This document provides an overview of Symbian OS and Carbide.c++ UI design, with guidance on installation, conventions, and application structure. It covers essential C++ differences in the mobile environment, UI development processes, and troubleshooting tips for working with the IDE. Additionally, it highlights the use of descriptors in string management within Symbian OS programming.













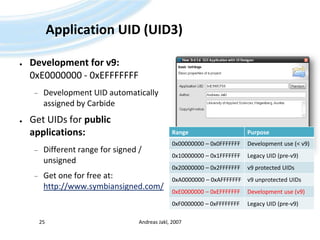

![Compile Project(optional) Project Build ProjectRun Run HelloWorld Emulator Debug […]Or:Andreas Jakl, 200729You can only use the mouse to navigate on the screen on touch-enabled emulators! Otherwise, use the buttons below.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickstartb-091203064528-phpapp01/85/Symbian-OS-Quick-Start-29-320.jpg)
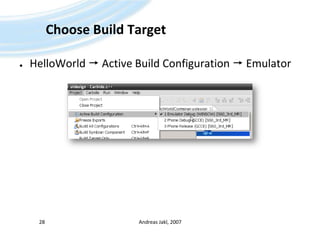
![Possible Problems IIEmulator starts in text shell modee.g. if configured like this by previous coursesOpen [SDK-directory]\Data\epoc.iniComment the entry textshell by putting a # in front of it #textshellAndreas Jakl, 200731](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickstartb-091203064528-phpapp01/85/Symbian-OS-Quick-Start-31-320.jpg)
![EmulatorApplication added to the end of the list in the “Installat.” folderCan be moved with “Options Move [to folder]”Useful when working on the same project for more than 10 minutesAndreas Jakl, 200732](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickstartb-091203064528-phpapp01/85/Symbian-OS-Quick-Start-32-320.jpg)


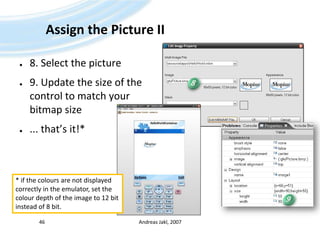




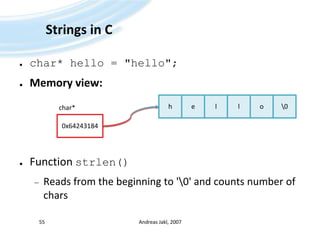
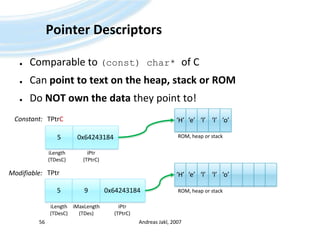
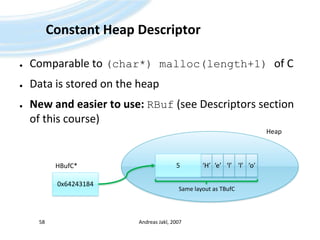
![Buffer DescriptorsComparable to (const) char[]of CDirectly contain the stringUse C++ templates to specify length (parameter)Andreas Jakl, 200757TBufC<5>Constant:‘H’5‘e’‘l’‘l’‘o’iLength(TDesC)Modifiable:TBuf<9>9‘H’5‘e’‘l’‘l’‘o’iLength(TDesC)iMaxLength(TDes)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickstartb-091203064528-phpapp01/85/Symbian-OS-Quick-Start-57-320.jpg)




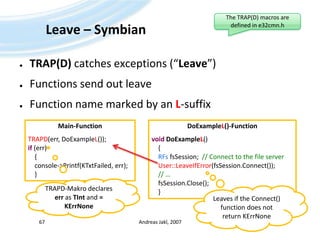
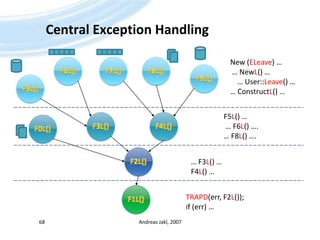





![What does a leave look like?Adapt the code:Trap the leave:Andreas Jakl, 200774void CHelloWorldContainer::SetLabelTextL(const TDesC& aText) {iLabelName->SetTextL (aText);User::Leave(KErrAccessDenied); }TBoolCHelloWorldContainerView::HandleEnter_name_MenuItemSelectedL( TIntaCommand ) { // […]TRAPD(err, iHelloWorldContainer->SetLabelTextL(userName)); // [...] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickstartb-091203064528-phpapp01/85/Symbian-OS-Quick-Start-74-320.jpg)
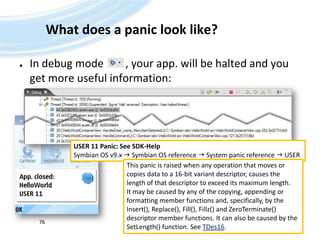
![What does a panic look like?Adapt the code: Will crash the emulator in release modeAndreas Jakl, 200775TBoolCHelloWorldContainerView::HandleEnter_name_MenuItemSelectedL( TIntaCommand ) {TBuf<20> userName;_LIT(KLongText, "This text is too long for a maximum length of 20, so a panic will occur.");userName.Copy(KLongText); // [...] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quickstartb-091203064528-phpapp01/85/Symbian-OS-Quick-Start-75-320.jpg)