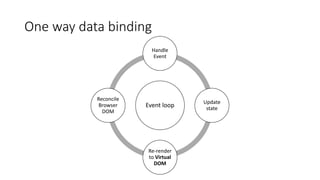
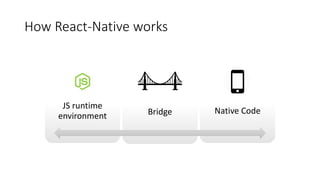
The document is an introduction to React Native, detailing its key concepts and comparing it to traditional mobile app development approaches. It covers the foundational elements such as components, virtual DOM, state management, and advanced topics like navigation and animation. The document emphasizes that React Native allows developers with web experience to create native mobile apps with some unique challenges related to performance and platform differences.






















![Styling and flexbox
<View style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.box}/>
<View style={[styles.box, styles.red]}/>
<View style={styles.box}/>
</View>
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'space-around',
alignItems: 'center',
},
box: {
height: 50,
width: 50,
backgroundColor: ’green',
},
red: {
backgroundColor: 'red',
},
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ivanovilya-react-nativeintroduction-180402134406/85/JS-Fest-2018-React-Native-24-320.jpg)






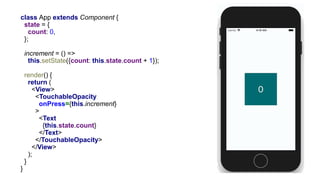







![Animation
class AnimatedBox extends Component {
scale = new Animated.Value(1);
animate = () => {
const animation = Animated.timing(
this.scale,
{
toValue: 6,
duration: 2000,
useNativeDriver: true,
},
);
animation.start();
};
render() {
const transform = [{scaleX: this.scale}, {scaleY: this.scale}];
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={this.animate}>
<Animated.View style={[styles.box, {transform}]}/>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ivanovilya-react-nativeintroduction-180402134406/85/JS-Fest-2018-React-Native-40-320.jpg)





