, memory, and hardware devices.
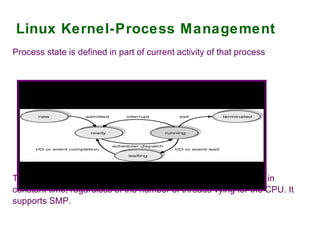
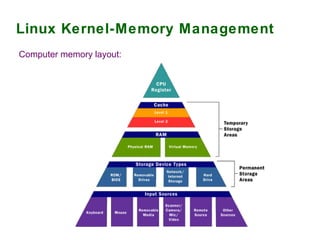
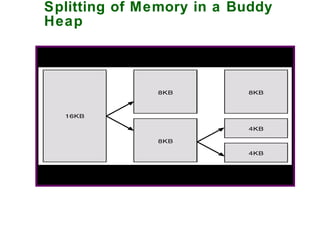
2) Process and memory management systems that control how processes are allocated and memory is allocated and freed.
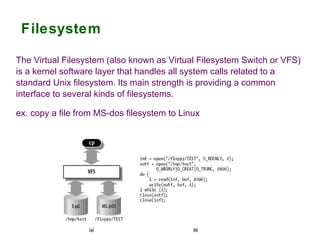
3) The file system which organizes how files are stored and accessed.
4) Device drivers that allow the operating system to interface with hardware.
5) The network stack which handles network protocols and connections.
6) Architecture-dependent code that provides hardware-specific implementations of core functions.