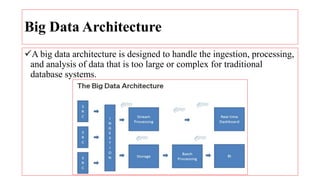
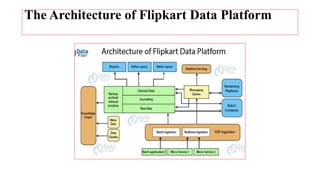
The document discusses the key components of a big data architecture. It describes how a big data architecture is needed to handle large volumes of data from multiple sources that is too large for traditional databases. The architecture ingests data from various sources, stores it, enables both batch and real-time analysis, and delivers business insights to users. It also provides examples of Flipkart's data platform which includes components like an ingestion system, batch/streaming processing, and a messaging queue.