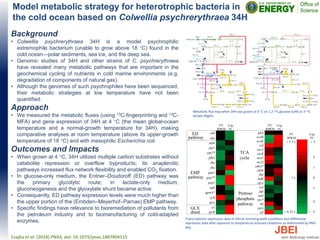
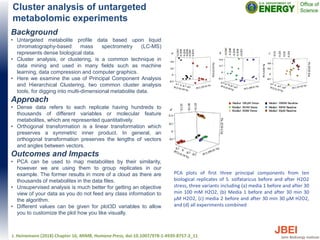
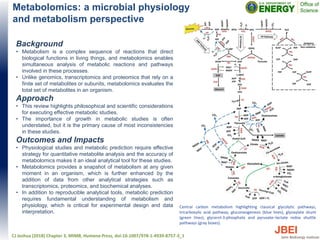
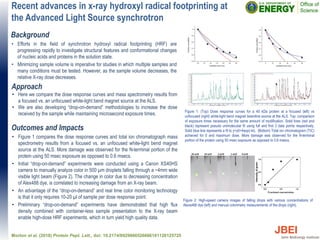
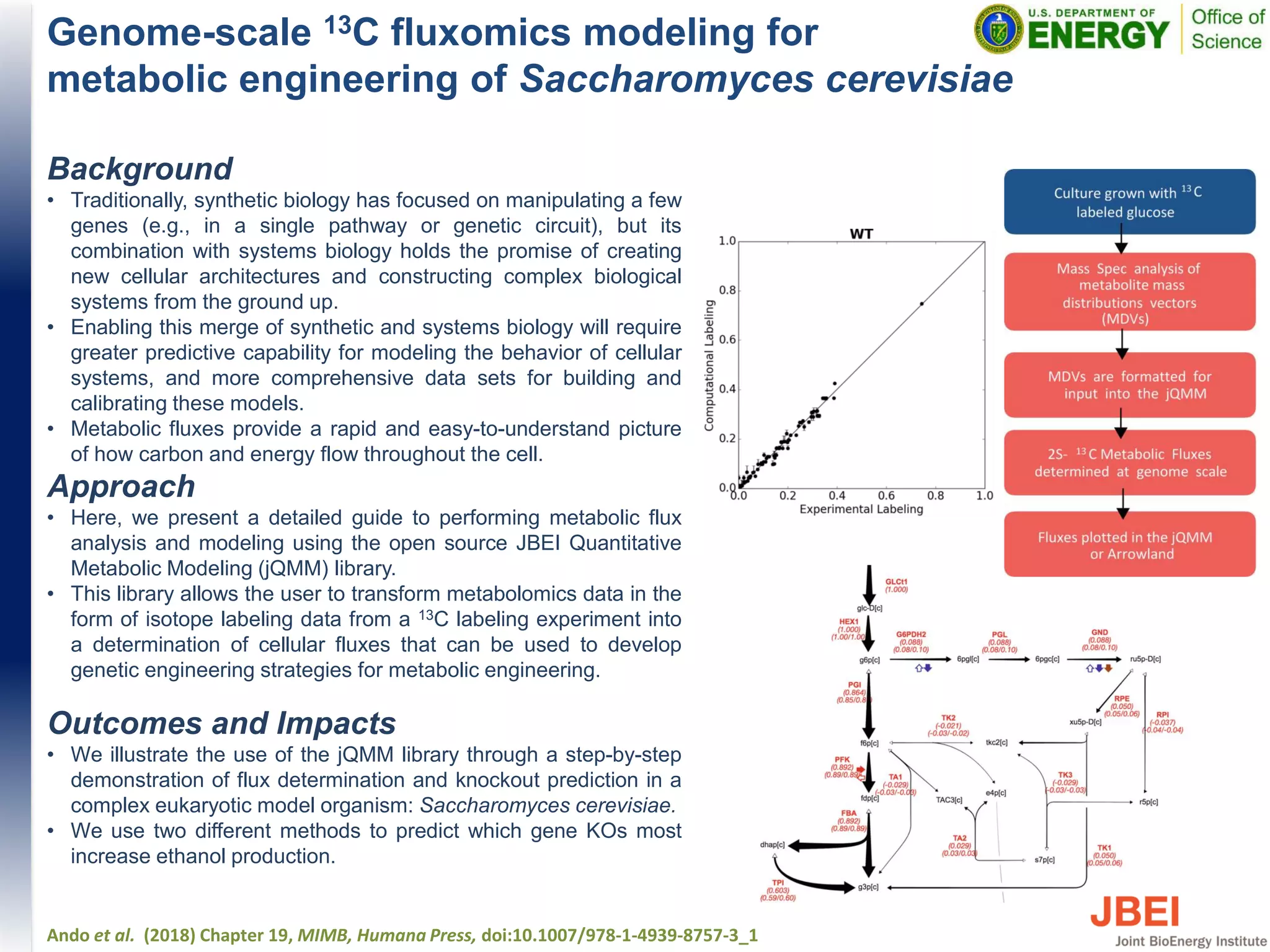
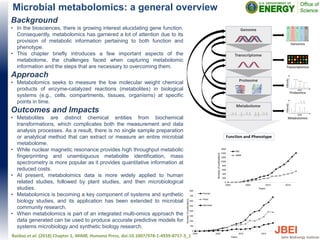
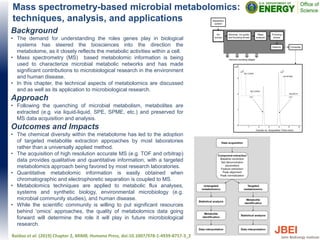
This document discusses recent advances in x-ray hydroxyl radical footprinting at the Advanced Light Source synchrotron. It compares dose response curves and mass spectrometry results from focused and unfocused white light sources. It also describes developing "drop-on-demand" methodologies to increase sample dose while maintaining microsecond exposure times, which enables high-dose experiments while minimizing sample volume. Preliminary experiments demonstrate this approach yields high quality data. The document contributes to improving synchrotron hydroxyl radical footprinting techniques for investigating protein and nucleic acid structures.
![Probabilistic lifecycle assessment of butanol
production from corn stover using different
pretreatment methods
Background
• Studies on cellulosic butanol have only considered sulfuric acid
pretreatment process and many of these studies present deterministic
results.
• This study seeks to bridge the research and modeling gaps by
developing stochastic process model integrating feedstock supply
logistics and the downstream butanol production process, and
considering the five most commonly considered biomass
deconstruction methods (e.g., steam explosion, sulfuric acid, ammonia
fiber explosion [AFEX], ionic liquid [IL] and biological)
Approach
• We developed stochastic lifecycle assessment models and
determined lifecycle energy use and greenhouse gas emissions.
• We demonstrated performance targets for future research.
Outcomes and Impacts
• Probabilistic results of these analyses describe a distribution of GHG
emissions with an average of 18.09-1056.12 gCO2e/MJ and a 95%
certainty to be less than 33.3-1888.3 gCO2e /MJ.
• The highest GHG emissions of IL-pretreatment of 1056.12 gCO2e/MJ
reaches to 89.8 gCO2e/MJ by switching IL-recovery from 80 to 99 wt%,
which is the most influencing parameter for IL-pretreatment.
• We propose alternative ionic liquid (IL) including cholinium lysinate
and triethylammonium hydrogen sulfate, as these ILs could reduce the
carbon footprint of IL-based biomass deconstruction process.
• When the influential inputs can be optimized, many of these
pretreatment methods can be used to realize GHG emissions and net
energy reduction goals.
Baral et al. (2018) Environ. Sci. Technol., doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b05176](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/november2018jbeihighlightslides-190122162859/85/JBEI-Research-Highlights-November-2018-4-320.jpg)