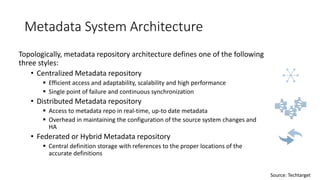
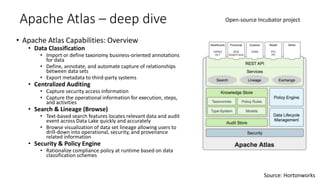
The document discusses the importance of metadata management in big data environments, outlining its principles and the technologies available for effective governance. It highlights the challenges faced by data scientists in finding and tracking data, as well as solutions like Apache Atlas for managing metadata. Key needs include creating a searchable platform for metadata, automating data ingestion, and ensuring compliance and security in data handling.


















![Where Else?
{ "Description": "A containerized foobar",
"Usage": "docker run --rm example/foobar [args]",
"License": "GPL",
"Version": "0.0.1-beta",
"aBoolean": true,
"aNumber" : 0.01234,
"aNestedArray": ["a", "b", "c"] } <meta name=”description” content=”155
characters of message matching text
with a call to action goes here”>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.JOSA.Meta</groupId>
<artifactId>project</artifactId> <version>1.0</version>
</project>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tareq-151227094907/85/JOSA-TechTalk-Metadata-Management-in-Big-Data-24-320.jpg)