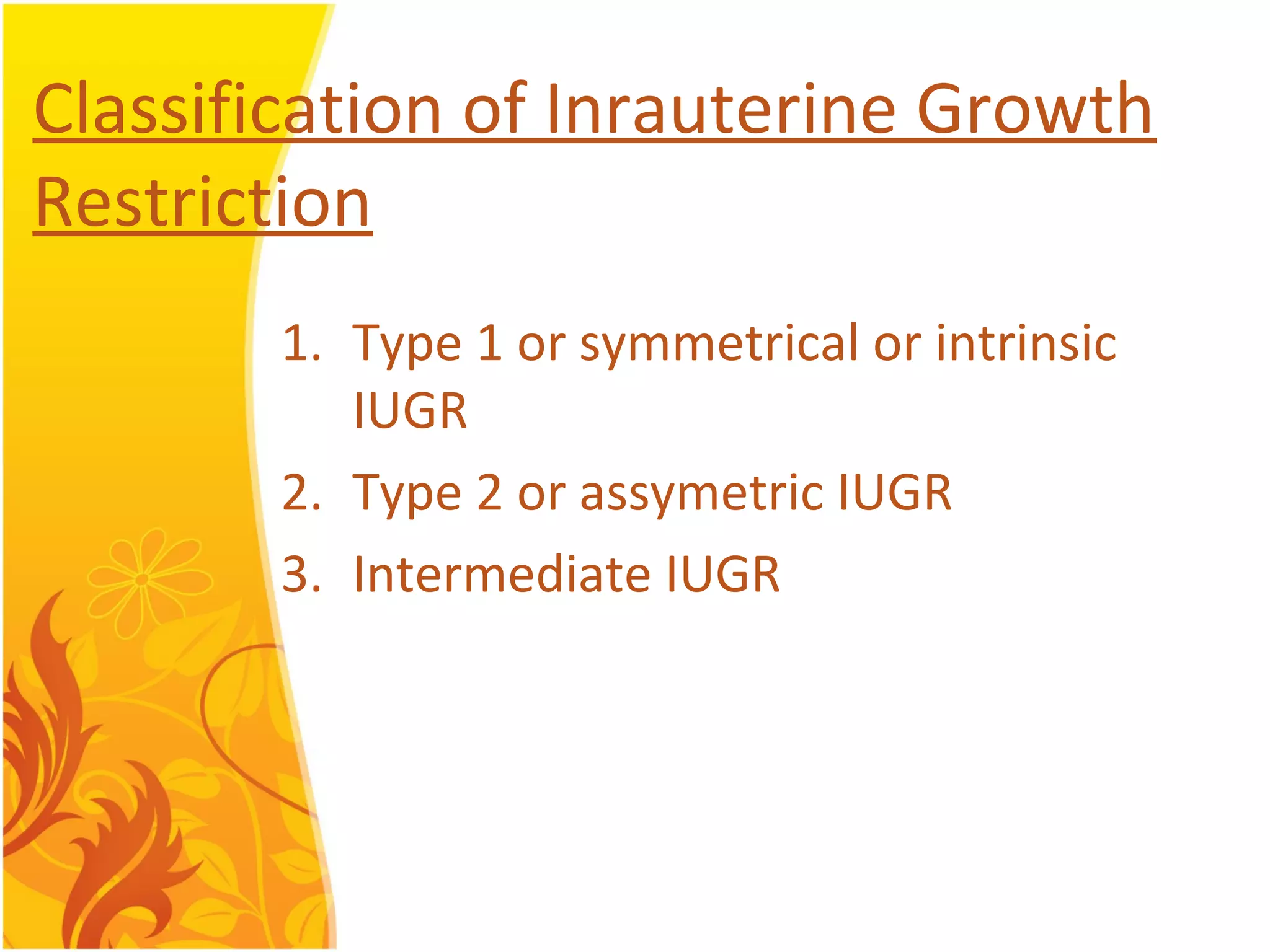
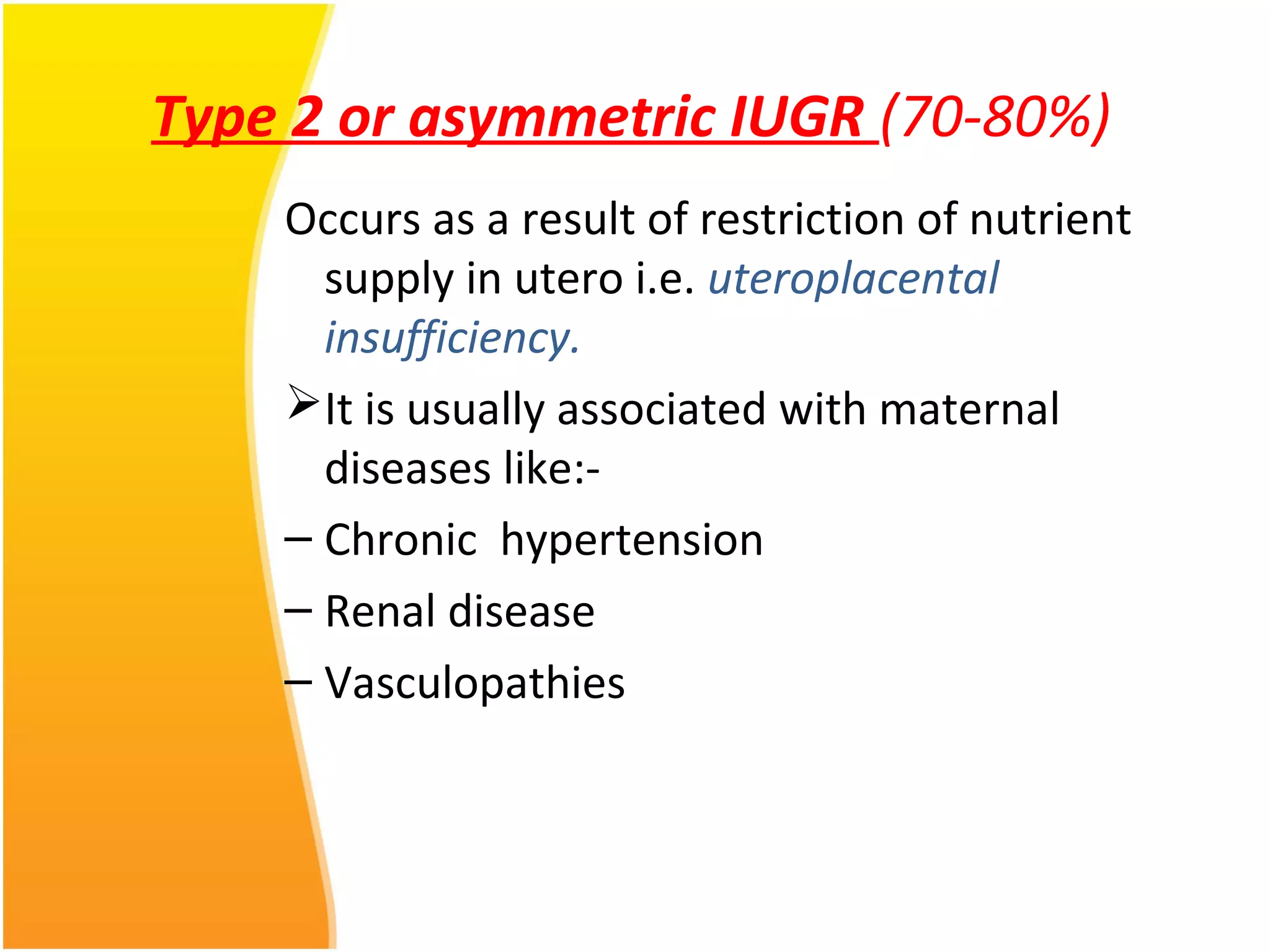
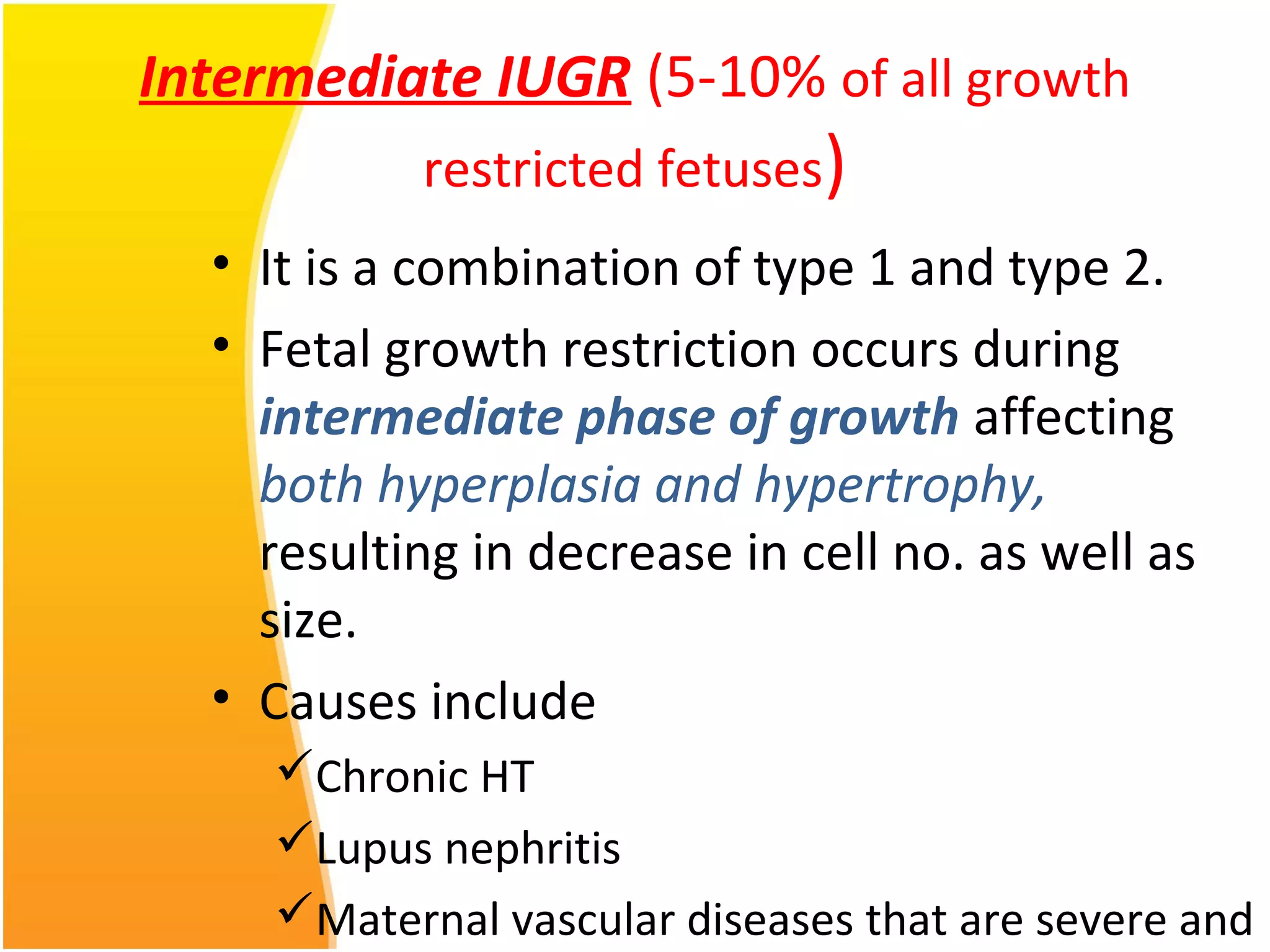
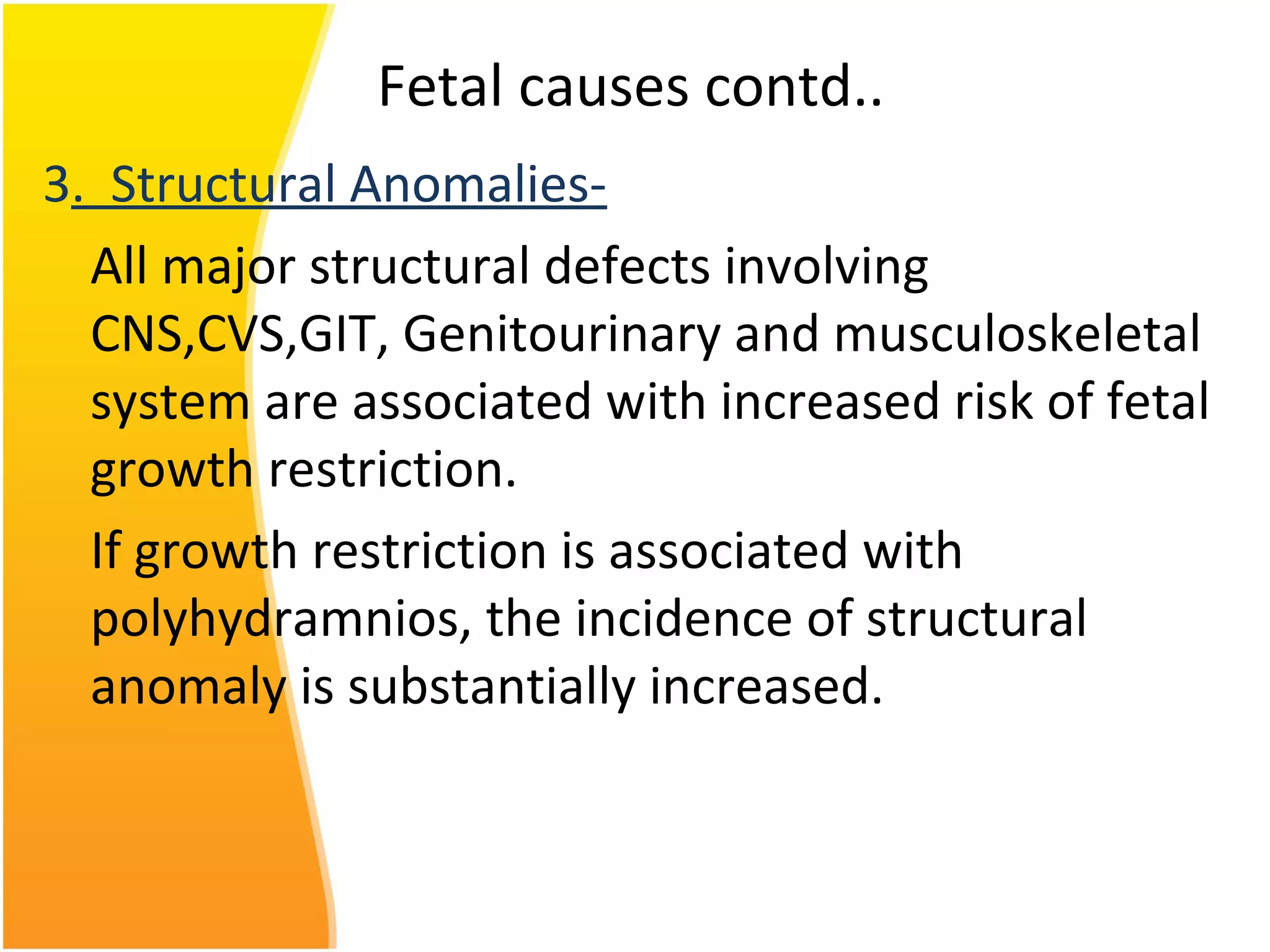
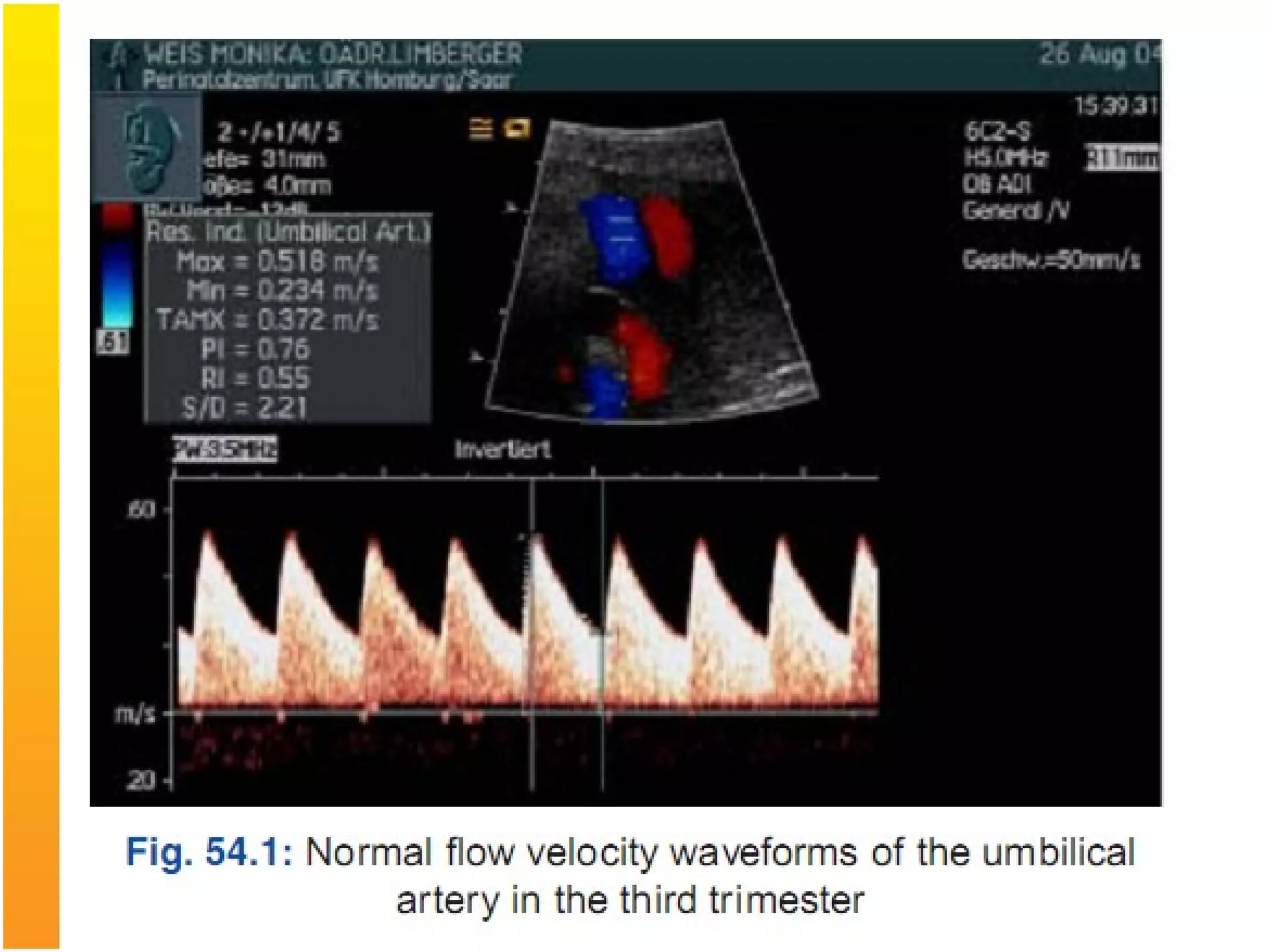
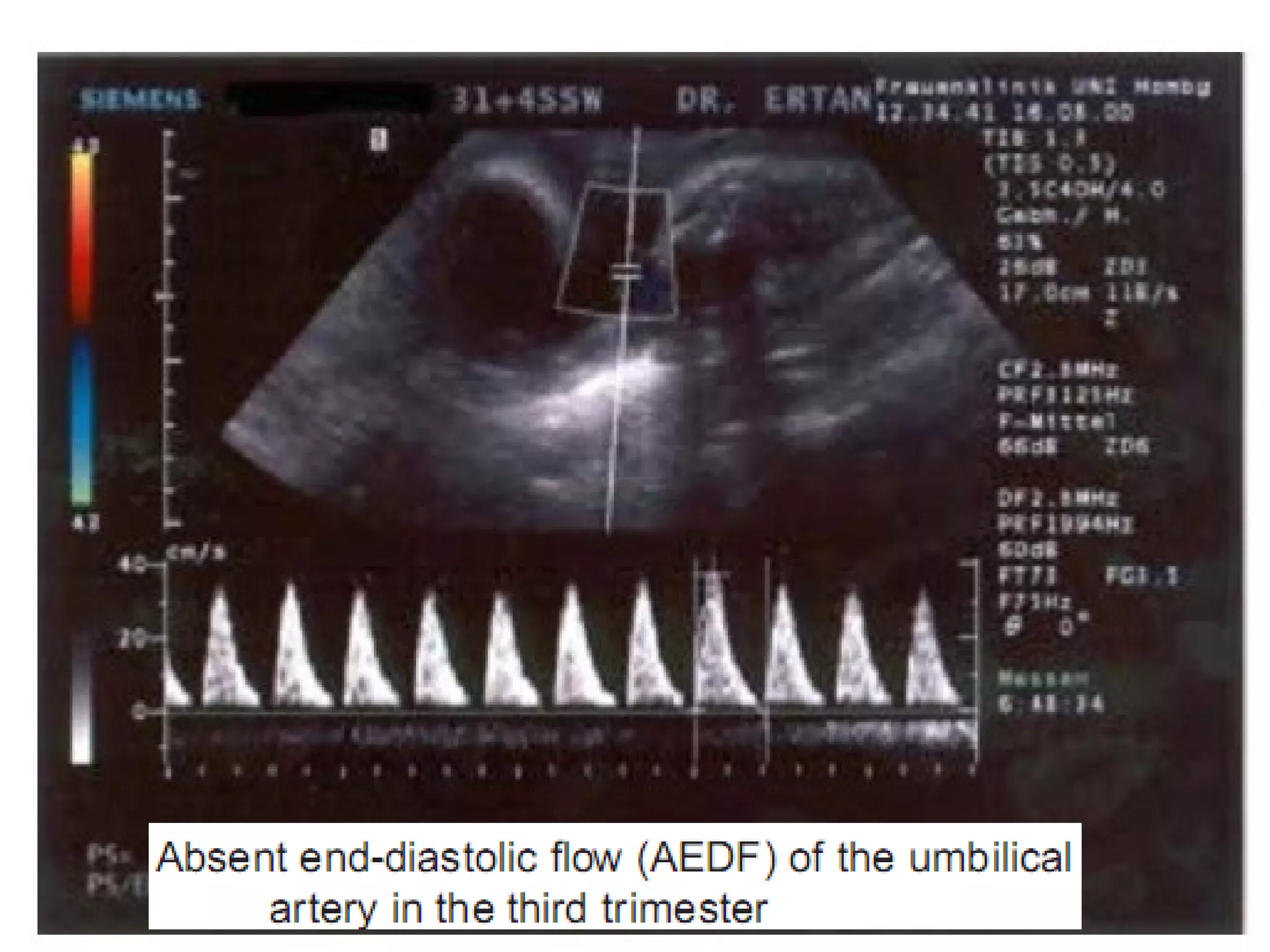
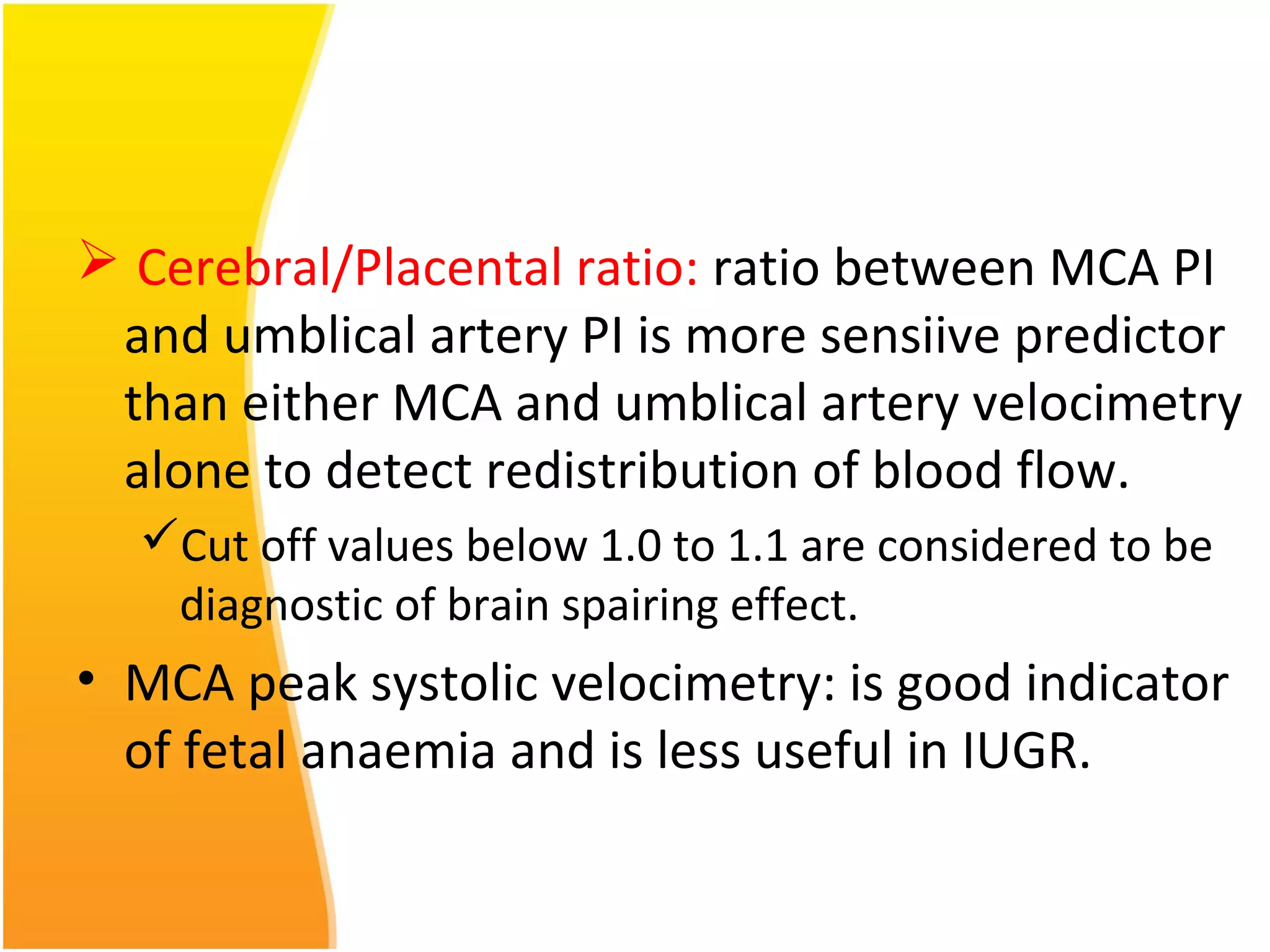
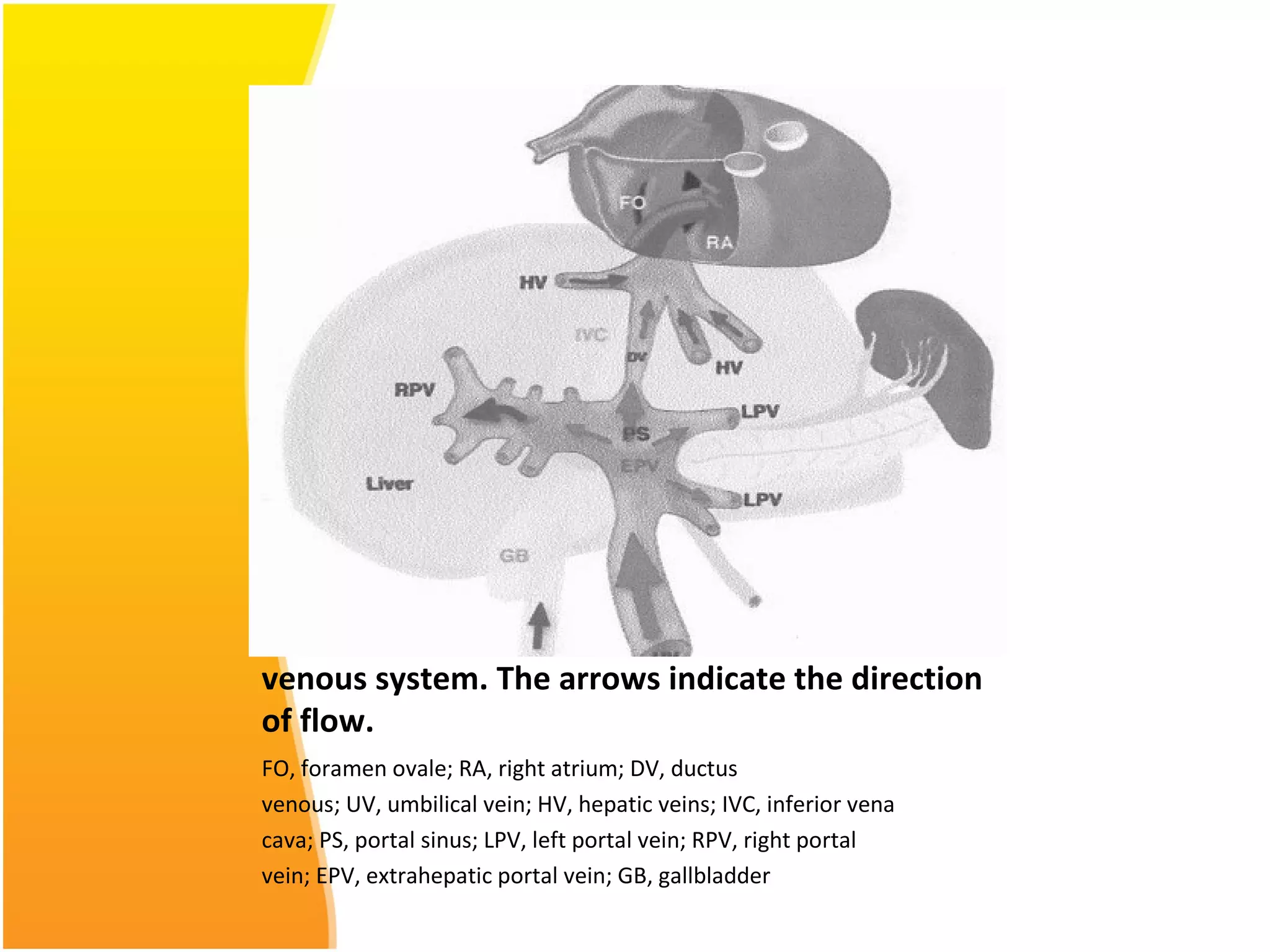
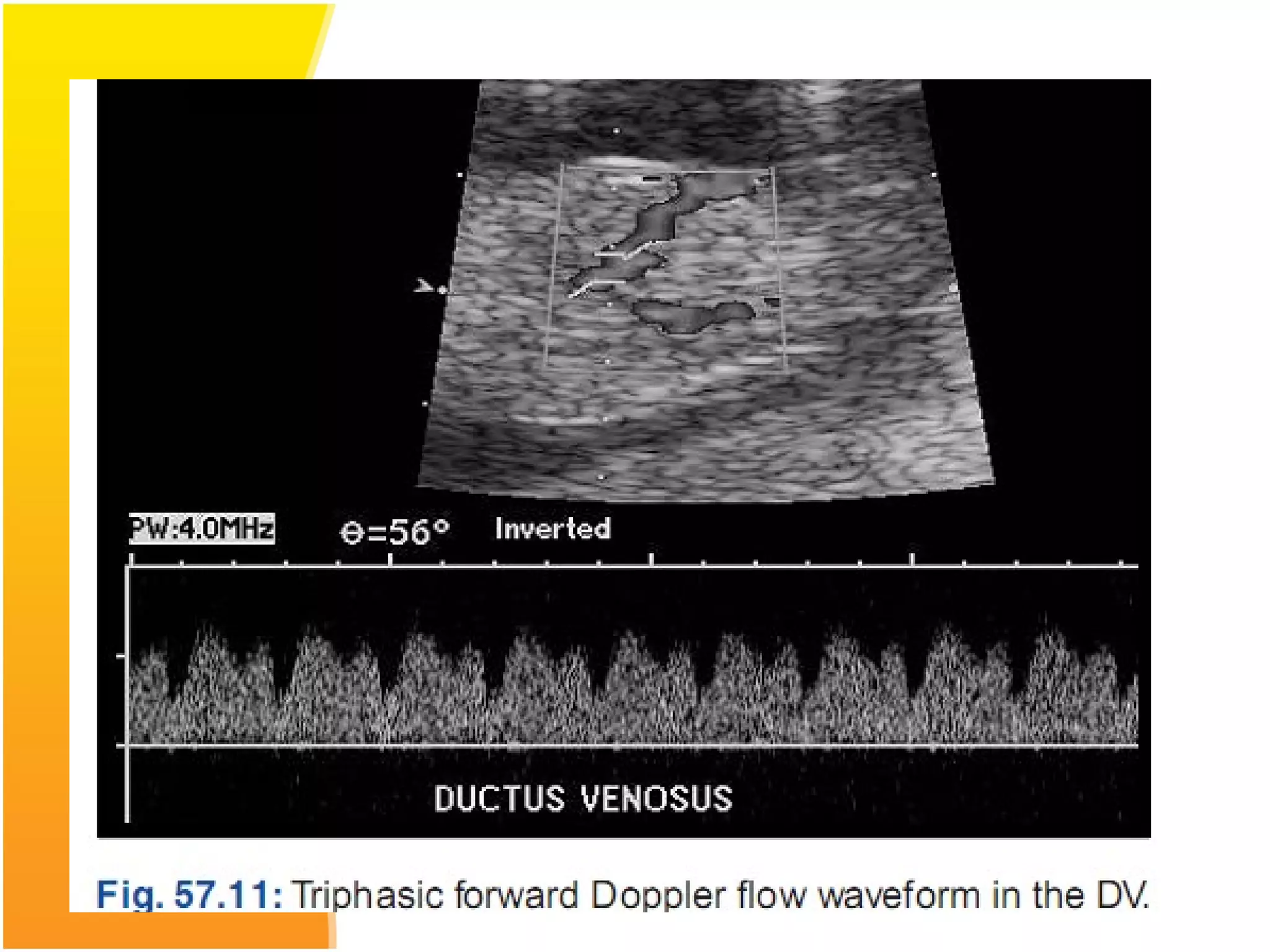
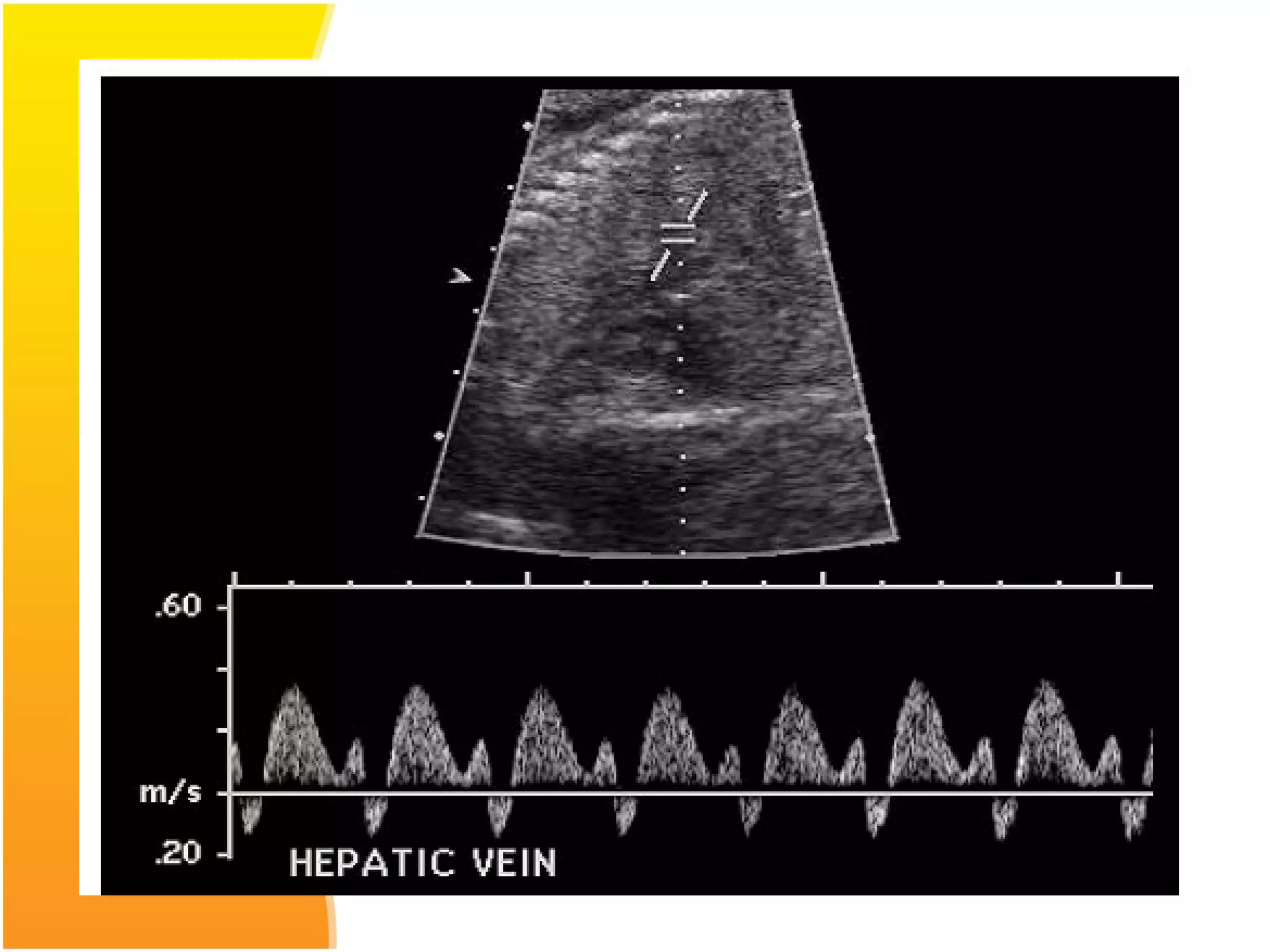
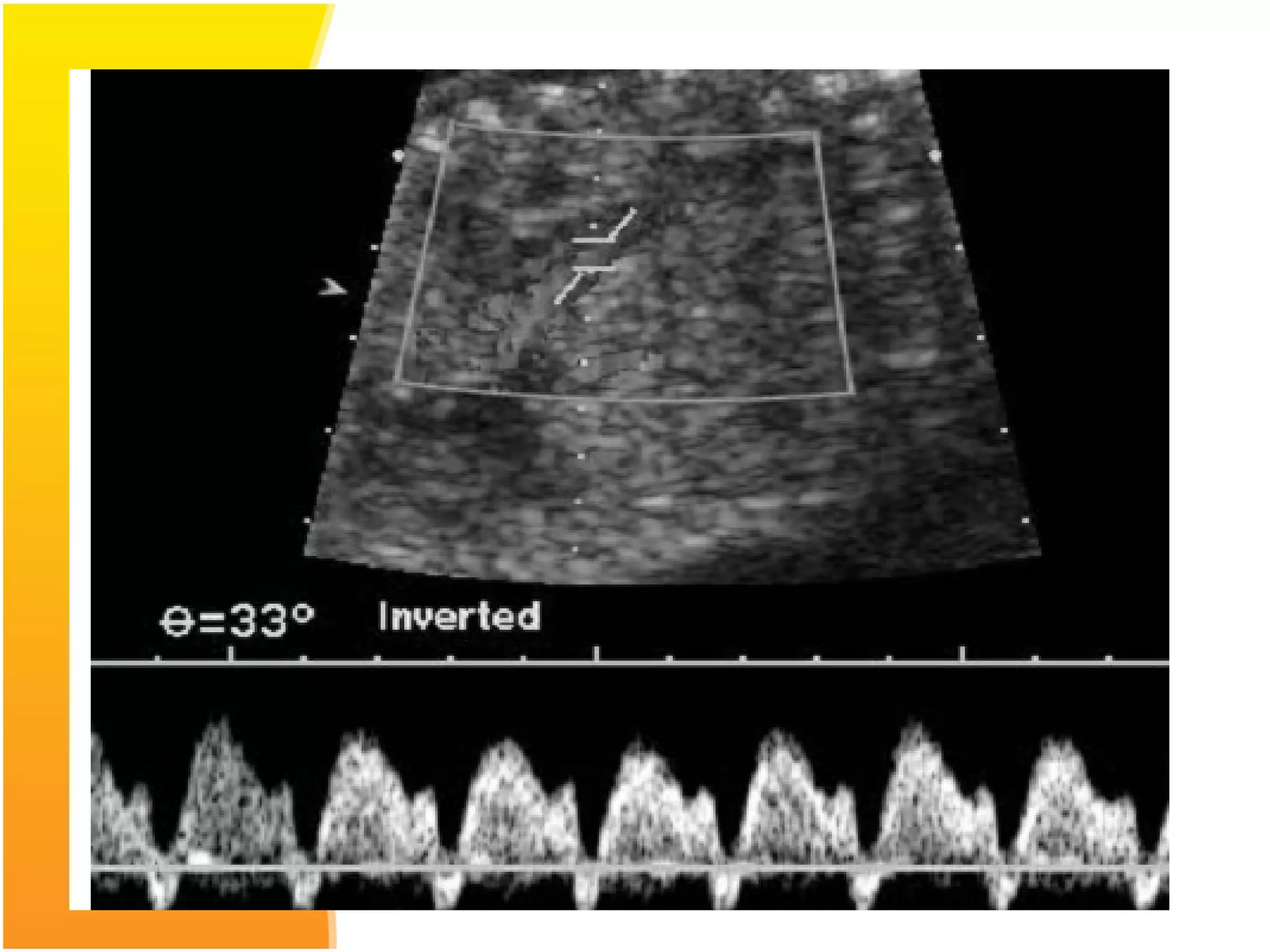
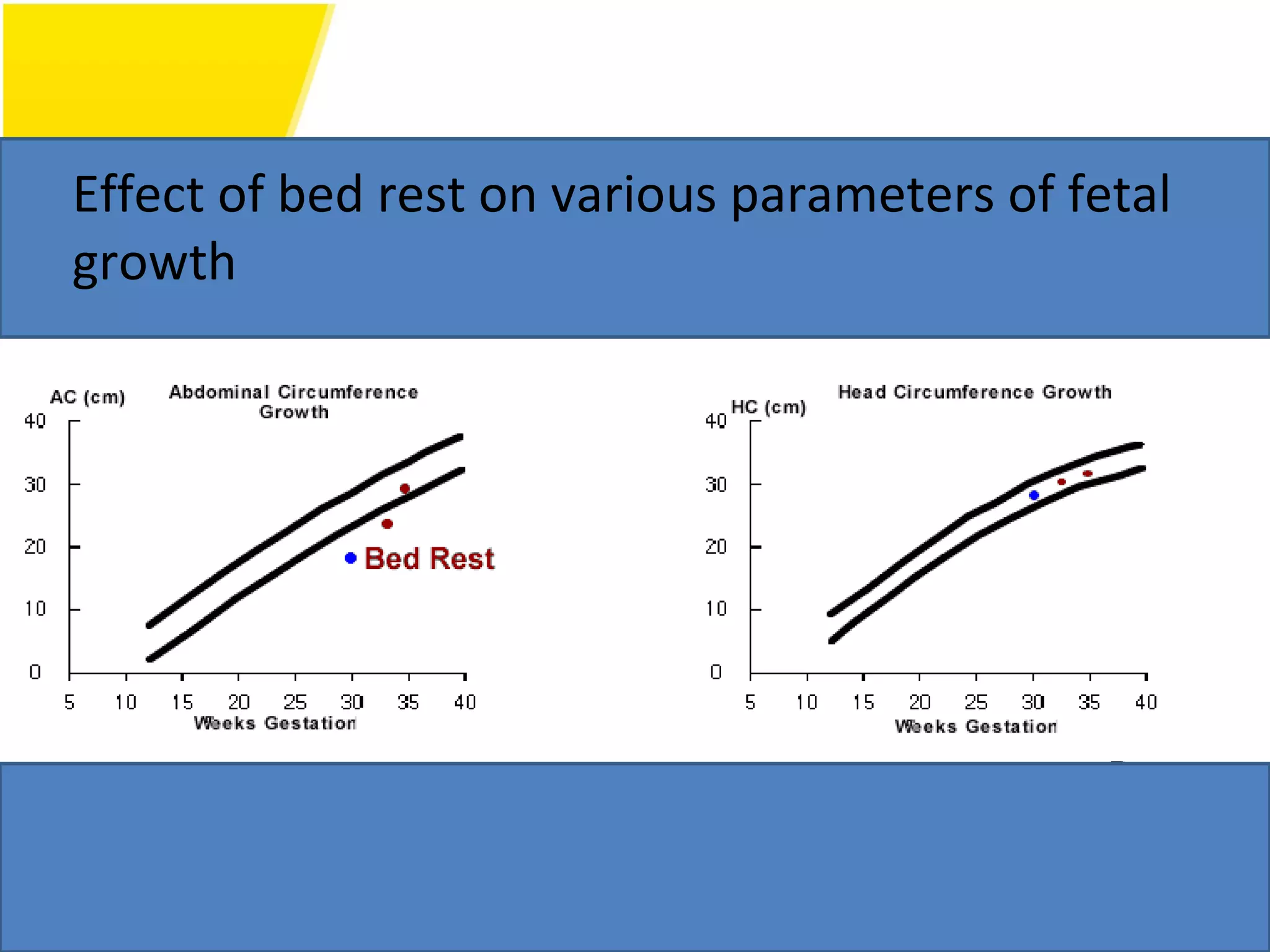
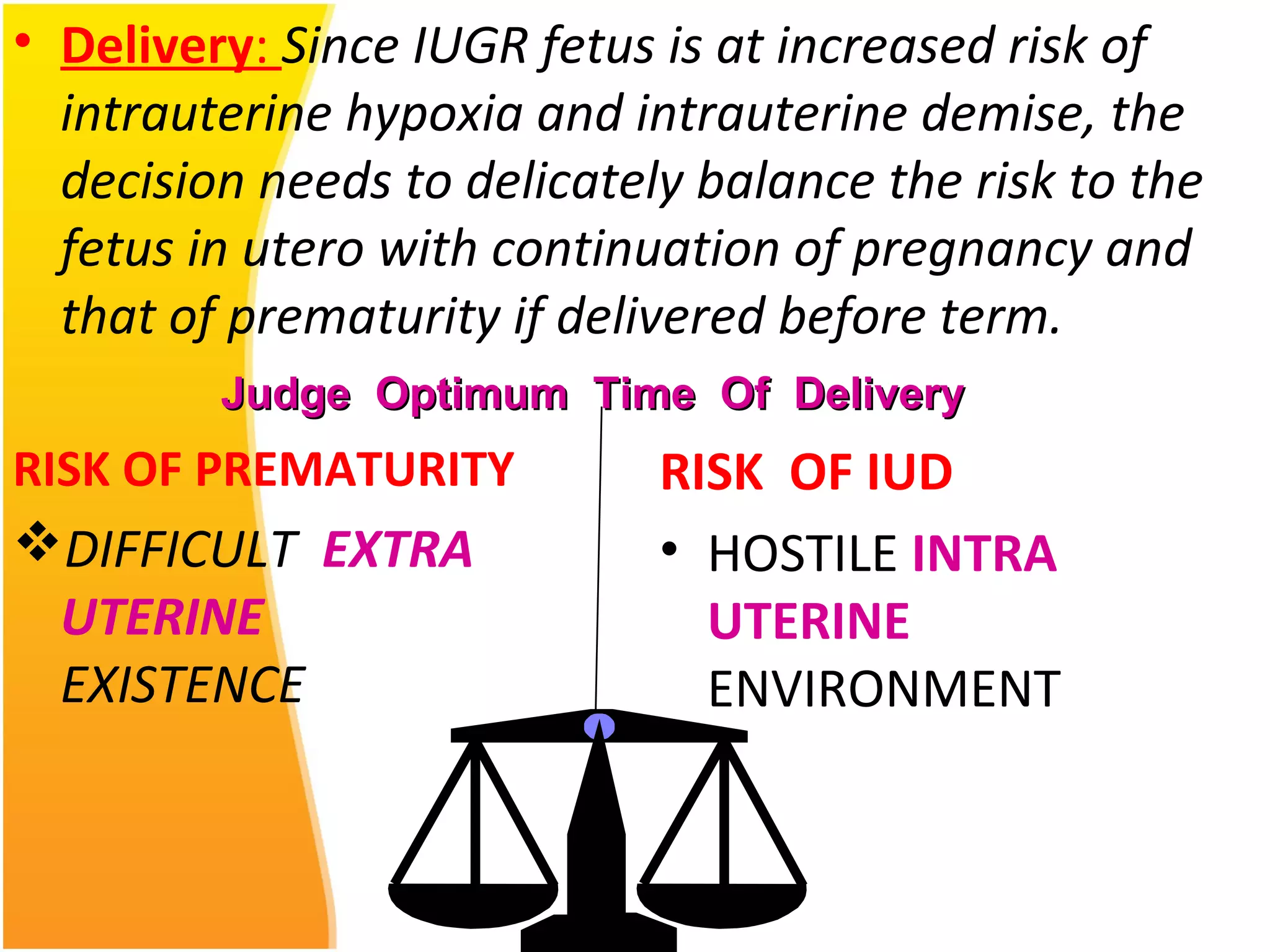
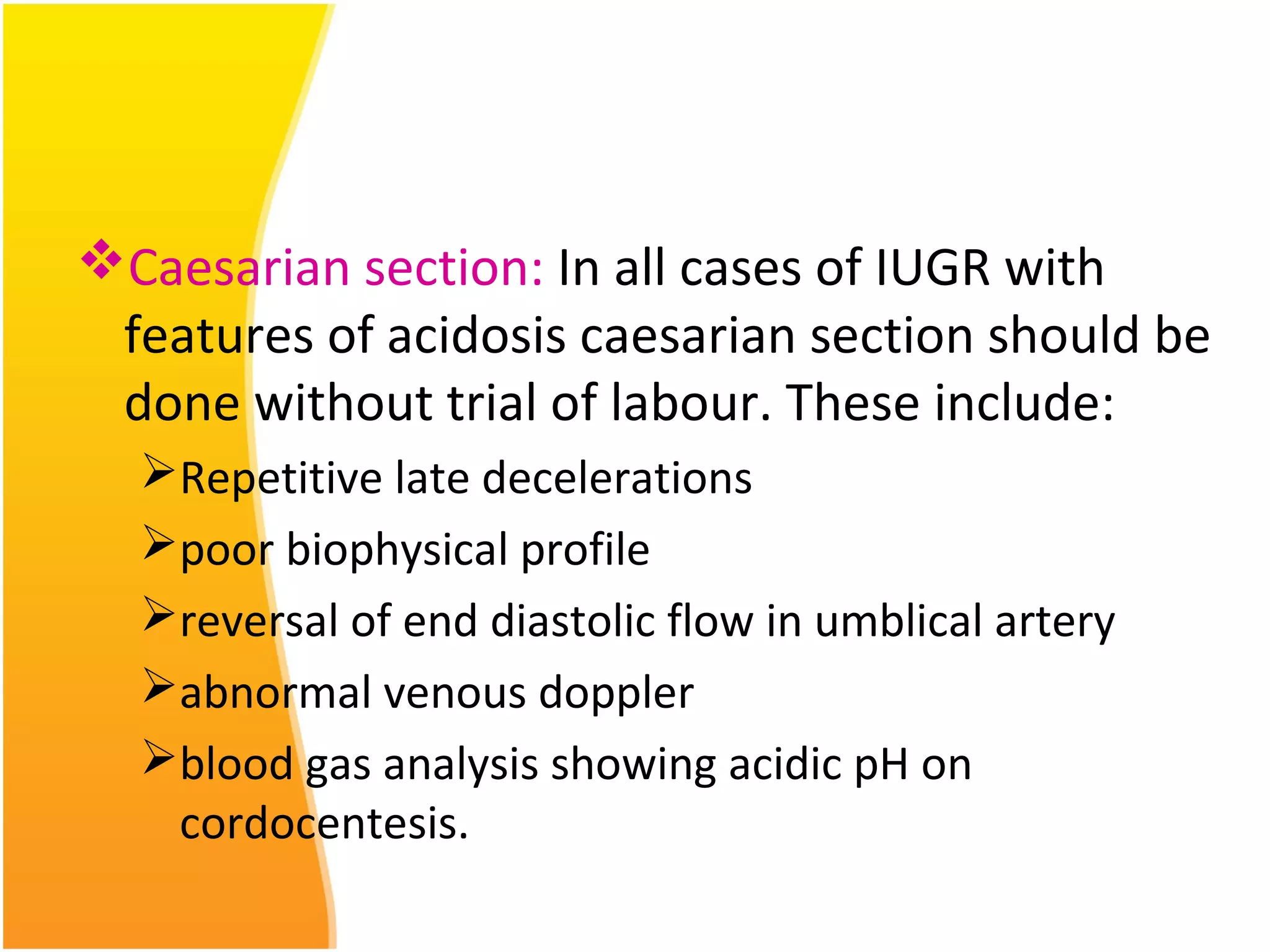
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) refers to fetuses that are small for their gestational age and display signs of chronic hypoxia or failure to thrive. It occurs in approximately 3-5% of pregnancies and can be caused by fetal, placental or maternal factors that restrict the fetus's growth. Diagnosis involves measuring fetal growth via ultrasound and Doppler to assess blood flow. Management focuses on identifying and treating the underlying cause, optimizing maternal nutrition, and monitoring the fetus for signs of worsening condition or need for delivery. The risks of IUGR include complications for both mother and baby during pregnancy, birth, and long term health issues.