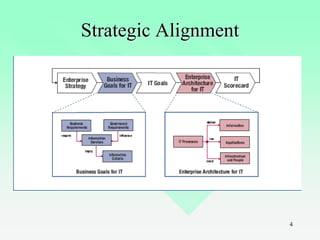
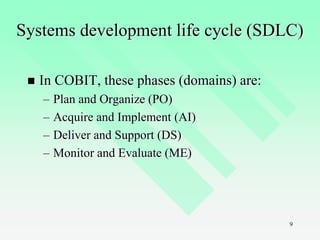
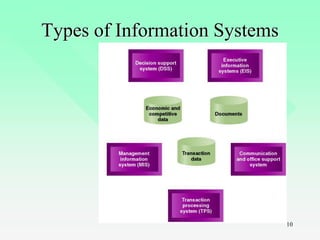
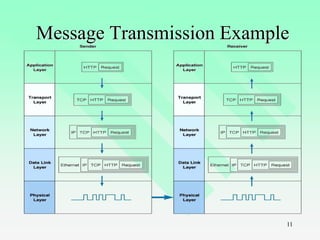
This chapter provides an introduction to IT auditing. It discusses IT governance and the role of ensuring strategic alignment of IT with business objectives. It also covers the systems development life cycle (SDLC) process and phases. The chapter defines different types of information systems and the role of IT auditors in assessing risks and controls over IT resources. It outlines the skills and certifications needed for IT auditors and how IT audits are structured.