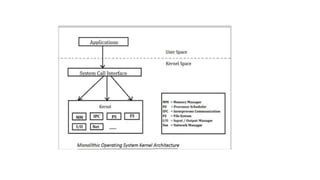
This document discusses monolithic kernels. It defines a kernel as the core component of an operating system that controls processes, memory management, I/O devices, and acts as an interface between hardware and applications. A monolithic kernel runs all basic system services like process management and I/O communication within the kernel space. While monolithic kernels provide rich hardware access and fast execution, they are difficult to maintain and debug due to their large size and lack of modularity.