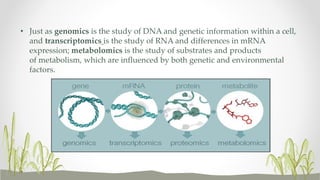
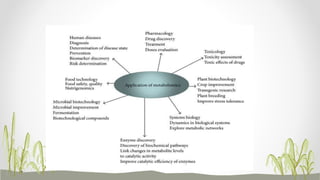
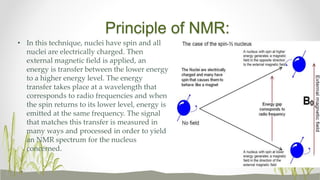
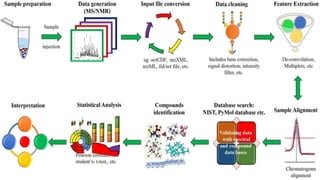
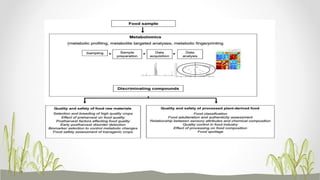
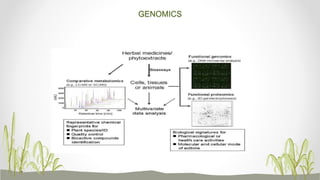
Plant metabolomics is the study of small molecule metabolites within plants. It is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Metabolomics can help understand plant phenotype, development, physiology, and stress responses. Modern platforms for plant metabolomics use techniques like gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to detect and quantify metabolites in plant extracts. GC-MS allows for non-targeted profiling while NMR is non-destructive and useful for quantification. Metabolite fingerprinting and profiling are used to identify markers of genetic or environmental disturbances by comparing metabolic states of plants under different conditions. Plant metabolomics has applications in understanding plant diseases, stress responses, and secondary metabolites of therapeutic importance.