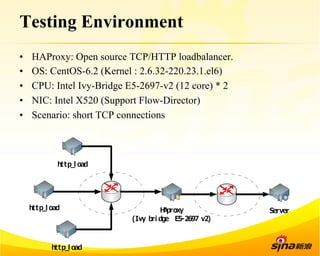
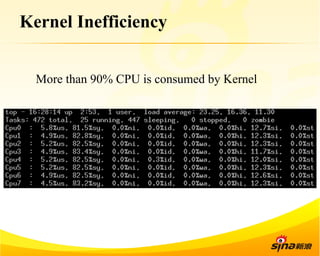
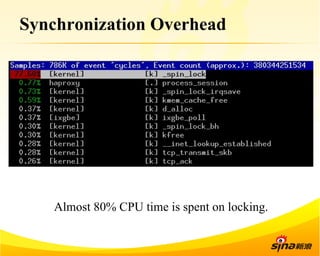
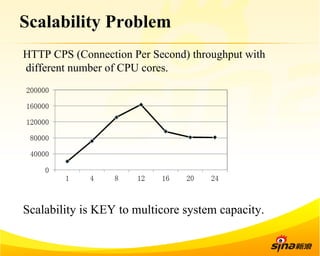
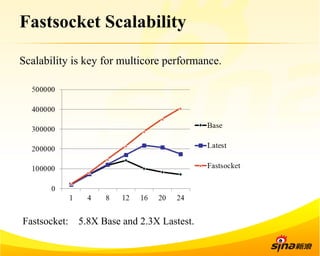
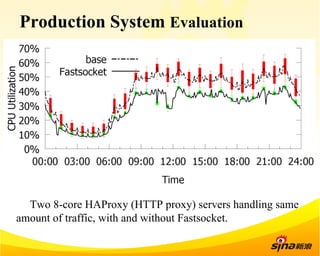
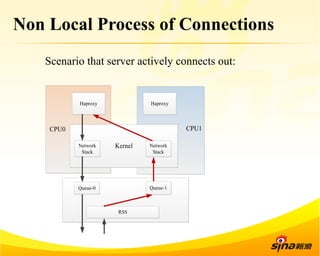
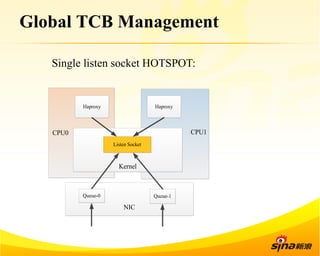
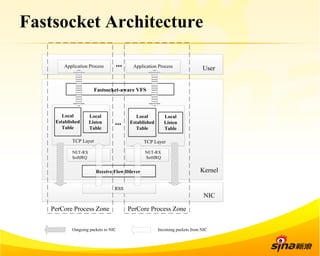
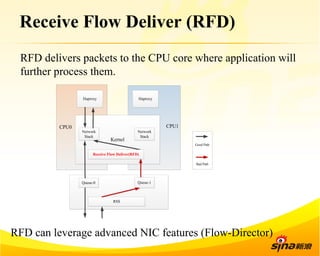
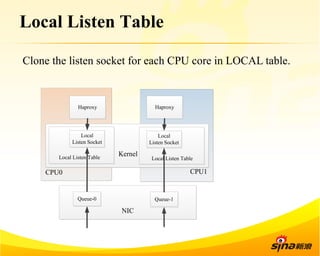
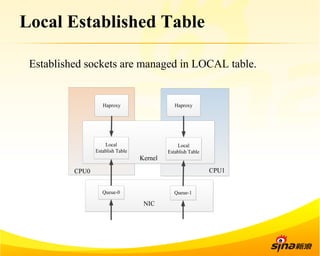
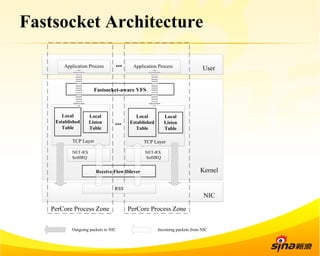
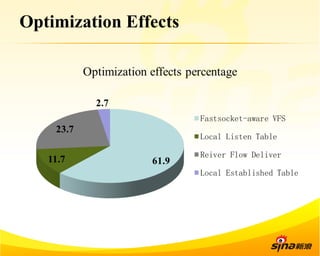
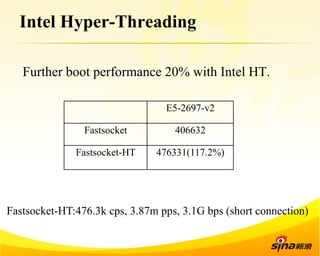
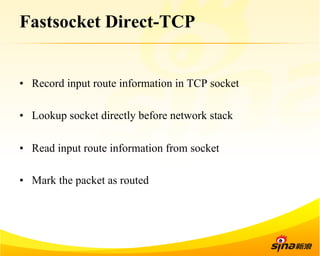
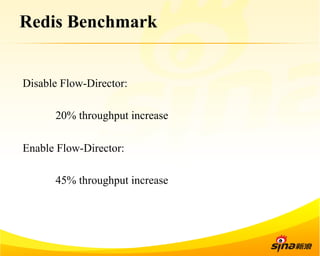
Fastsocket is a software that improves the scalability and performance of socket-based applications on multicore systems. It addresses kernel inefficiencies like synchronization overhead that consume over 90% of CPU cycles. Fastsocket introduces techniques like receive flow delivery, local listen/established tables, and a fastsocket-aware VFS to partition resources and process connections locally on each CPU core. In production at SINA, Fastsocket improved HTTP load balancing throughput by 45% on a 16-core system. Future work aims to further optimize performance through techniques like improved interrupt handling and system call batching.