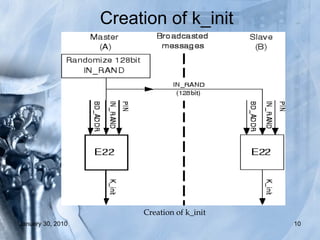
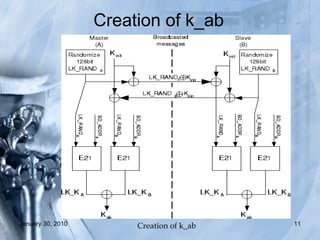
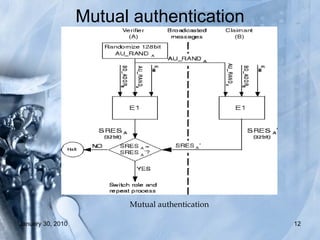
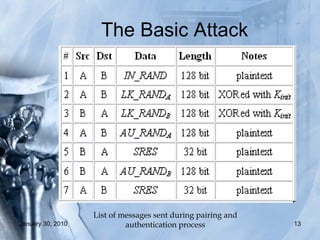
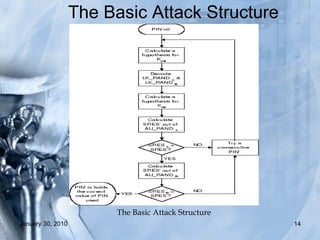
The document discusses various Bluetooth hacking techniques such as Bluejacking, Bluesnarfing, Bluebugging and Blueprinting which can steal sensitive data or take control of Bluetooth devices, and outlines security measures like enabling encryption and changing default settings to protect against attacks. Common attacks explored are Bluejacking to send messages, Bluesnarfing to extract data, and Bluebugging which allows full phone control via AT commands. Countermeasures recommended are disabling Bluetooth when not needed, not accepting unknown files/cards, using long secure pairing codes, and changing default names.
![Seminar on Blue tooth Hacking [security and threats] By- Dhanashree Waikar Roll No – 3379 Project Guide – Prof. N. R. Talhar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bluetoothhacking-100129220932-phpapp02/75/Bluetooth-Hacking-1-2048.jpg)
![Overview Introduction Bluejack attack Bluespamming The Bluesnarf attack The Bluebug attack Helomoto Crack pin code Blueprinting Other attacks [Trojans, Viruses, worms] Security levels Countermeasures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bluetoothhacking-100129220932-phpapp02/85/Bluetooth-Hacking-2-320.jpg)