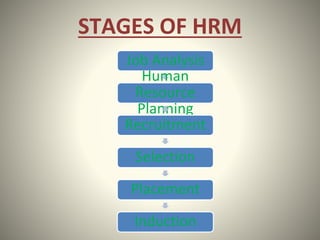
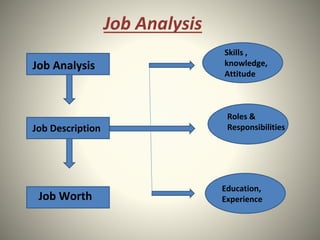
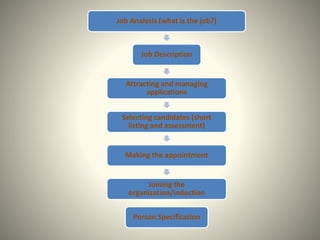
Job analysis is the process of collecting information about the tasks, duties, skills, and requirements of a job. It involves creating a job description and person specification. Common methods of job analysis include observation, interviews, questionnaires, reviewing previous studies, and examining employee work diaries. The results of job analysis provide the foundation for HR activities like recruitment, selection, training, performance management, and job design. Conducting regular job analysis helps ensure jobs remain relevant and meet organizational needs.