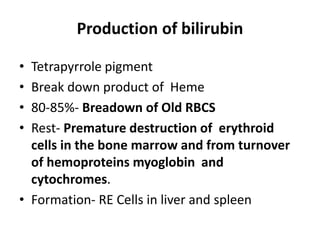
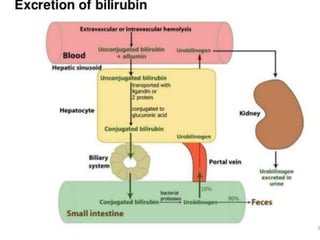
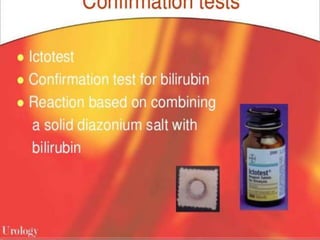
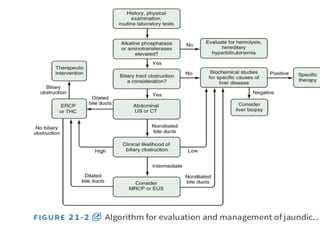
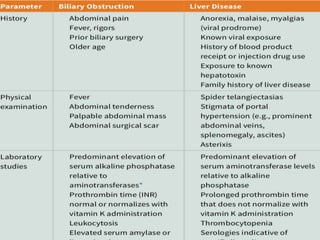
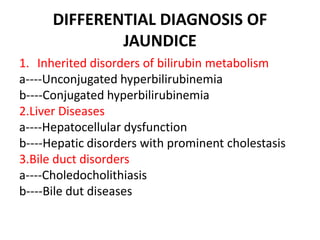
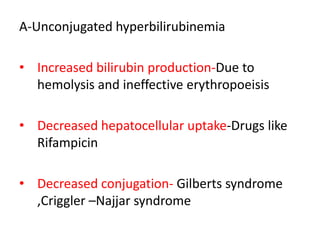
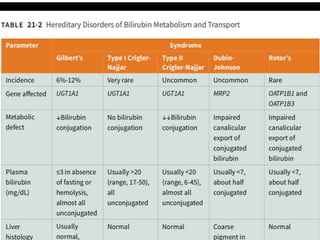
This document discusses jaundice, including its signs, stages, causes, differential diagnosis, and approach. Jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes caused by high bilirubin levels. It is often a sign of liver disease or hemolytic disorders. The document outlines the sequential sites of jaundice, metabolism of bilirubin, measurement of bilirubin levels, differential diagnosis between liver diseases and bile duct disorders, and three patient cases presenting with different causes of jaundice.