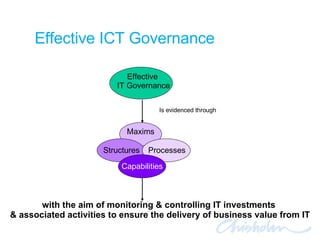
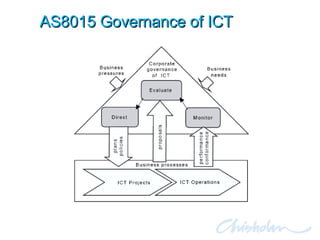
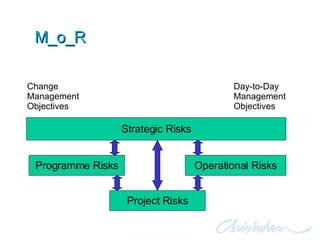
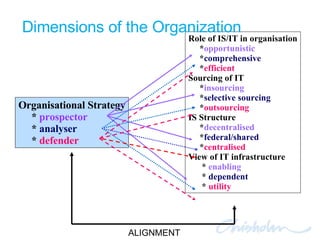
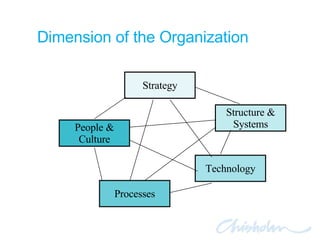
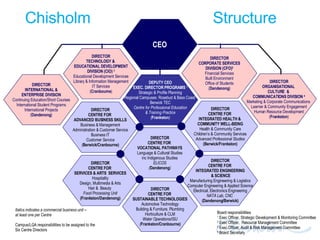
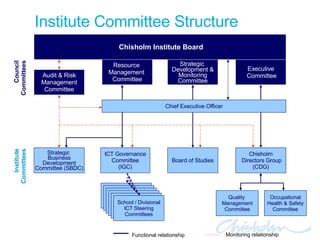
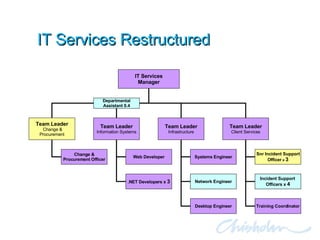
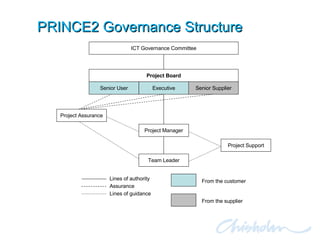
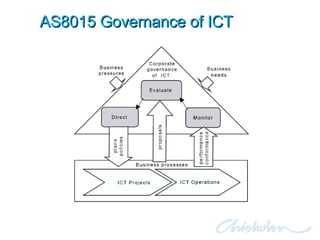
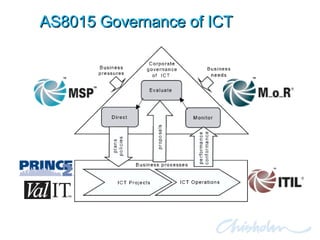
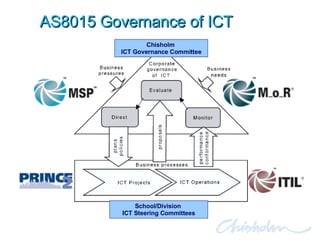
The document discusses IT governance challenges at Chisholm Institute and strategies for improvement. It summarizes frameworks like COBIT, ITIL and PRINCE2 that can help with governance. It then details how Chisholm restructured its IT department and implemented an ICT Governance Committee aligned with the AS8015 standard to better link IT with organizational strategy and priorities.































![Thank you Questions? [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chris-vanderweylan-9126/85/Chris-Vanderweylan-50-320.jpg)