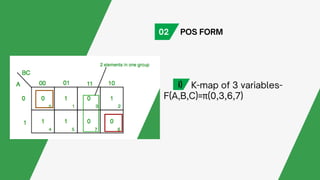
The document discusses Karnaugh maps (k-maps), a graphical tool used for simplifying boolean expressions with benefits including ease of data representation and straightforward implementation. It outlines the properties, operations, and simplification processes involved in solving k-maps for both sum of products (SOP) and product of sums (POS) forms. Additionally, it touches on the 'don't care' condition, which can aid in further simplification.