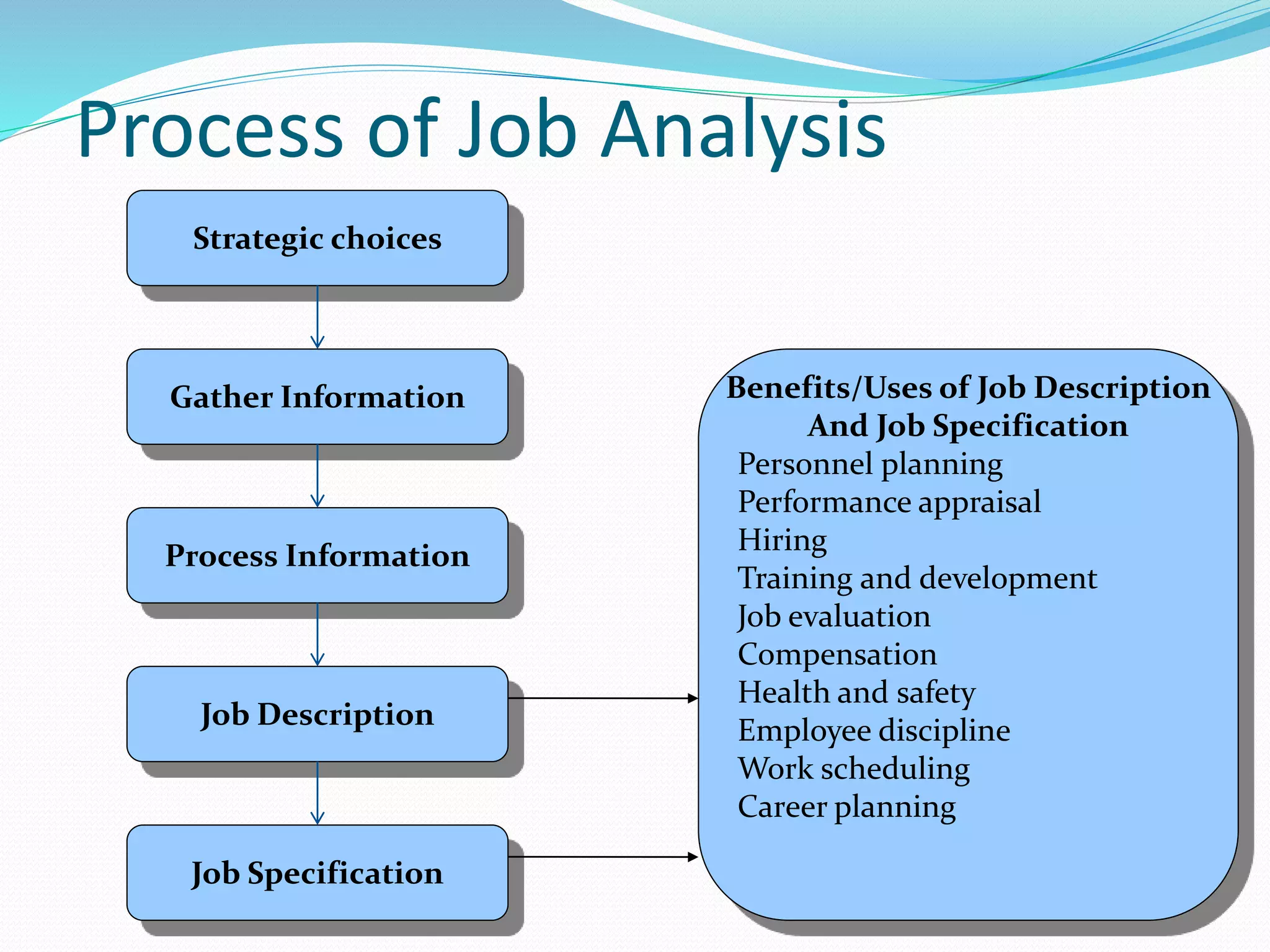
The document discusses terminology used in job analysis such as job, position, job family, task, duty, and responsibility. It also outlines the process of job analysis including strategic choices, gathering information, processing information, and developing the job description and specification. Various methods for conducting job analysis are described like observation, interviews, questionnaires, previous studies, work diaries, and having managers try the job. Each method is examined in terms of information sources, advantages, and disadvantages.