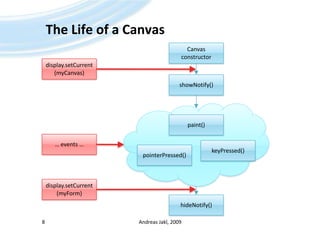
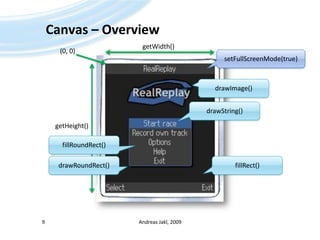
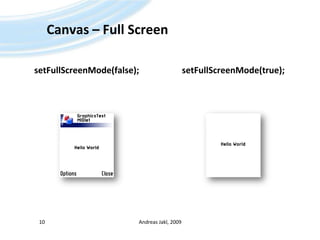
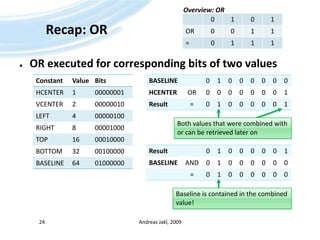
The document is a training presentation on Java Platform, Micro Edition (Java ME) focusing on low-level graphics and canvas manipulation. It covers key components including the canvas class, handling key events, and drawing graphics, text, and images. The content is intended for educational use and adheres to copyright guidelines, providing examples and detailed explanations for building applications within Java ME.





![Example: Canvas – Quick OverviewAndreas Jakl, 20097public class MenuCanvasextends Canvas {privateRealReplayMIDletiMidlet; private intiWidth; private intiHeight;publicMenuCanvas(RealReplayMIDletaMidlet) {iMidlet = aMidlet; // Needed to quit the gamesetFullScreenMode(true); // Activate full screen modeiWidth = getWidth(); // Query screen sizeiHeight = getHeight(); }public void paint(Graphics aGraphics) { // Draw backgroundaGraphics.setColor(255, 255, 255);aGraphics.fillRect(0, 0, iWidth, iHeight); // [...] }protected void keyPressed(intaKeyCode) { // Process key events [...] repaint(); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javame-03-lowlevelgraphicse-091203070816-phpapp01/85/Java-ME-03-Low-Level-Graphics-E-7-320.jpg)



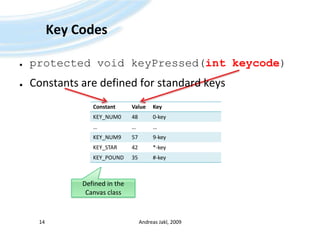
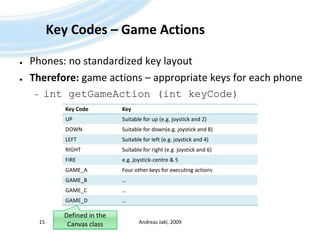
![Key Codes – ExampleAndreas Jakl, 200916protected void keyPressed(intkeycode) {SimplePlayerGUIgui = getGUI();switch (keycode) { // This variant does not allow handling multiple simultaneous keypressescase Canvas.KEY_NUM1: // (which are not supported by many phones)// Jump backwardgui.skip(true);break;caseCanvas.KEY_NUM2:gui.togglePlayer();break;// [...]caseCanvas.KEY_POUND:gui.changeVolume(false);break;default: // Handle both keys and game actions – keys first, as they might be game actions as wellintgameAction = getGameAction(keycode);if (gameAction == Canvas.RIGHT) {// Jump forwardgui.skip(false); // [...] } elseif (gameAction == Canvas.FIRE) {gui.togglePlayer(); } }Adapted from the Sun WTK 2.5.2. MobileMediaAPI-examle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javame-03-lowlevelgraphicse-091203070816-phpapp01/85/Java-ME-03-Low-Level-Graphics-E-16-320.jpg)
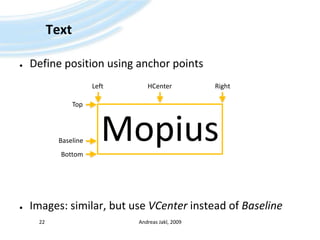
![Canvas – PaintIf repaint is necessary (e.g. info dialog was on top of MIDlet)Framework calls Canvas.paint()Request repaint yourselfCall: repaint()Optional: specify regionpaint()will be called automatically andasynchronously, at a “fitting” momentDouble BufferingUsually supported and activatedQuery: booleandblBuf = canvas.isDoubleBuffered();If not: create off-screen bitmap yourselfAndreas Jakl, 200918void keyPressed(int aKeyCode) { // Process key events [...] repaint();}paint() not called instantly;usually through an extra threadvoid paint(Graphics g) { // Draw...}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javame-03-lowlevelgraphicse-091203070816-phpapp01/85/Java-ME-03-Low-Level-Graphics-E-18-320.jpg)






![ImagesMain image format for JavaME (must be supported):.png (Portable Network Graphics)Similar to .gif (which was patented until 2003 because of its LZW compression)Features:Compression: works well for graphics, not so well for photosTransparency: support depends on device – 1 bit transparency or full alpha-channel. Query:int levels = [Display].numAlphaLevels()Usually used for phones:8 bit colour depth (file size), 1 bit transparency (compatibility)Andreas Jakl, 200930](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javame-03-lowlevelgraphicse-091203070816-phpapp01/85/Java-ME-03-Low-Level-Graphics-E-30-320.jpg)