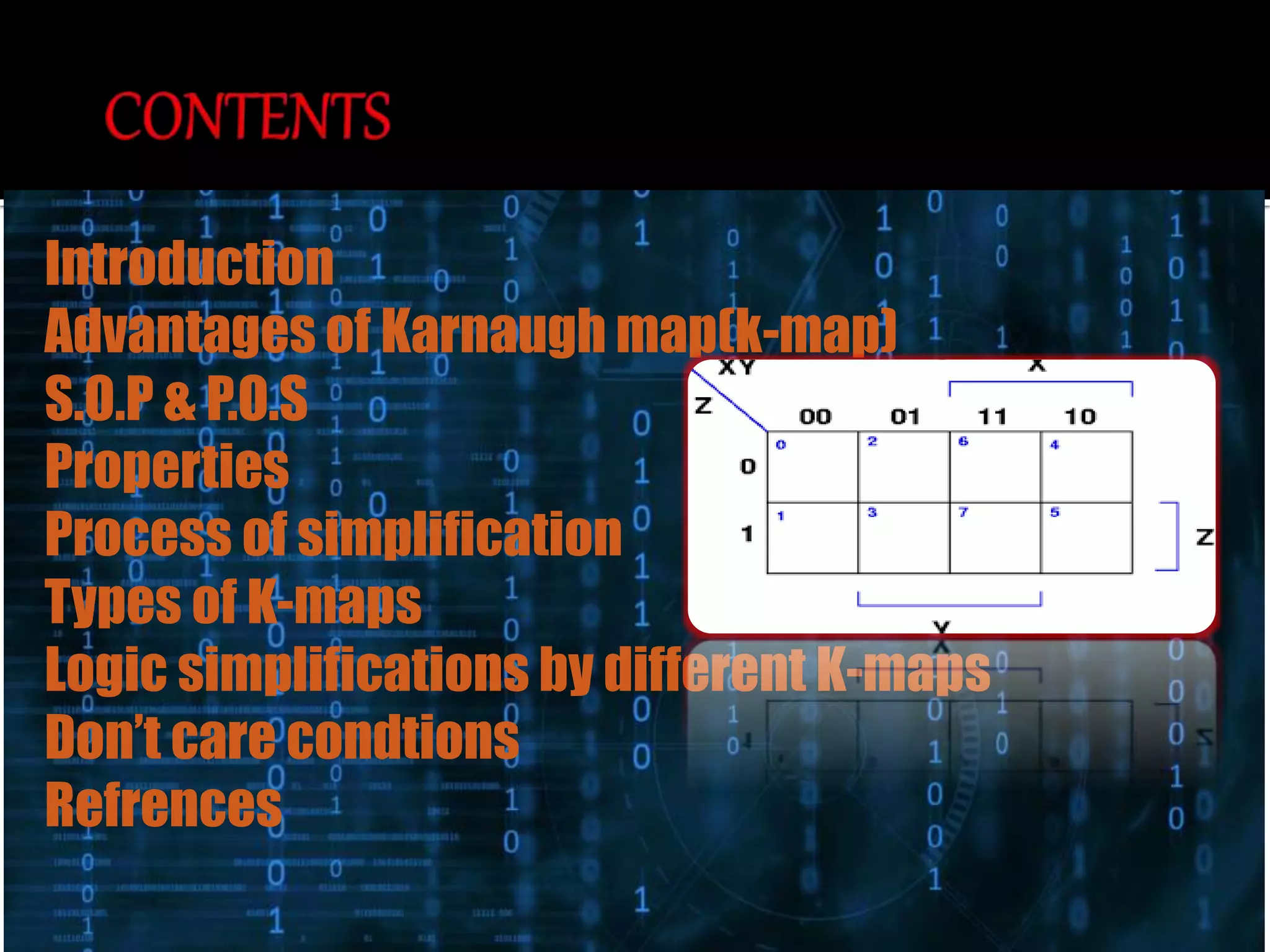
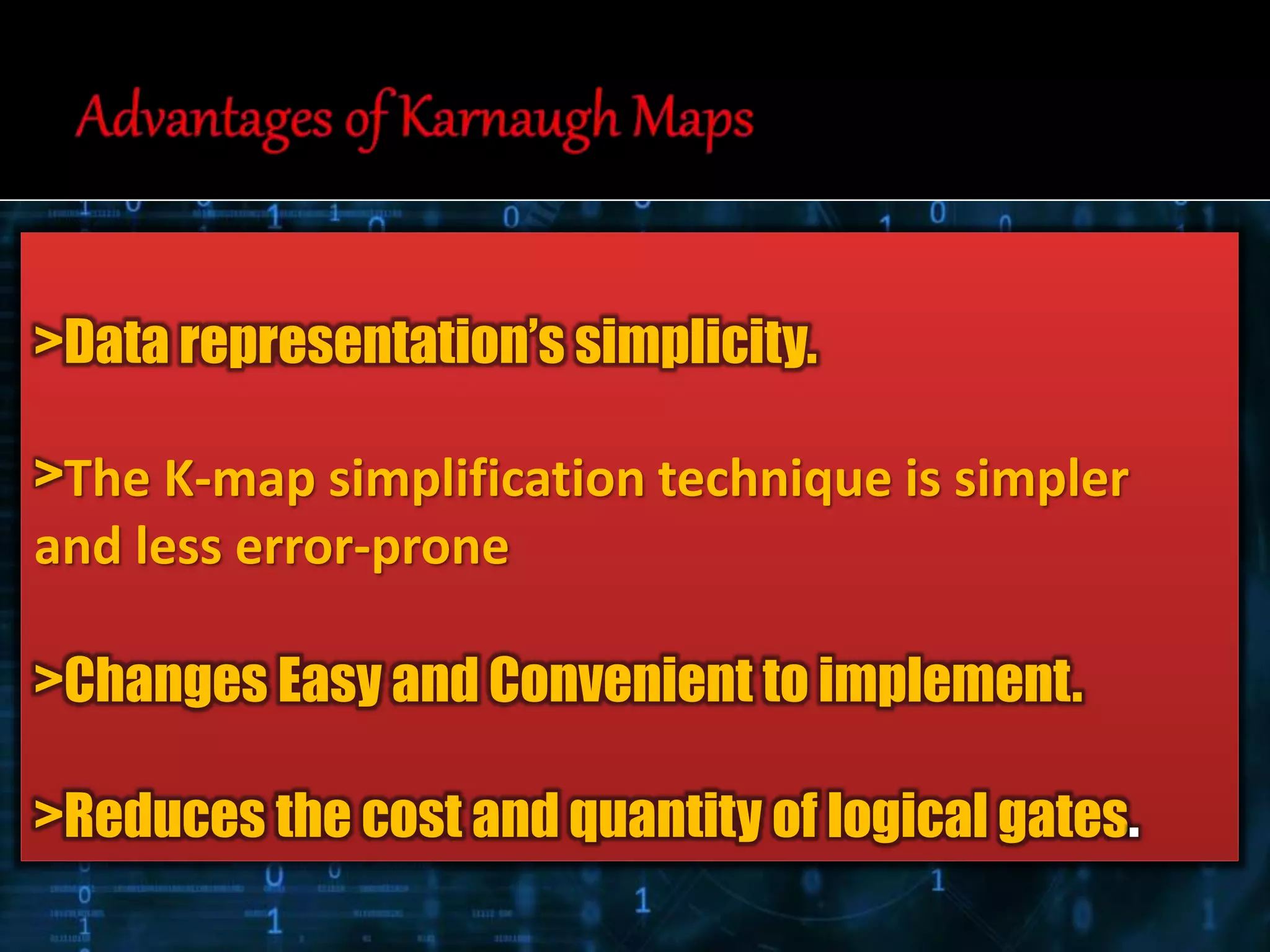
The document discusses Karnaugh maps (k-maps), a graphical method for minimizing boolean expressions, initially invented by Maurice Karnaugh in 1953. It outlines the advantages of k-maps, such as simplicity in representation and ease of implementation, and explains different types of k-maps alongside simplification techniques using sum of products (SOP) and product of sums (POS) expressions. Additionally, it mentions the handling of don't care conditions to further simplify logical expressions.