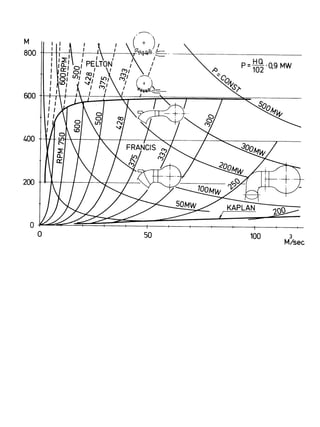
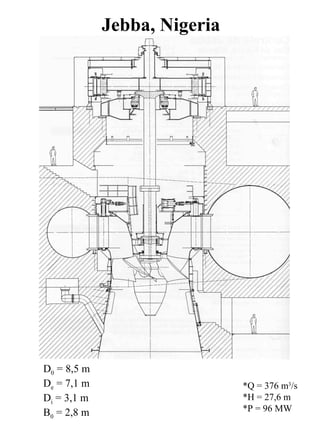
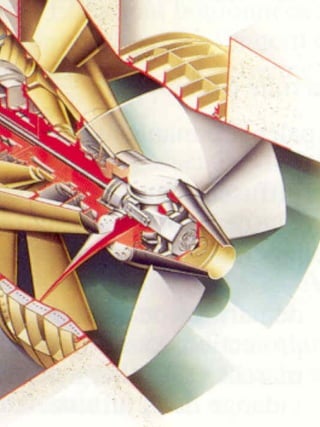
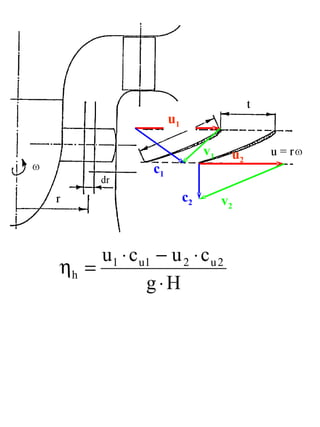
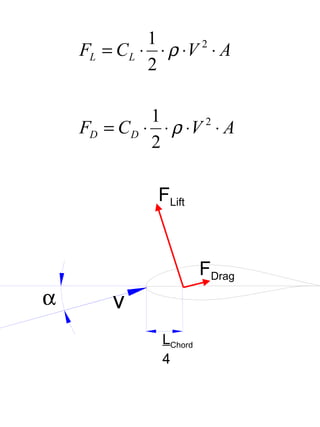
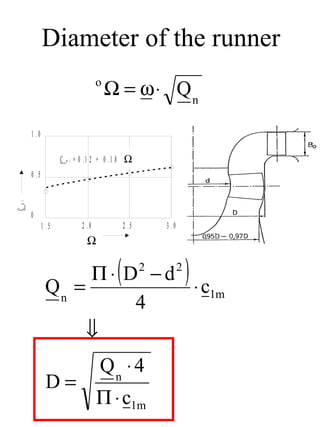
The document provides information on the dimensions and performance of Kaplan turbines, including diagrams showing dimensions such as diameter, blade height and spacing for turbines in Nigeria and Chile. It also contains graphs depicting hydraulic efficiency and cavitation effects in relation to parameters like speed and blade angle. The example calculation at the end demonstrates how to determine the diameter, blade height and number of vanes given design criteria like power output, head and flow rate.