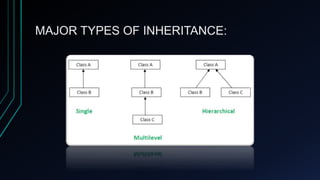
Inheritance in Java allows classes to inherit properties and behaviors from other classes. This encourages code reusability. The extends keyword establishes inheritance, allowing subclasses to access members of the superclass. Examples demonstrate single inheritance with an Employee superclass and Programmer subclass, multilevel inheritance with classes inheriting from grandparents and parents, and hierarchical inheritance with subclasses of the Animal superclass like Dog and Cat. Multiple inheritance is not directly supported in Java to avoid the "diamond problem" of ambiguous inheritance relationships.




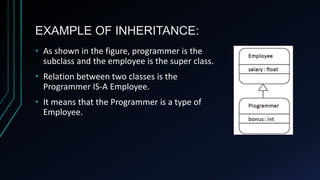
![EXAMPLE OF INHERITANCE:
class Employee {
float salary=40000; }
class Programmer extends Employee {
int bonus=10000;
public static void main (String args[]) {
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritanceinjava-230923134044-f9059806/85/INHERITANCE-IN-JAVA-pptx-6-320.jpg)


![EXAMPLE OF SINGLE INHERITANCE
public class SingleInheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Dog
Dog myDog = new Dog();
// Call methods from both Animal and Dog
classes
myDog.eat(); // Inherited from Animal
myDog.bark(); // Specific to Dog
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritanceinjava-230923134044-f9059806/85/INHERITANCE-IN-JAVA-pptx-10-320.jpg)

![EXAMPLE OF MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE
class Child extends Parent {
void childMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a method in the Child class."); } }
public class MultilevelInheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child(); // Calling methods from
each class
child.grandparentMethod(); // Inherited from Grandparent
child.parentMethod(); // Inherited from Parent
child.childMethod(); // Method in Child class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritanceinjava-230923134044-f9059806/85/INHERITANCE-IN-JAVA-pptx-12-320.jpg)

![EXAMPLE OF HIERARCHAL INHERITANCE
public class HierarchicalInheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
Cat cat = new Cat();
System.out.println("Dog:");
Dog.eat(); // Inherited from Animal
dog.bark();
System.out.println("nCat:");
cat.eat(); // Inherited from Animal
cat.meow();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritanceinjava-230923134044-f9059806/85/INHERITANCE-IN-JAVA-pptx-14-320.jpg)

