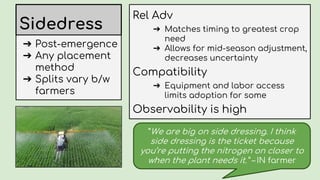
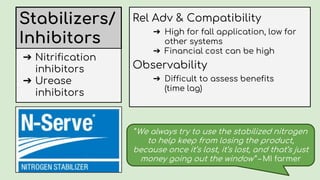
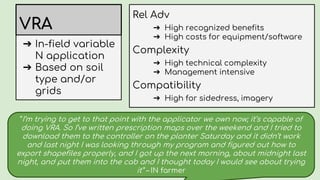
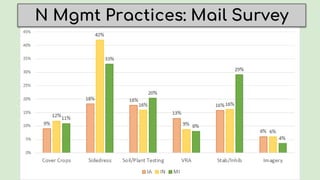
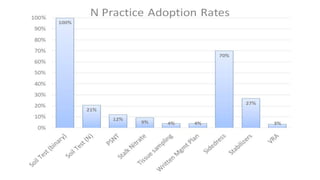
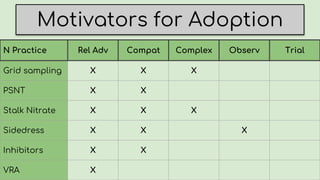
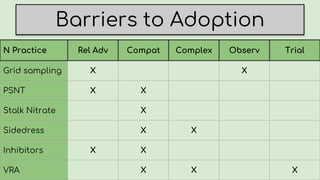
This document summarizes research on nitrogen management practices among farmers. It finds that while many practices have relative advantages in terms of efficiency, adoption is limited by complexity, compatibility with existing systems, and difficulty observing benefits due to various uncertainties. Soil testing has low adoption rates due to timing mismatches and challenges incorporating data. Sidedressing has high observability but equipment access limits some farmers. Stabilizers have clear advantages for fall application but benefits are difficult to observe. Variable rate application has high recognized benefits but also high costs and complexity, limiting adoption. Overall, compatibility with timing, nitrogen source and placement is important for farmers, while complexity and uncertainties around benefits serve as barriers.



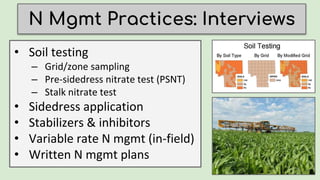

![Soil Testing
Rel Adv
➔ Low for N grid sampling (timing
mismatch)
➔ Low capacity to interpret,
incorporate data
Compatibility
➔ High for PSNT/Stalk test when
used with sidedress, manure
➔ Grid/zone
sampling
➔ PSNT
➔ Stalk nitrate
testing
“[PSNT] is basically another piece of
data that we use to come up with a
number as far as what we think the
cornfield needs that year.” – MI farmer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/july30-130-adamreimer-190815140429/85/July-30-130-Adam-Reimer-9-320.jpg)