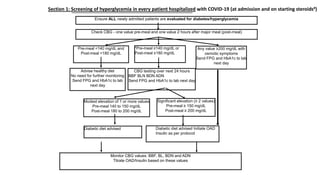
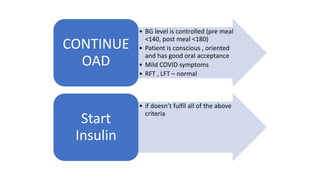
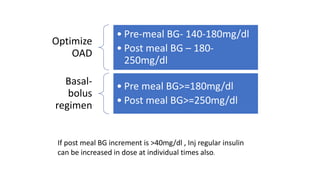
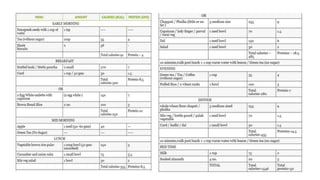
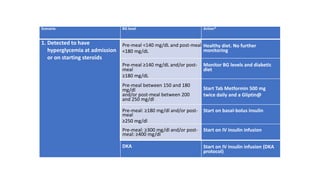
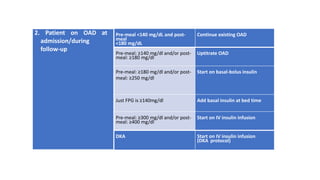
The document provides clinical guidance on diabetes management for patients at COVID-19 patient management facilities. It outlines protocols for screening and monitoring blood glucose levels in patients with and without diabetes. It recommends starting diabetic diets for all patients. The guidance also covers indications for initiating or adjusting oral anti-diabetic drugs and insulin regimens based on blood glucose levels and patient condition. Protocols are provided for managing patients on steroids, those who are nil by mouth, and switching from insulin infusion to subcutaneous insulin.