This document provides an overview of Kerberos authentication, including:
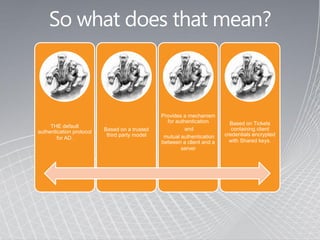
- Kerberos was developed at MIT and adopted as the default authentication protocol in Windows 2000.
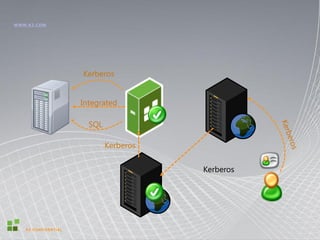
- It provides mutual authentication between a client and server based on tickets containing encrypted client credentials.
- The Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) issues encryption keys to authenticate entities using a shared master key.






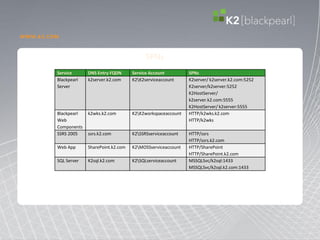







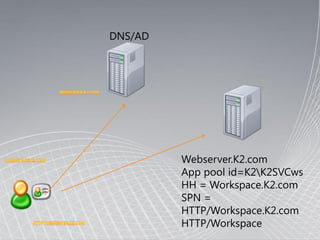




![MSSQLSvc/FQDN:[port | instancename],
MSSQLSvc/FQDN:port | MSSQLSvc/FQDN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kerberospresentation-111112103133-phpapp01/85/Kerberos-presentation-28-320.jpg)