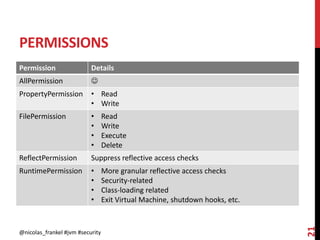
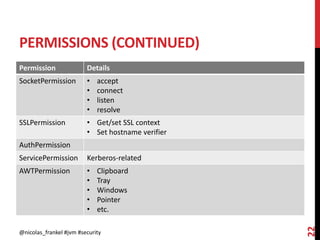
This document discusses securing the Java Virtual Machine. It describes how the reflection API allows dynamic behavior but can enable dangerous actions if not secured properly. It also discusses using a security manager to run code in a sandbox with limited permissions defined in a policy file. The principle of least privilege and default permissions are explained.