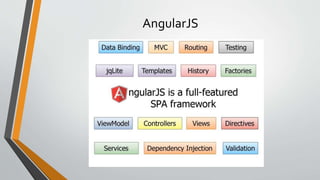
This document provides an overview of AngularJS including:
- What AngularJS is and its features such as directives, filters, data binding, views, controllers and scope
- How it can be used to build single page applications (SPAs)
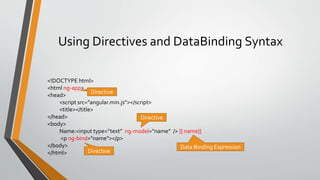
- Key directives like ng-app, ng-bind, and ng-model
- How to use filters, iterate with ng-repeat, and bind data
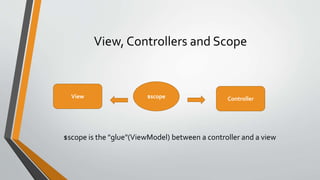
- The roles of views, controllers and scopes in AngularJS
- How to create controllers within modules and use factories
- How to create custom directives
- The differences between values, services, factories and providers
- How $watch and $watchCollection work








![Angular Expressions
• Angular expressions are JavaScript-like code snippets that are usually
placed in bindings such as {{ expression }}.
• For example, these are valid expressions in Angular:
• 1+2
• a+b
• user.name
• Items[index]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-11-320.jpg)
![Lterating with the ng-repeat Directive
<div data-ng-init="names=['John Smith', 'John Doe', 'Jane Doe']">
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="name in names">
{{name}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-12-320.jpg)
![Using Filters
<input type="text" data-ng-model="nameText" />
<div data-ng-init="names=['John Smith', '1John Doe', 'Jane Doe']">
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="name in names | filter:nameText">
{{name | uppercase}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-13-320.jpg)



![Creating a View and Controller
<div class="container" data-ng-controller="SimpleController">
<h3>Adding a Simple Controller</h3>
<input type="text" data-ng-model="name" />
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="cust in customers">
{{ cust.name }} - {{ cust.city}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
Access $scope
<script>
Basic controller
function SimpleController($scope)
{
$scope.customers = [
{name : 'Dave Jones', city:'Phoenix'},
{name : 'Jamie Riley', city:'Atlanta'},
{name : 'Heedy Wahlin', city:'Chandler'},
{name : 'Thomas Winter', city:'Seattle'},
];
}
</script>
So now we have two properties in the scope. The ng-model is going to add a property in the scope
called name, and we can actually get to that now in the controller by saying $scope.name](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-18-320.jpg)
![Create a Controller in a Module
Module that demoApp
depends on
var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', []);
demoApp.controller('SimpleController', function($scope) {
$scope.customers = [
{name : 'Dave Jones', city:'Phoenix'},
{name : 'Jamie Riley', city:'Atlanta'},
{name : 'Heedy Wahlin', city:'Chandler'},
{name : 'Thomas Winter', city:'Seattle'}
];
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-19-320.jpg)
![Create a Controller in a Module
var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', []);
demoApp.controller('SimpleController', ['$scope', function(scope){
scope.customers = [
{name : 'Dave Jones', city:'Phoenix'},
{name : 'Jamie Riley', city:'Atlanta'},
{name : 'Heedy Wahlin', city:'Chandler'},
{name : 'Thomas Winter', city:'Seattle'}
];
}]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-20-320.jpg)
![Create Multi Controller in a Module
var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', []);
var controllers = {};
controllers.SimpleController = function($scope) {
……
};
controllers.SimpleController2 = function($scope) {
……
};
demoApp.controller(controllers);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-21-320.jpg)
![The Role of Factories
var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', [])
.factory('simpleFactory', function(){
var factory = {};
var customers = [………];
factory.getCustomers = function(){
return customers;
};
return factory;
}).controller('SimpleController', function($scope, simpleFactory)
{
$scope.customers = simpleFactory.getCustomers();
});
Factory injected into
controller at runtime](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-22-320.jpg)
![Create Custom Directive
angular.module('docsSimpleDirective', []).controller('Controller', function($scope) {
$scope.customer = {
name: 'Naomi',
address: '1600 Amphitheatre'
};
}).directive('myCustomer', function() {
return {
restrict: 'A',
template: 'Name: {{customer.name}} Address: {{customer.address}}'
};
});
<div ng-controller="Controller">
<div my-customer></div>
</div>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-23-320.jpg)
![$inject
• If a function has an $inject property and its value is an array of strings, then
the strings represent names of services to be injected into the function.
var MyController = function(renamed$scope, renamedGreeter) {
...
}
MyController['$inject'] = ['$scope', 'greeter'];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-24-320.jpg)

![$watch
• $watch(watchExpression, listener, [objectEquality])
• Registers a listener callback to be executed whenever the watchExpression changes
• $watchCollection(watchExpression, listener)
• Shallow watches the properties of an object and fires whenever any of the properties
change](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-141031050211-conversion-gate02/85/AngularJS-26-320.jpg)
