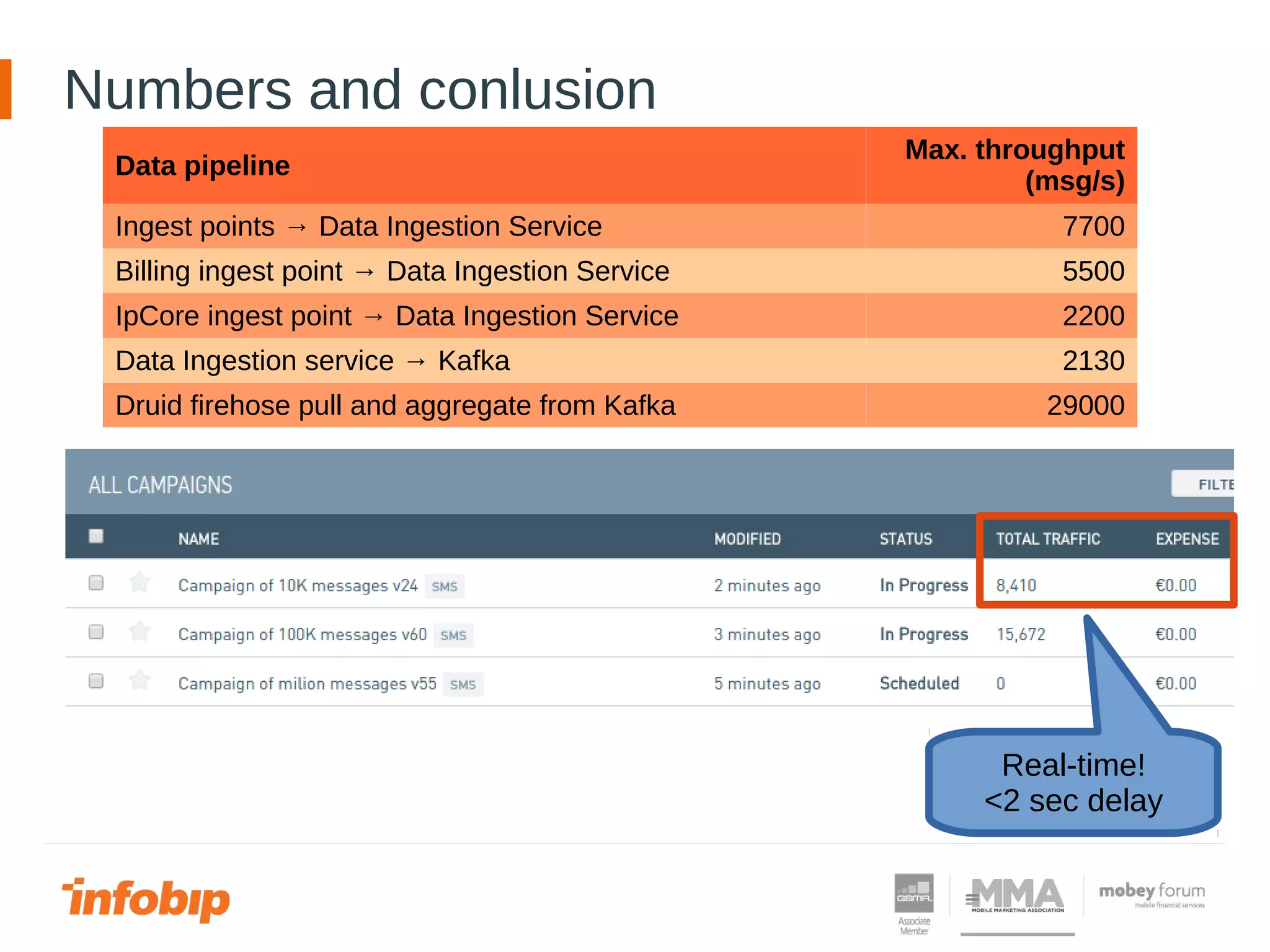
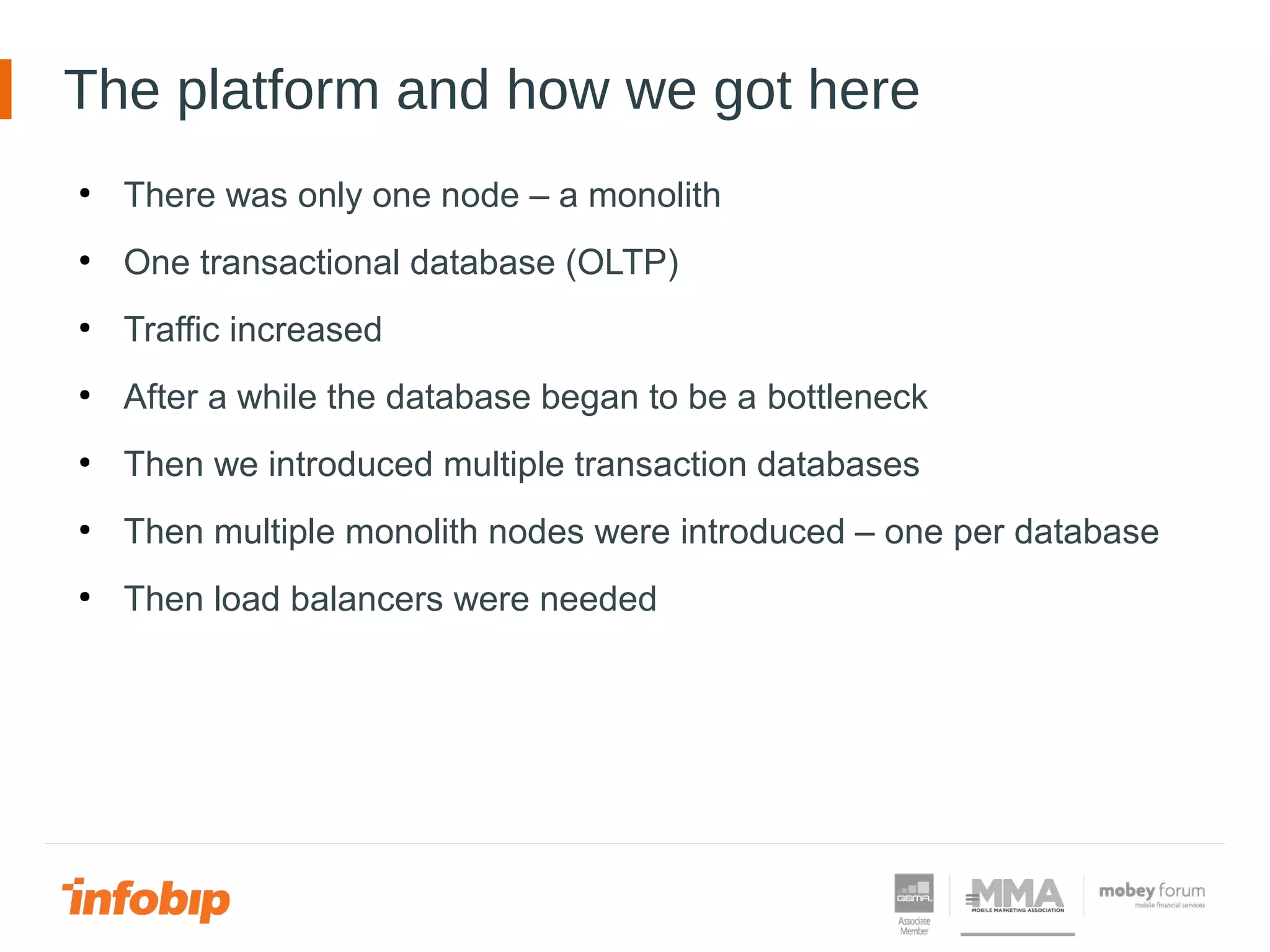
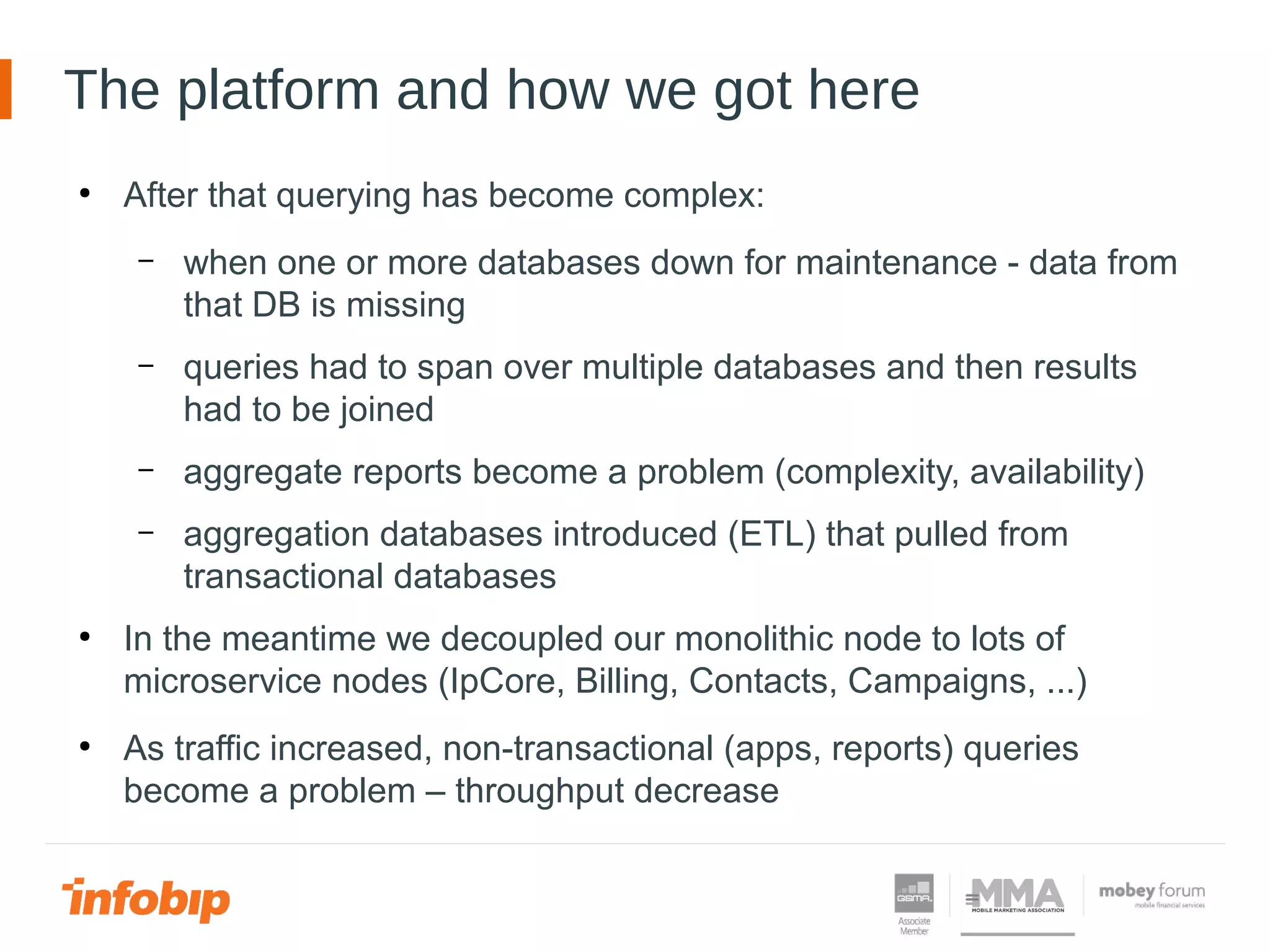
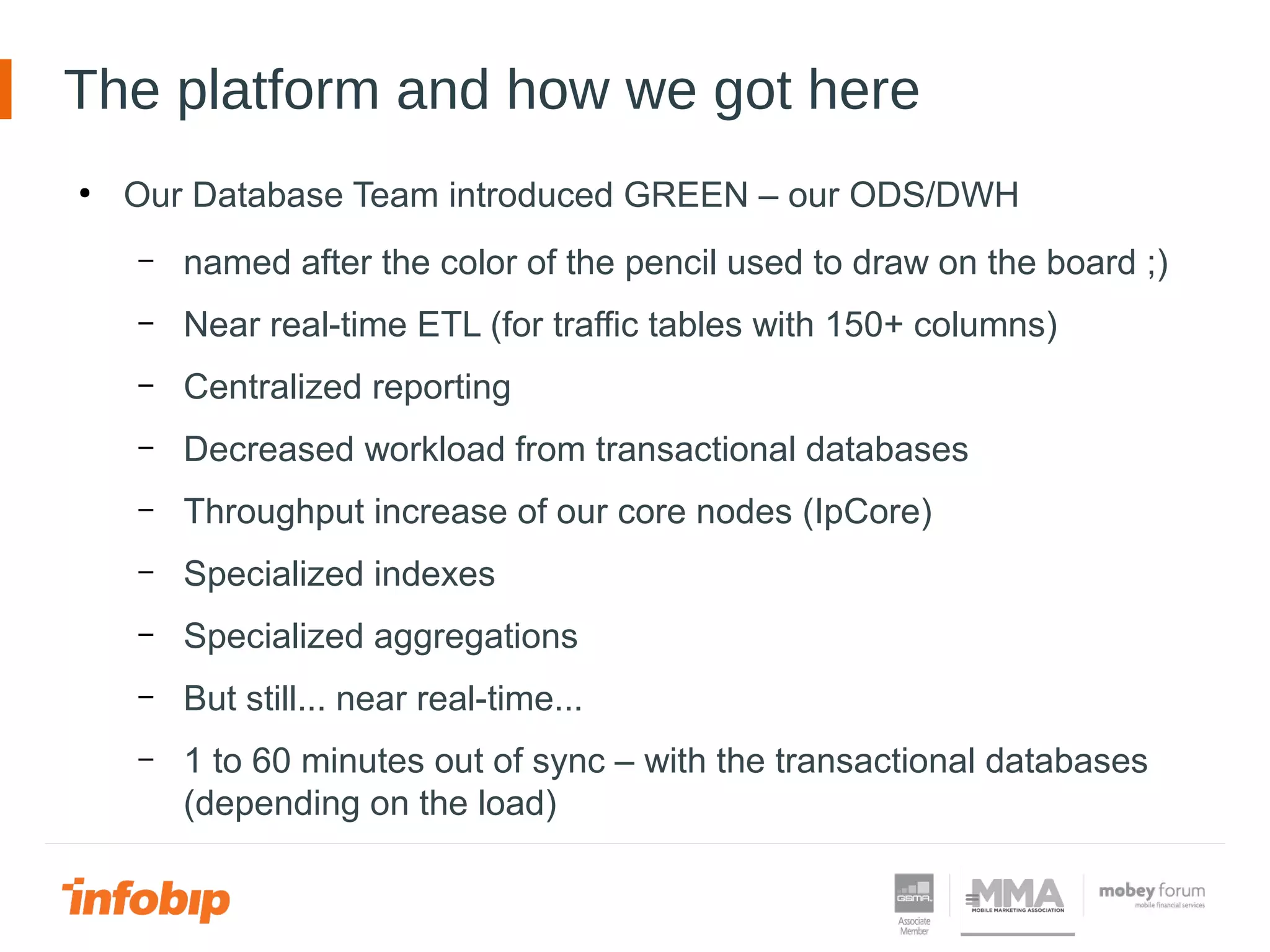
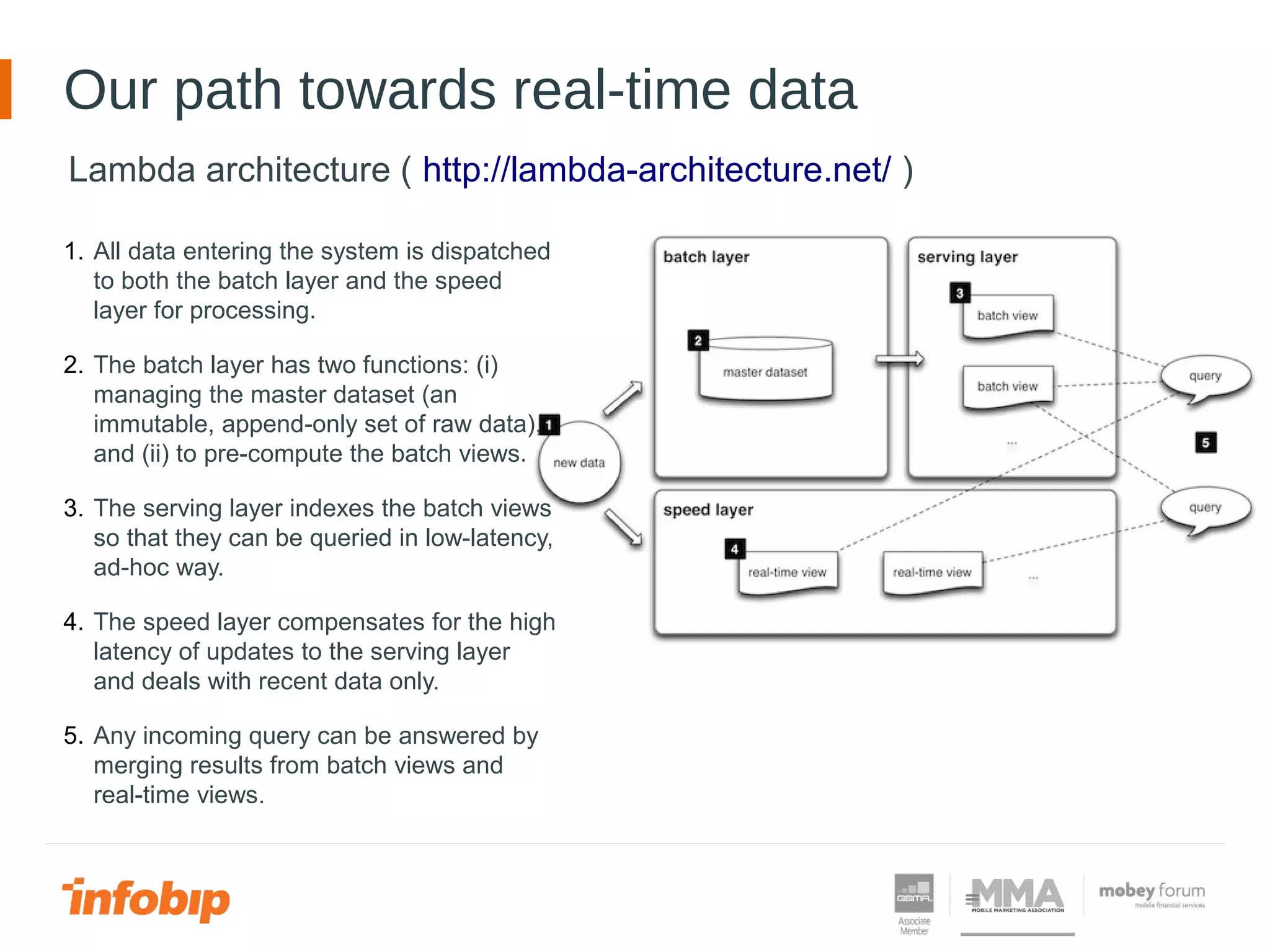
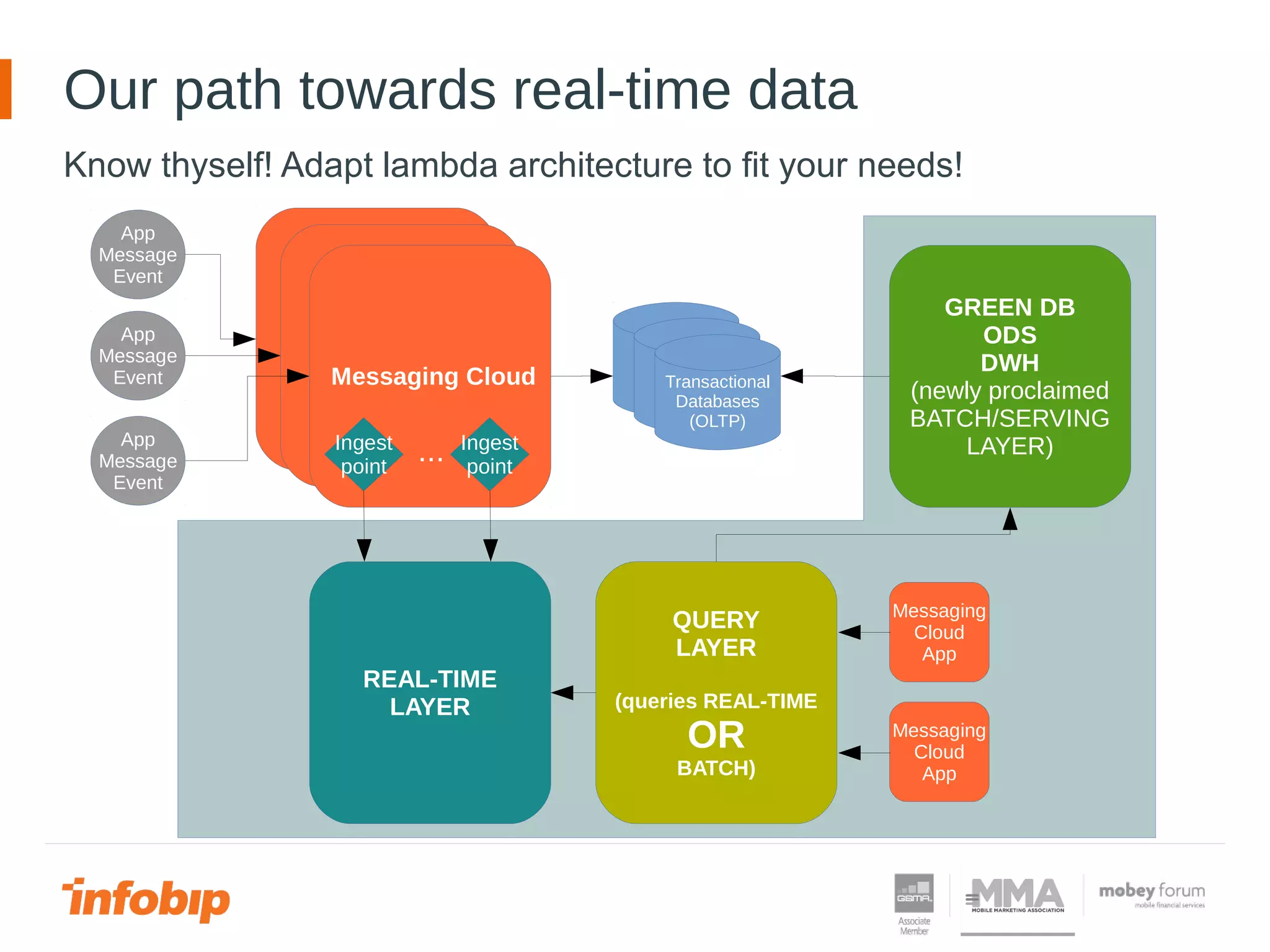
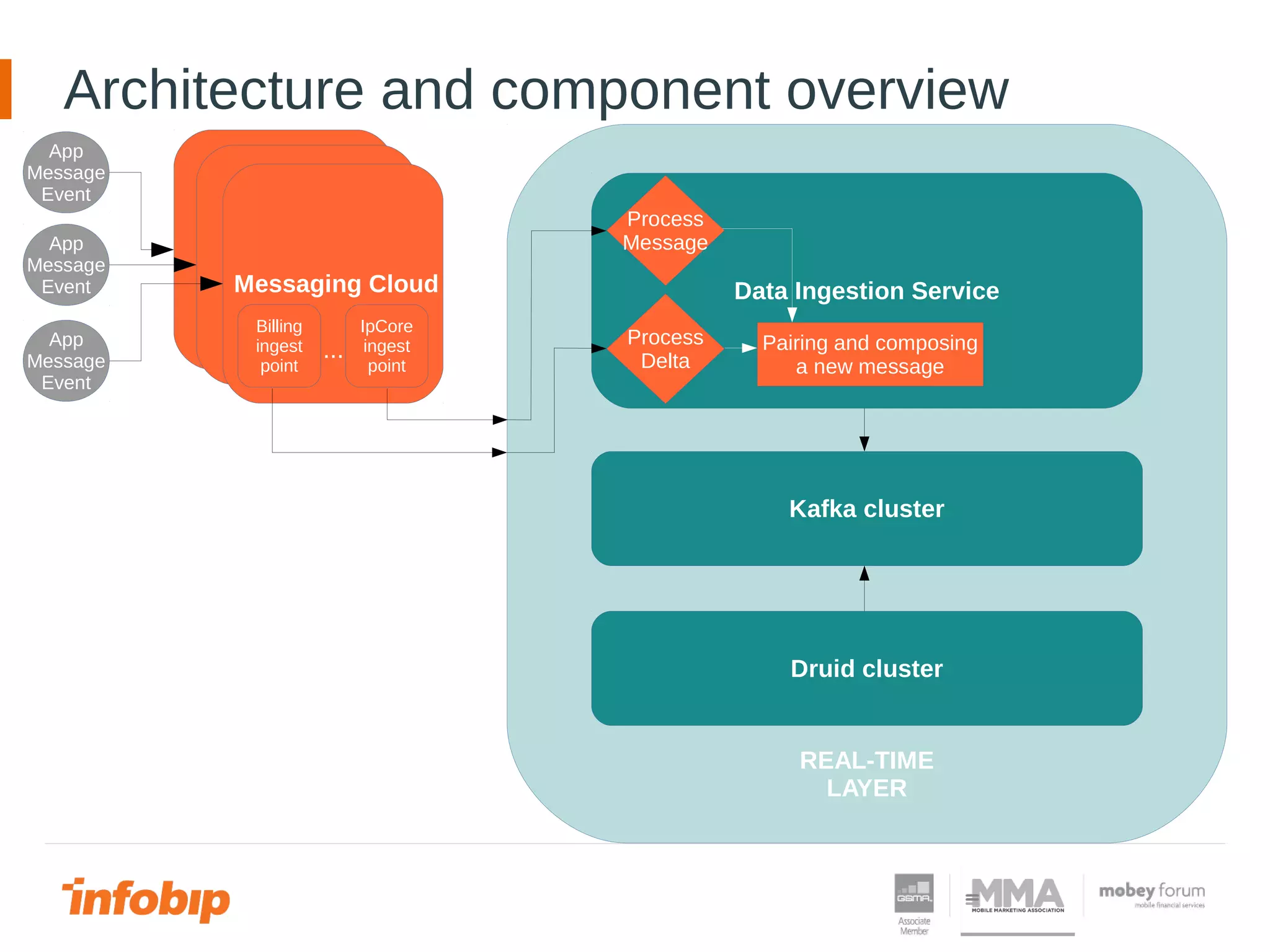
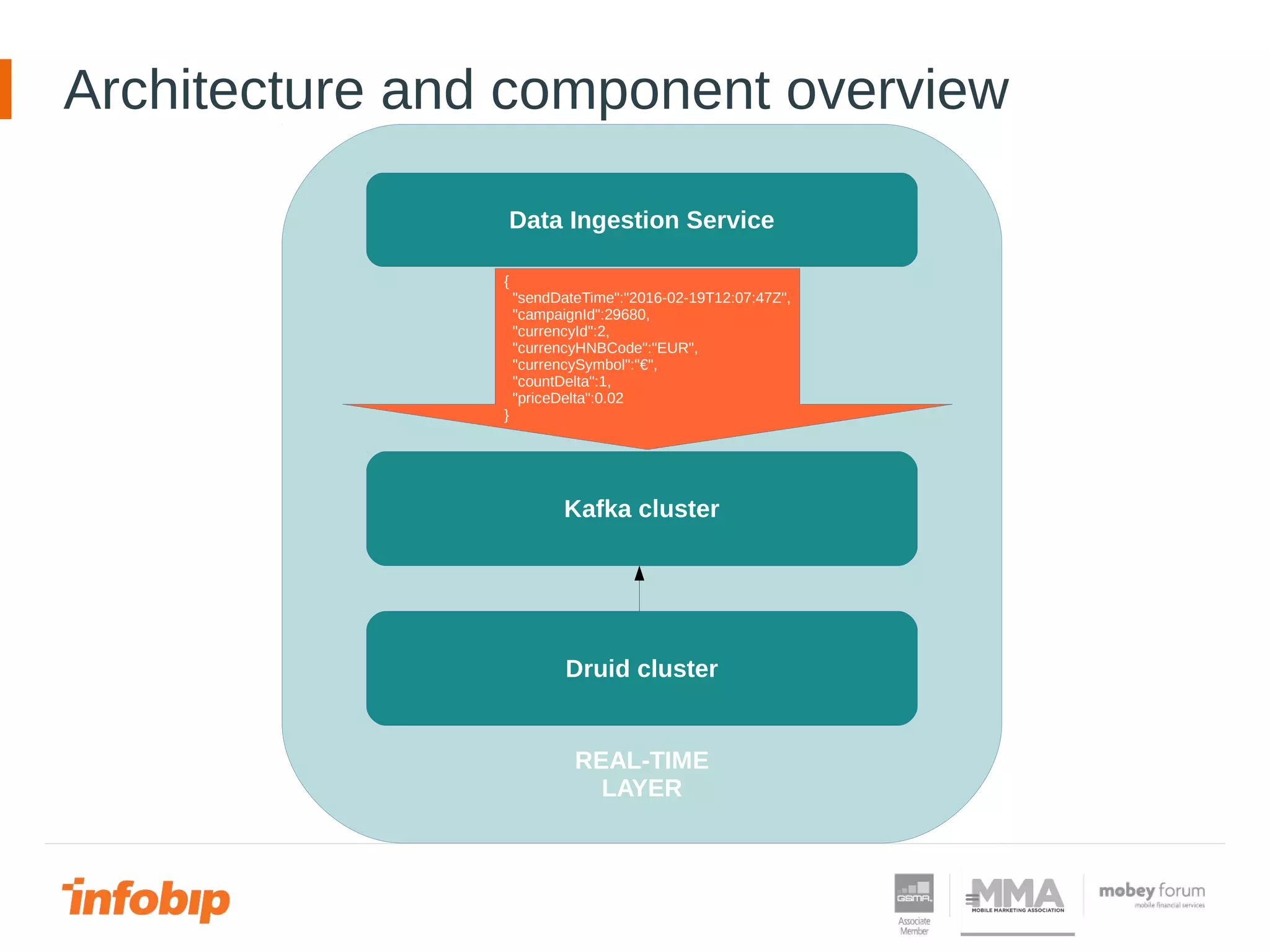
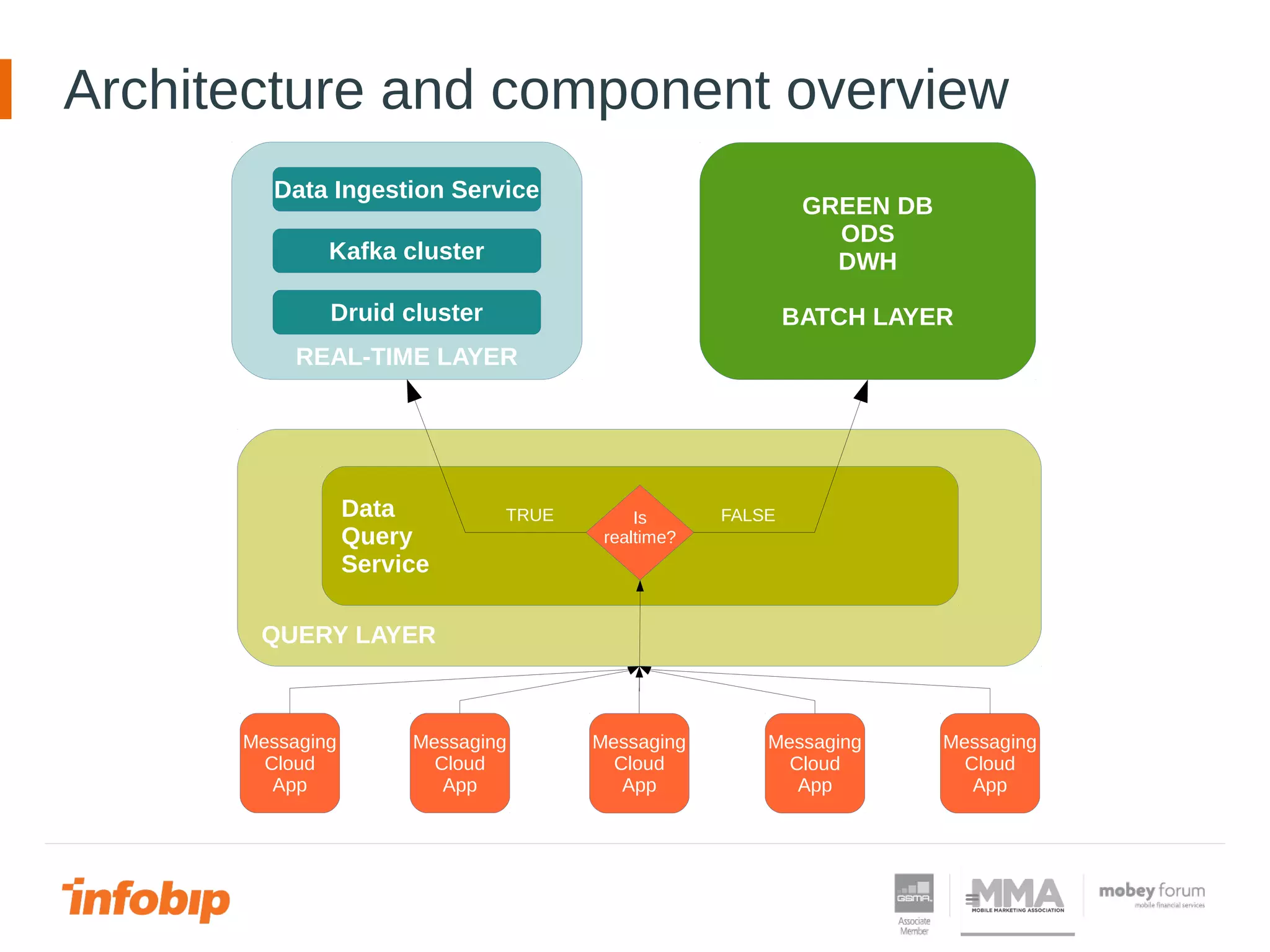
This document discusses Infobip's journey towards enabling real-time querying of aggregated data. Initially, Infobip had a monolithic architecture with a single database that became a bottleneck. They introduced multiple databases and microservices but querying spanned databases and results had to be joined. A data warehouse (GREEN) provided reporting but was not real-time. To enable real-time queries, Infobip implemented a lambda architecture using Kafka as the real-time data pipeline and Druid for real-time querying and aggregations, achieving sub-second responses and less than 2 seconds of data delay. This allows real-time insights from ingested messaging data while GREEN remains the batch/serving layer.




![Dictionary
INGEST verb
“to take (something, such as food) into your body : to swallow
(something)
— sometimes used figuratively
She ingested [=absorbed] large amounts of information very quickly.”
http://www.learnersdictionary.com/definition/ingest
I'll use this figurative meaning... in context of data ingestion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javanturav3-real-timebigdataingestionandqueryingofaggregateddatadavorpoldrugo-160222091006/75/Javantura-v3-Real-time-BigData-ingestion-and-querying-of-aggregated-data-Davor-Poldrugo-8-2048.jpg)


![Architecture and component overview
REAL-TIME LAYER
Druid cluster
QUERY LAYER
Data
Query
Service
POST /druid/v2 HTTP/1.1
Host: druid-broker-node:8080
Content-Type: application/json
{
"queryType": "groupBy",
"dataSource": "campaign-totals-v2",
"granularity": "all",
"intervals": [ "2012-01-01T00:00:00.000/2100-01-01T00:00:00.000" ],
"dimensions": ["campaignId", "currencyId", "currencySymbol", "currencyHNBCode"],
"filter": { "type": "selector", "dimension": "campaignId", "value": 29680 },
"aggregations": [
{ "type": "longSum", "name": "totalCountSum", "fieldName": "totalCount" },
{ "type": "doubleSum", "name": "totalPriceSum", "fieldName": "price" }
]
}
Request to Druid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javanturav3-real-timebigdataingestionandqueryingofaggregateddatadavorpoldrugo-160222091006/75/Javantura-v3-Real-time-BigData-ingestion-and-querying-of-aggregated-data-Davor-Poldrugo-19-2048.jpg)
![Architecture and component overview
REAL-TIME LAYER
Druid cluster
QUERY LAYER
Data
Query
Service
Response from Druid
[
{
"version": "v1",
"timestamp": "2012-01-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"event": {
"totalCountSum": 1000000,
"currencyid": "2",
"totalPriceSum": 20000,
"currencysymbol": "€",
"currencyhnbcode": "EUR",
"campaignid": "29680"
}
}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javanturav3-real-timebigdataingestionandqueryingofaggregateddatadavorpoldrugo-160222091006/75/Javantura-v3-Real-time-BigData-ingestion-and-querying-of-aggregated-data-Davor-Poldrugo-20-2048.jpg)