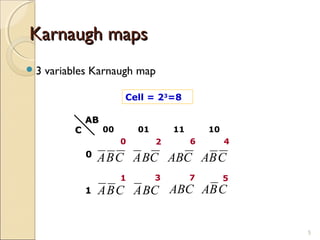
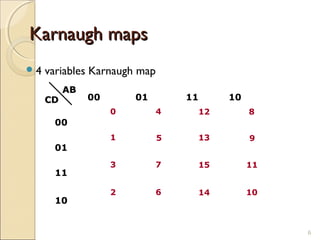
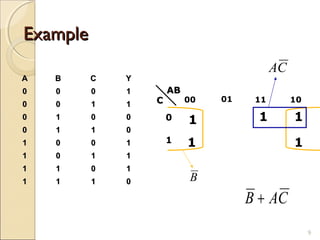
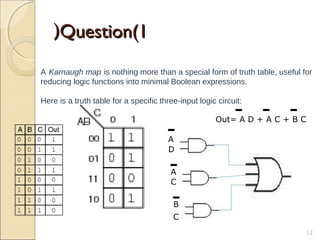
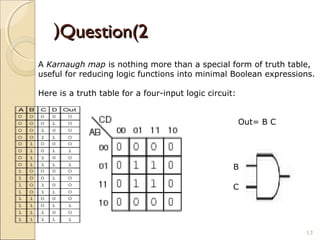
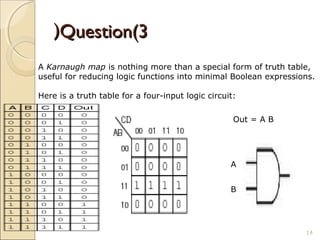
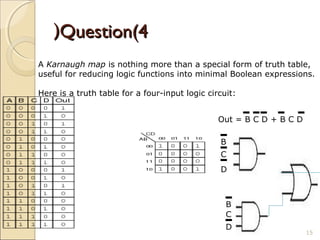
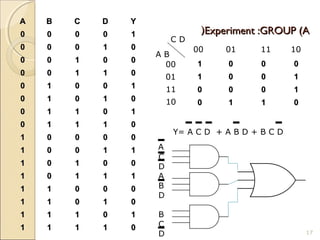
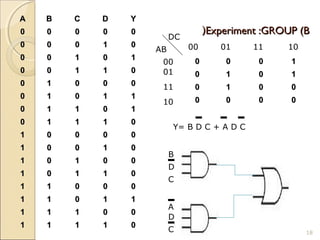
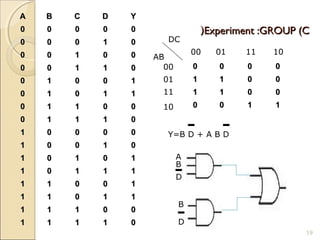
Karnaugh maps provide an alternative way to simplify logic circuits by visually grouping adjacent cells containing 1's and 0's in a map based on the truth table. The document provides examples of 2, 3, and 4 variable Karnaugh maps and explains how to construct the maps from truth tables and simplify logic functions into minimal Boolean expressions.