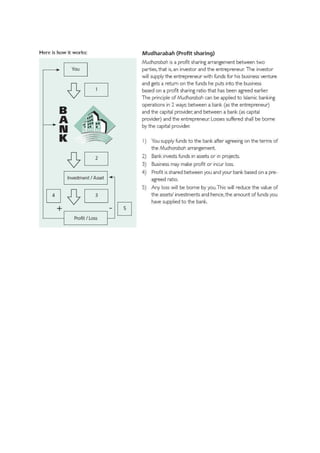
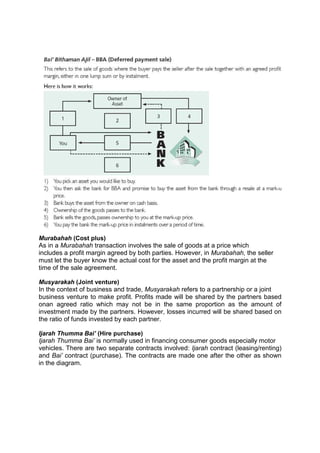
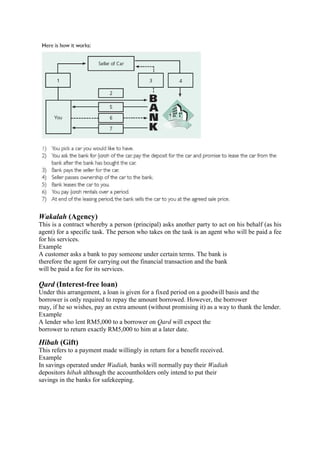
The document discusses Islamic banking and its principles and concepts. It provides background on the origins of Islamic banking in Egypt in 1963 and outlines some of the key differences from conventional banking, such as prohibitions on riba (interest) and investing in industries like alcohol or gambling. It defines common Islamic banking contracts and instruments like murabahah, mudarabah, and ijara. It also notes that while Islamic banking has grown significantly in many Muslim-majority countries, establishing it in India could help address the needs of its large Muslim population and attract their savings within the banking system.