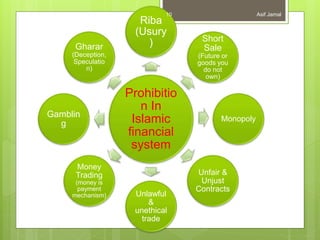
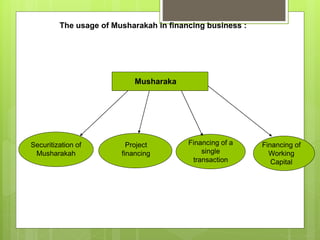
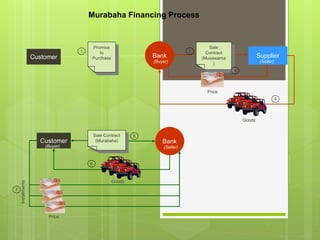
Islamic finance, rooted in Shari'ah law, is defined as a modern banking system that relies on risk-sharing and prohibits practices such as usury (riba) and deception (gharar). It aims to mobilize Muslim savings for economic development, focusing on ethical investment and trade that adheres to Islamic principles. Key concepts include financial instruments like musharakah (joint venture) and murabaha (sale contract), designed to align with Islamic values of fairness and morality.