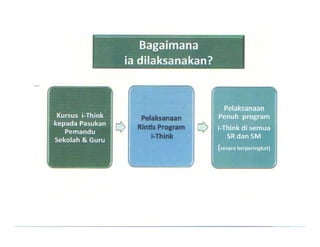
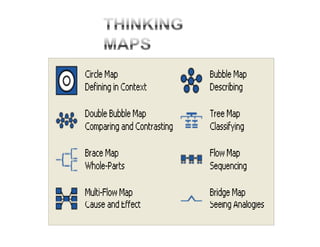
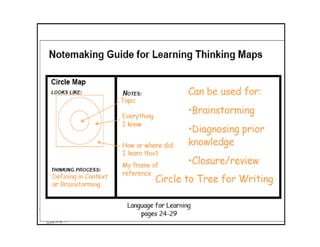
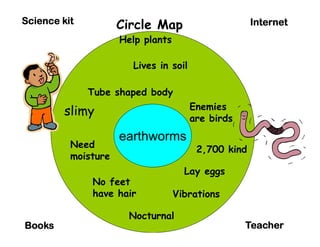
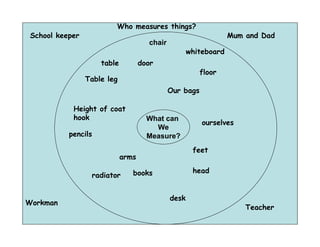
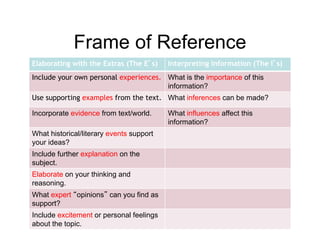
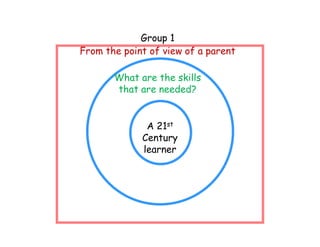
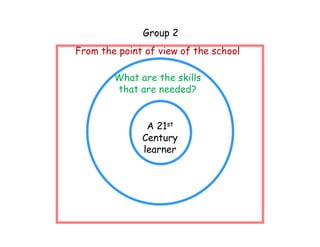
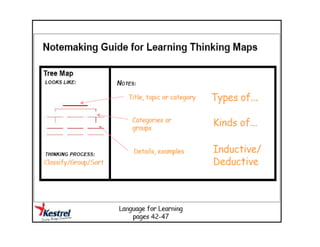
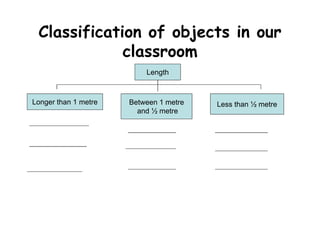
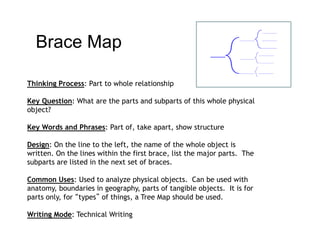
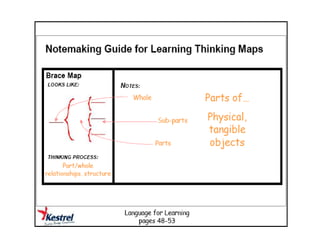
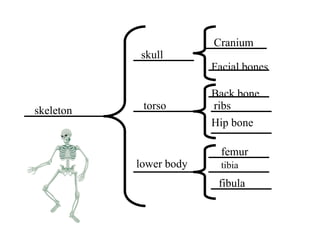
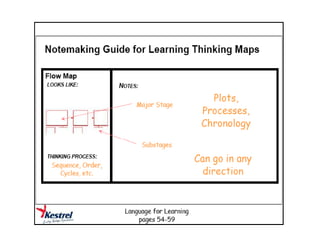
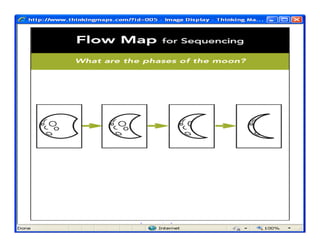
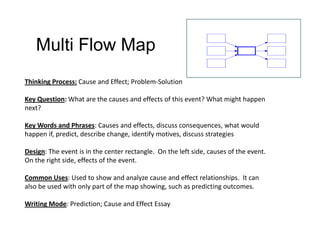
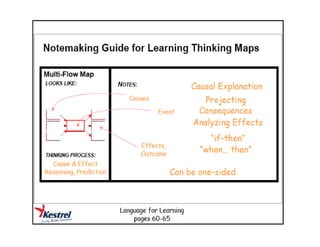
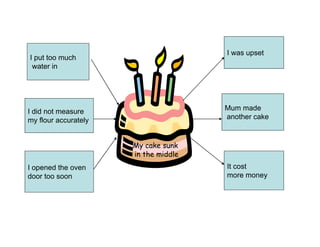
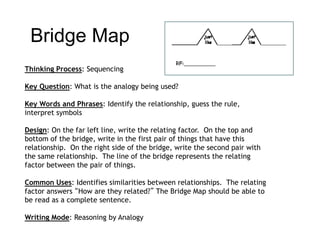
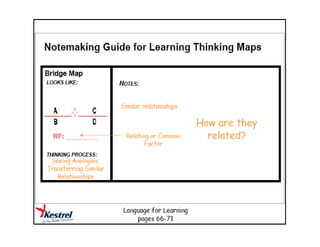
The document summarizes the phases of implementation of the i-Think program in Malaysian schools between 2012-2015. It involved a gradual rollout starting with 10 pilot schools in 2012 and expanding to include more schools each year, with the goal of having all schools participating by 2015. The program trained students and teachers in the use of Thinking Maps, which are visual tools to help organize and express thinking.