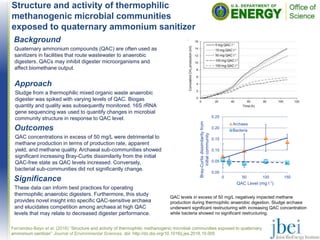
This document summarizes research that evaluated the impact of varying concentrations of quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs), commonly used as sanitizers, on the structure and activity of microbial communities in thermophilic anaerobic digesters. The study found that QAC concentrations over 50 mg/L reduced methane production rates and altered the archaeal communities significantly, while bacterial communities were not significantly impacted. The results provide insight into specific QAC-sensitive archaea and how competition within archaeal communities changes at high QAC levels, decreasing digester performance.