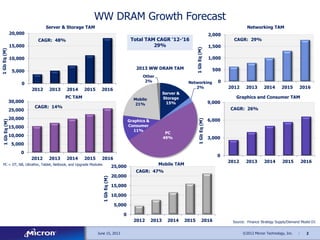
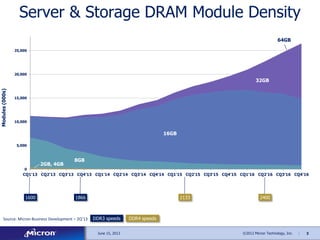
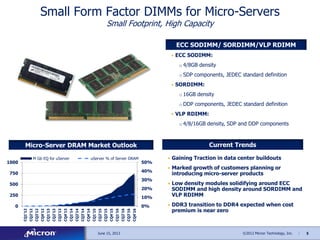
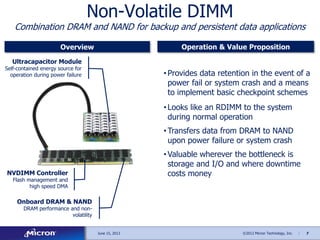
The document discusses memory solutions and trends in enterprise computing. It forecasts strong growth in the total available market for DRAM through 2016. It outlines opportunities for Micron to provide memory architectures like DDR4, small form factor DIMMs for microservers, and non-volatile DIMMs that combine DRAM and NAND flash.