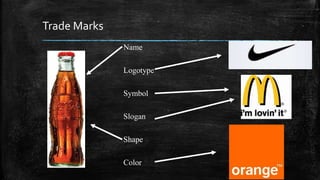
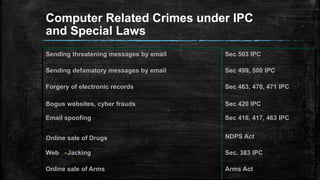
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on cyber crime, the Indian Penal Code (IPC), and the Information Technology Act of 2008. It discusses the history of cyber crime, types of cyber crimes like viruses and phishing, categories of cyber crimes against persons, property, and government. It also outlines cyber criminals like children, dissatisfied employees, and professional hackers. The document then discusses intellectual property rights including patents, copyright, and trademarks. It provides an overview of the IT Act of 2000 and its amendments in 2008 regarding cyber laws in India. It also discusses challenges facing law enforcement in dealing with cyber crime and some positive initiatives taken.