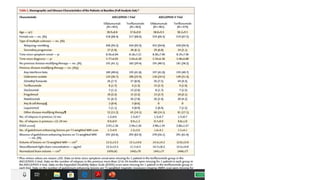
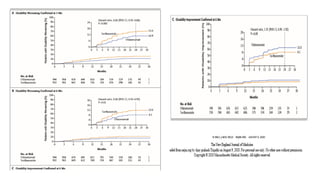
This document summarizes two phase 3 clinical trials that compared the multiple sclerosis drugs ofatumumab and teriflunomide. Ofatumumab is a subcutaneous anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that selectively depletes B cells, while teriflunomide is an oral drug that reduces T-cell and B-cell activation. Across both trials, 946 patients were assigned to receive ofatumumab and 936 were assigned to receive teriflunomide, with a median follow-up of 1.6 years. The studies found that the annual relapse rate was significantly lower for patients taking ofatumumab compared to teriflunomide, and ofatumumab was also superior in suppressing lesion activity on MRI scans