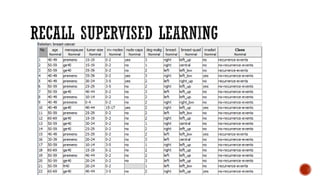
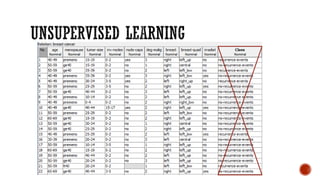
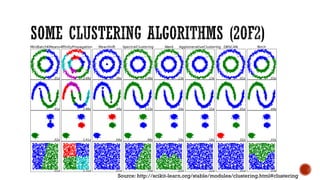
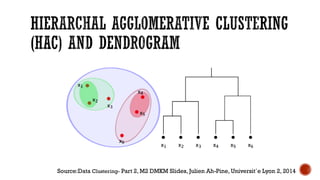
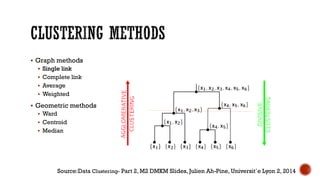
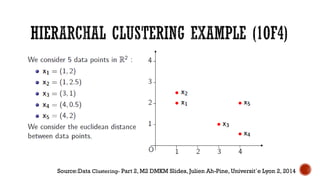
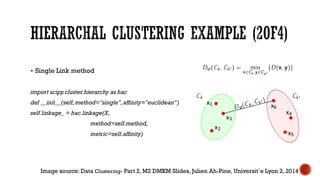
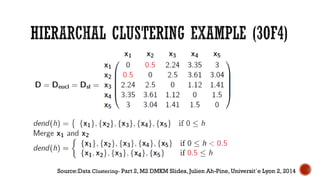
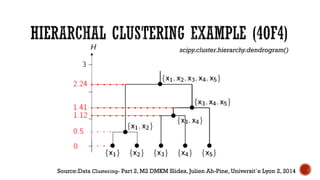
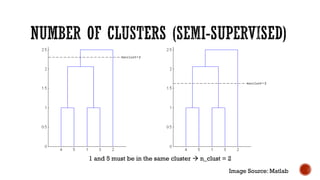
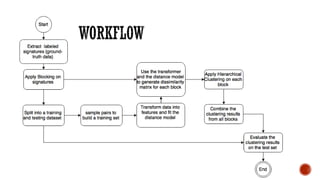
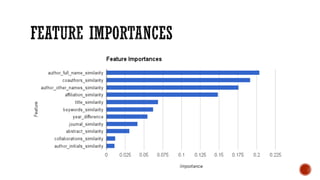
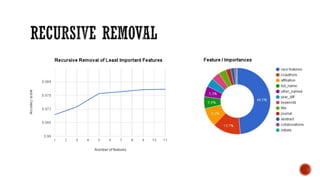
This document provides an overview of unsupervised machine learning techniques for clustering. It discusses different types of clustering including flat partitions, hierarchical trees, and hard vs soft memberships. Specific clustering algorithms are covered like K-means, hierarchical agglomerative clustering (HAC), DBSCAN, and graph-based clustering. Distance functions and linkage methods for HAC are also summarized. The document concludes with examples of applications for different clustering techniques.