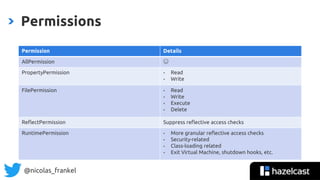
The document discusses the security aspects of JVM with a focus on permissions and the reflection API, highlighting tools like Hazelcast for distributed computing and stream processing. It details the principle of least privilege, different permission types, and how to configure policy files for secure execution of code. Additionally, it touches on steganography and the management of security within Java applications.