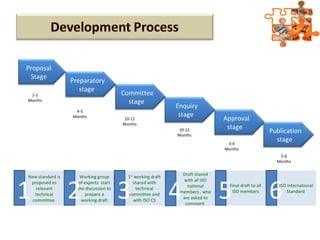
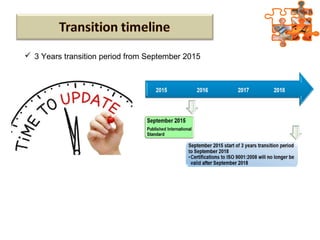
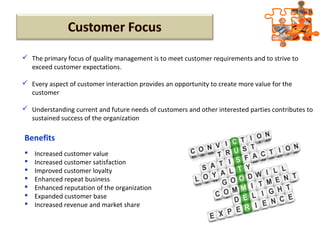
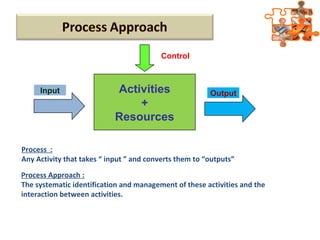
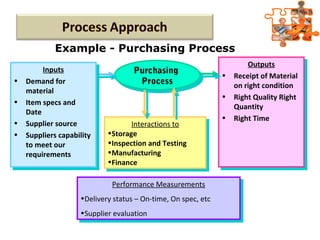
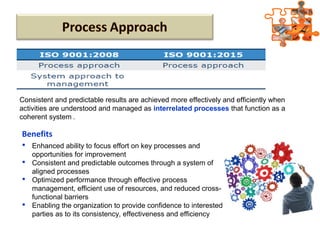
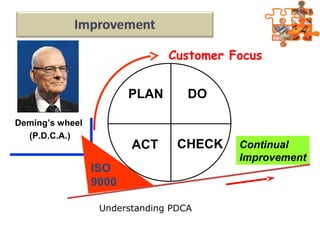
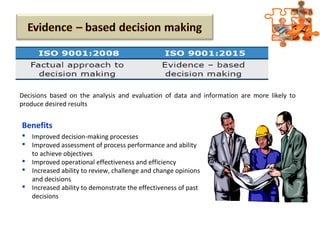
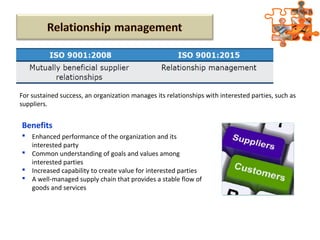
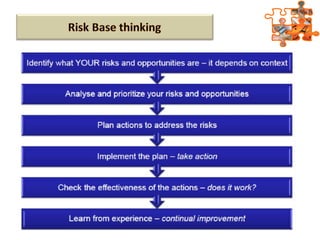
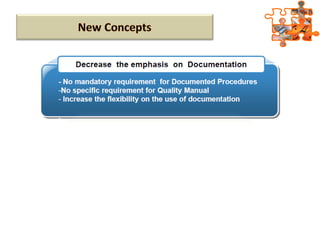
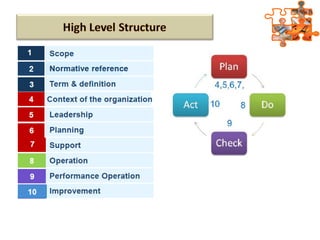
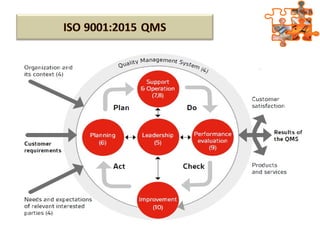
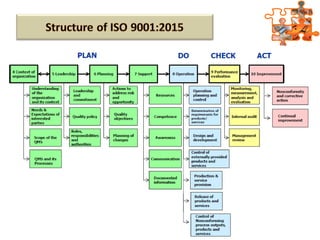
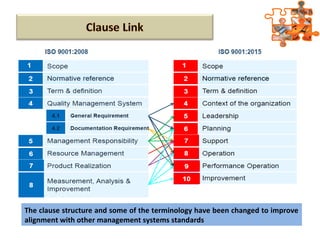
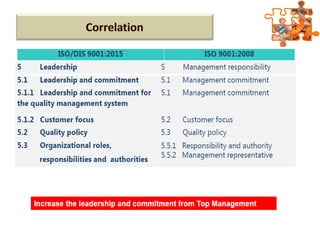
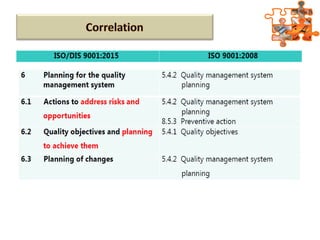
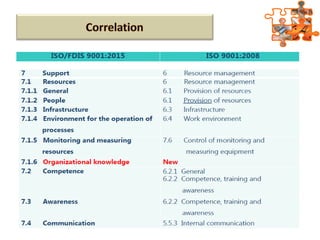
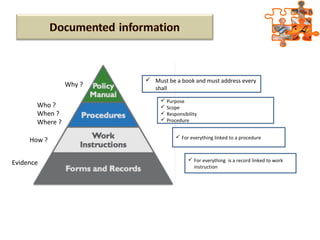
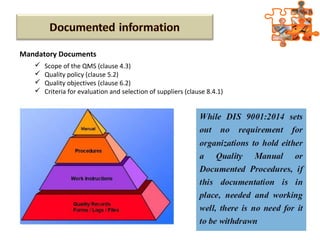
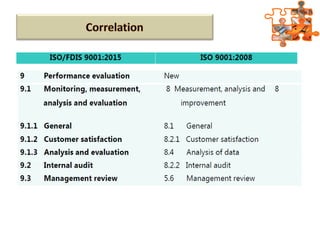
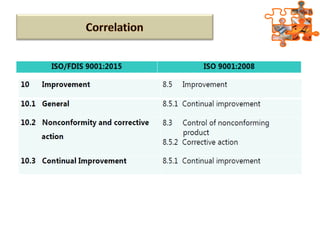
The document provides an overview of ISO (International Organization for Standardization), focusing on ISO 9001:2015 principles and its development, structure, and requirements aimed at improving organizational performance and customer satisfaction. It outlines the changes and significance of ISO standards, emphasizing quality management principles such as customer focus and continual improvement and detailing the relationship and processes essential for effective quality management systems. The document also highlights the importance of documentation, records, and mandatory requirements to ensure adherence to quality standards.