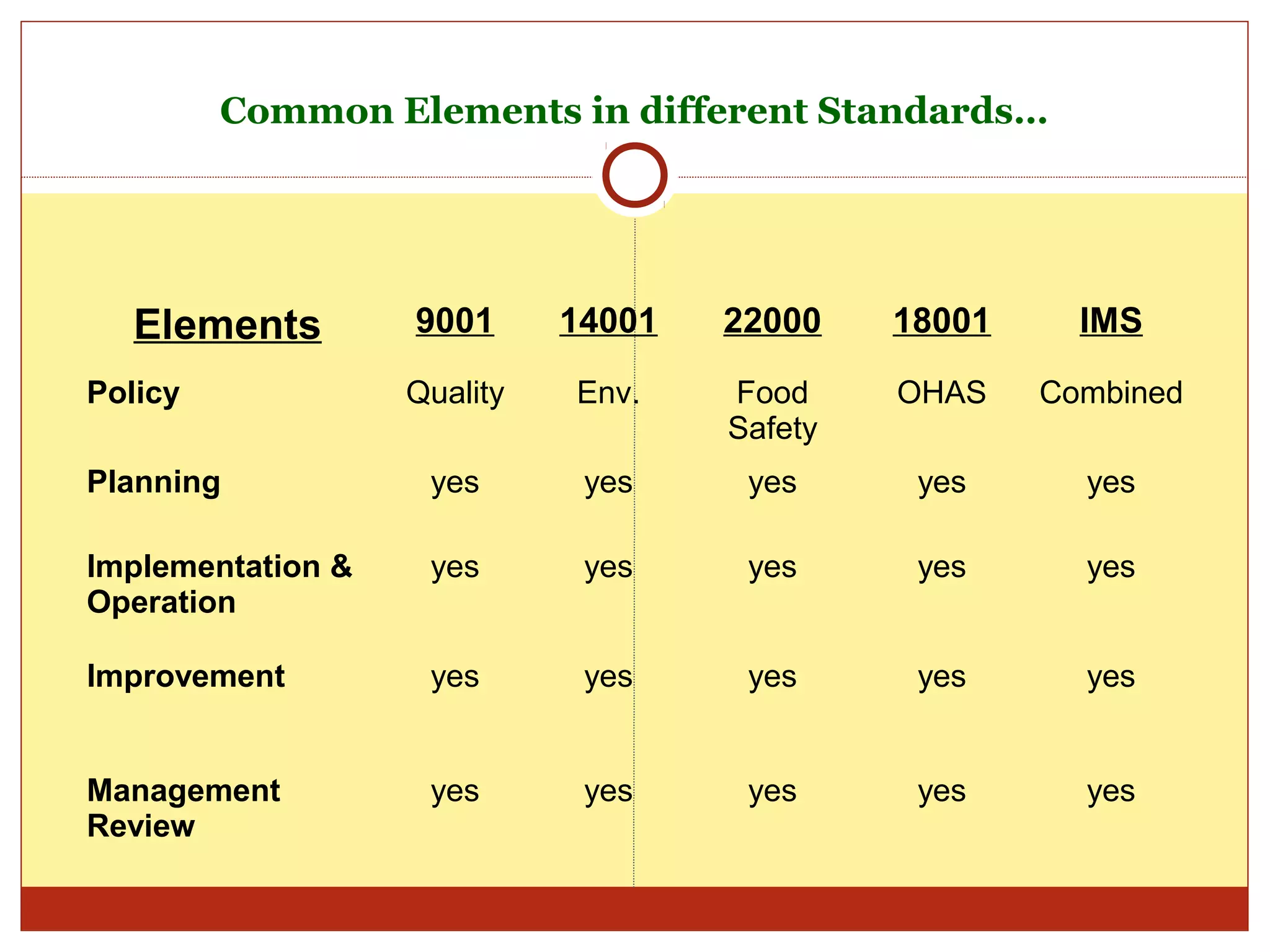
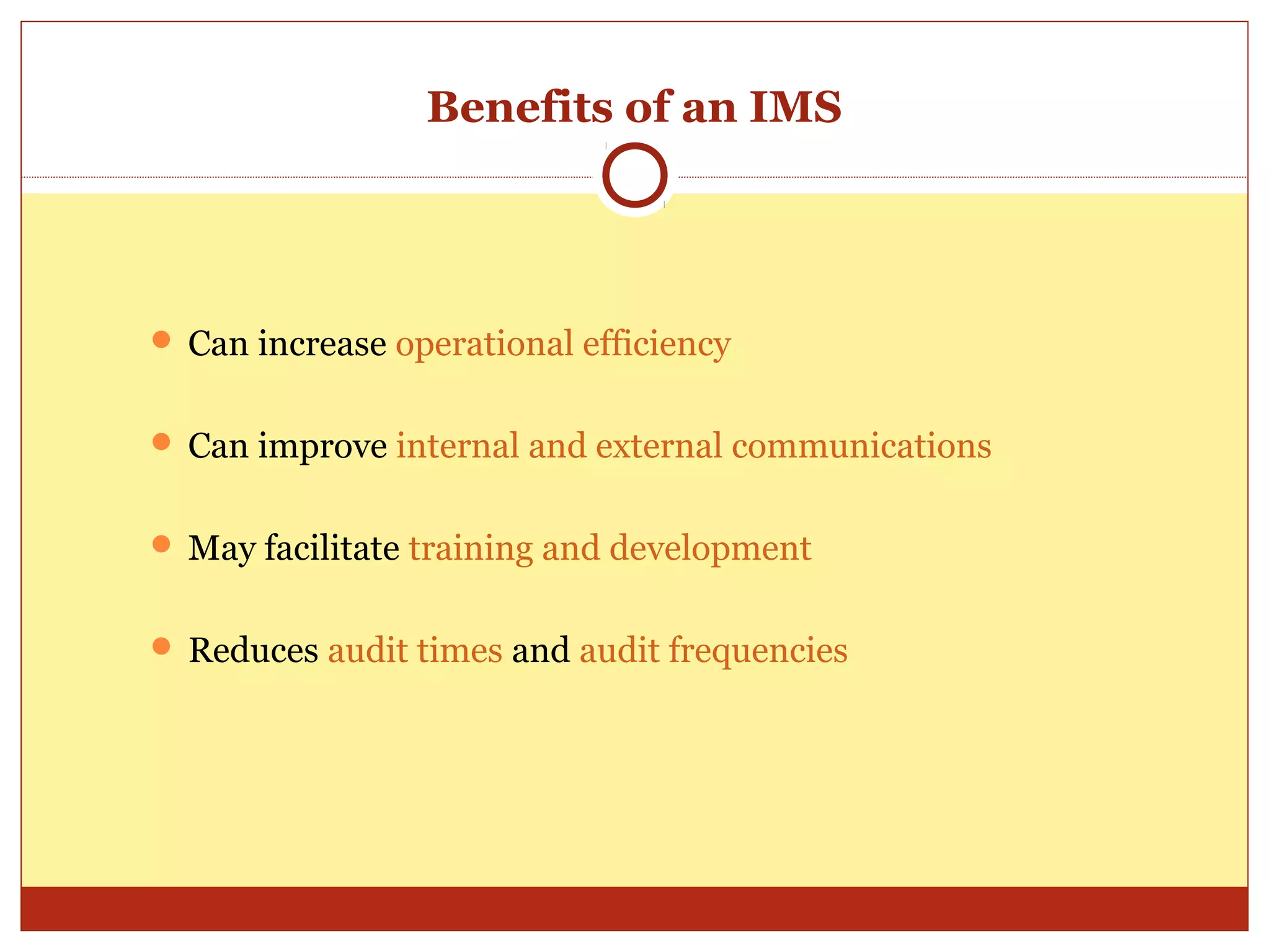
The document discusses the history of management system standards from military standards in the 1960s to more recent standards for quality, environment, food safety, and occupational health and safety. It notes that users requested compatibility between standards to reduce audit disruptions and costs. Key common elements were examined across standards like policies, planning, implementation, and management reviews. The conclusion is that integrating multiple standards into an integrated management system provides benefits like reduced costs and duplication as well as improved efficiency and communications.







![New Fields being considered at ISO
Organizational (Corporate) Social Responsibility [OSR] Including:
Business Ethics
Sustainable Development
Organizational (Corporate) Responsibility
Social Accountability
I.T. Services Management.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/historicbackgroundofstandards-130304001227-phpapp02/75/Historic-background-of-ISO-standards-8-2048.jpg)