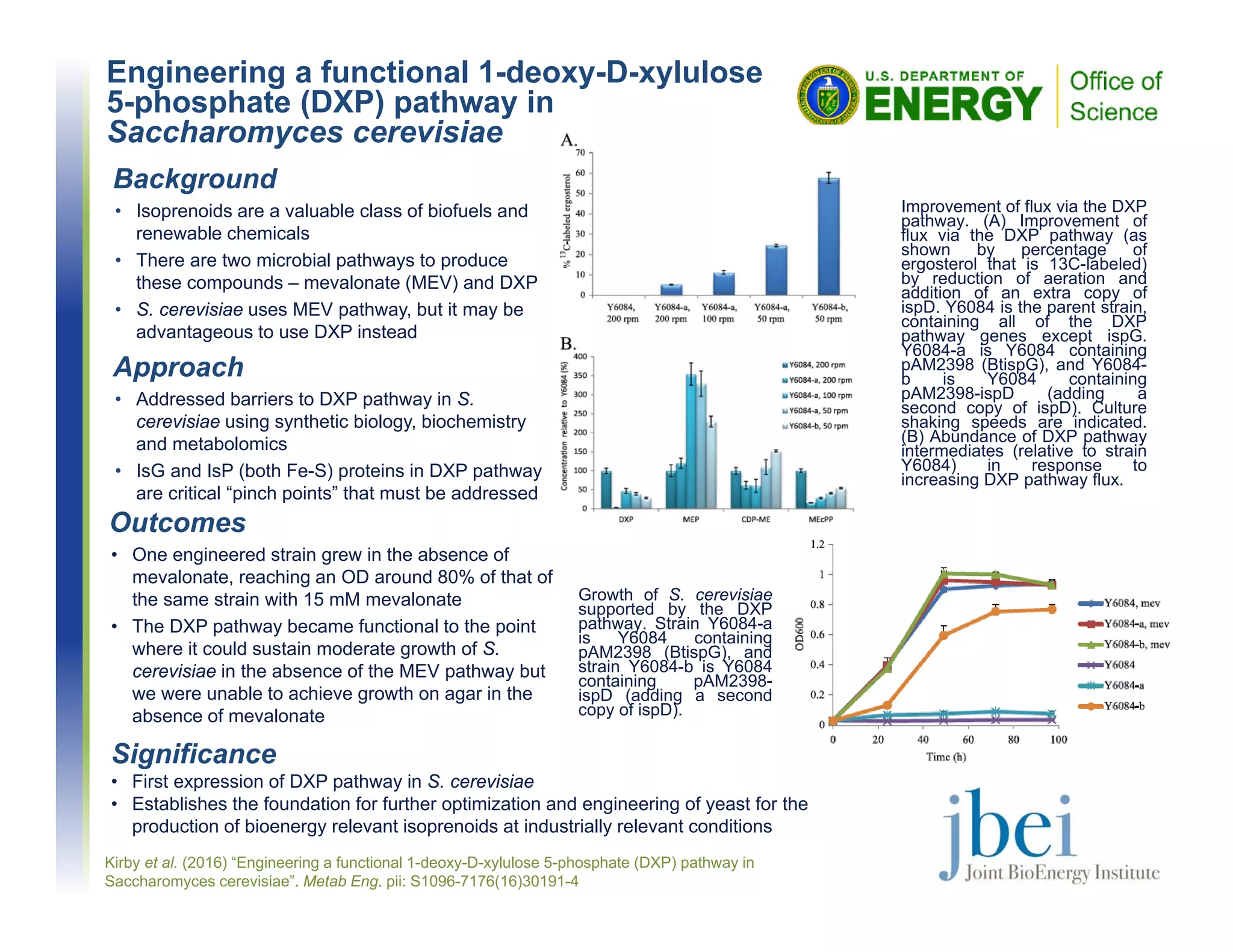
The document describes research that engineered the 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Key findings include:
- An engineered strain was able to grow in the absence of mevalonate, reaching 80% of growth compared to strains with mevalonate added.
- The DXP pathway became functional enough to support moderate growth without the mevalonate pathway, but growth on agar without mevalonate was not achieved.
- This work established a foundation for further optimizing yeast to produce bioenergy-relevant isoprenoids through the DXP pathway under industrial conditions.

![Genome-resolved metagenomics defines a
community response to ionic liquid challenge
Outcomes
• Increasing levels of ionic liquid amendment in the cultures selects for a Firmicutes-dominated communities that retain the
ability to produce glycoside hydrolases up to 2% [C2C1im][OAc]. At 2% [C2C1im][OAc], the community switches to acetate
metabolism
• The combination of genome-resolved metagenomics (>100 genomes were recovered from the metagenomic dataset) and
metatranscriptomics allowed the identification of individual community members that were tolerant of [C2C1im][OAc] and
were able to produce cellulases and xylanases in the presence of [C2C1im][OAc]
Significance
• This study provides insights into a community-level reponse to ionic liquid challenge and demonstrates the use of
genome-resolved metagenomics to identify active microbes that can tolerate industrially relevant amounts of ionic liquids
used in the deconstruction of lignocellulose.
Wu et al. (2017) "Ionic Liquids Impact the Bioenergy Feedstock-Degrading Microbiome and Transcription of
Enzymes Relevant to Polysaccharide Hydrolysis". mSystems, 1(6). doi, 10.1128/mSystems.00120-16
Background
• Previous work at JBEI has defined the response
of bacterial isolates to ionic liquids
• Cultivation of biomass-deconstructing microbial
consortia in response to ionic liquid challenge
would illuminate community responses to these
promising pretreatment chemicals
Approach
• A consortia of microbes was adapted to grow on
switchgrass under solid state cultivation and this
adapted community inoculated into switchgrass
cultures amended with increasing levels of
[C2C1im][OAc]. The response of the community to
this challenge was measured by respiration,
enzymatic assays and metatranscriptomics.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jbeidecember2016highlights-170119171747/85/JBEI-Research-Highlights-December-2016-4-320.jpg)

![Development of an integrated approach for
α-pinene recovery and sugar production
from loblolly pine using ionic liquids
Outcomes
• [C2C1Im][OAc] is very efficient at extracting
terpenes (i.e., α-pinene) from loblolly pine while
generating a carbohydrate-enriched stream suitable
for bioconversion into renewable biofuels and
chemicals
• Techno-economic analysis (TEA) revealed that the
α-pinene recovery after IL pretreatment could
reduce the minimum ethanol selling price (MESP)
by $0.6-1.0/gal
Papa et al. (2016) “Development of an integrated approach for α-pinene recovery and sugar
production from loblolly pine using ionic liquids", Green Chemistry, DOI: 10.1039/C6GC02637K”.
Background
• Terpenes are produced in high concentrations from
loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) that could represent a
valuable supplement to bioenergy production chains
Approach
• We investigated imidazolium-based ionic liquid (IL)
[C2C1Im][OAc] pretreatment in conjunction with
different analytical protocols using GC–MS, to extract
α-pinene and simultaneously pretreat the pine to
generate high yields of fermentable sugars after
saccharification
Terpene recovery (left) and glucose release (right) of different tissues of loblolly pine
Significance
• This integrated terpene extraction/lignocellulose pretreatment approach may provide a
compelling model for a biorefinery, reducing costs and increasing commercial viability
• ILs can be used to selectively extract volatile compounds from plants during pretreatment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jbeidecember2016highlights-170119171747/85/JBEI-Research-Highlights-December-2016-6-320.jpg)